Claudins家族靶点:CLDN4接踵而至,展示联合用药潜力!
日期:2022-09-26 09:54:20
近期,Nature旗下Cell Death & Disease杂志,一篇标题为“TGF-β induces GBM mesenchymal transition through upregulation of CLDN4 and nuclear translocation to activate TNF-α/NF-κB signal pathway”文章首次发现,CLDN4在胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)组织和细胞中上调,研究提示,CLDN4通过调节TNF-α诱导的NF-κB活性,诱导GBM细胞的间质转化,增强GBM细胞的迁移能力。进一步的实验数据表明,稳定敲低CLDN4,可抑制异种移植小鼠胶质瘤的生长和侵袭,且联合ITD-1治疗,对小鼠肿瘤的抑制效果更好 [1]。CLDN4作为Claudins家族的重要分子,在各种类型肿瘤中广泛出现高表达或表达缺失。陆续有研究表明,CLDN4可作为治疗肿瘤的特定靶点。令人鼓舞的是,已有多篇文献报道将抗CLDN4抗体联合治疗,可增强抗肿瘤作用。因此,继CLDN18.2、CLDN9、CLDN6等靶点后,CLDN4接踵而至,有望成为Claudins家族肿瘤靶向治疗的有效靶点,且在联合用药方面展示出潜力。
1. 什么是CLDN4?
紧密连接蛋白4(Claudin 4/CLDN4)属于Claudins家族的一员,也是紧密连接(Tight Junctions,TJ)的重要连接蛋白之一。Claudins蛋白均由4个跨膜结构域构成,N端和C端均位于细胞内部,C-末端上存在结合域,可与胞质内层的蛋白结合(如:ZO-1),在信号转导中发挥重要的作用。细胞膜外有2个长度不等的环(ECL1和ECL2),它们可以和临近其他同类型的环相接触,构成细胞间的紧密连接(图1) [2]。细胞外环是维持紧密连接功能和上皮屏障完整性所必需的。紧密连接是位于上皮细胞和内皮细胞顶端的细胞间黏附结构。Claudins作为紧密连接的重要组成部分,可调节上皮细胞通透性及维持细胞极性等方面发挥作用。当Claudins蛋白发生变化时,将影响细胞间的通透性,可引起疾病的发生 [2, 3]。越来越多研究揭示CLDN4在癌症中发挥着调控作用,或可作为潜力肿瘤治疗靶标 [4-6]。事实上,大量证据已表明Claudins成员在肿瘤免疫治疗中扮演重要的角色,且在临床中具有极大的成药性。针对Claudins家族火热研究靶点,可点击以往Claudins蛋白相关文章(CLDN6;CLDN9;CLDN18.2)。
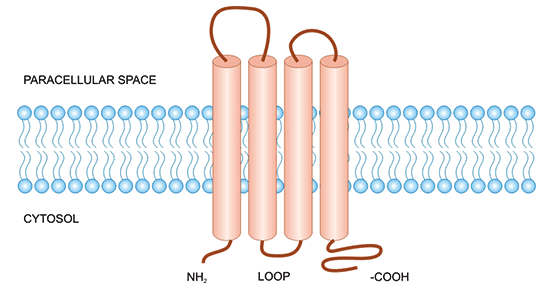
图1. CLDN4的结构 [2]
2. CLDN4的作用机制
相关文献指出,Claudins参与肿瘤的机制途径可能为:1)Claudins异常表达引起紧密连接紊乱和渗漏,促进肿瘤细胞的转移和侵袭;2)细胞极性的降低增加肿瘤的营养和生长因子供应,使肿瘤细胞的增殖加快;3)细胞间黏附的减少,会增加转移风险并促进肿瘤的发展 [7-9]。如今,CLDN4作为常见的肿瘤异常表达基因,对其研究仍处于初步阶段,其在肿瘤中的信号调节机制有待深入了解。
在胶质瘤中,研究发现CLDN4/TNFα/NF-κB信号轴,在胶质瘤的生物学进展中起关键作用,揭示CLDN4诱导胶质瘤EMT是通过调节TNF-α介导的NF-κB信号通路(图2) [1]。在卵巢癌中,CLDN4的过表达,可通过PI3K/Akt和EMT转录因子Twist1信号通路,诱导卵巢癌细胞EMT [10, 11]。在胰腺癌中,转化生长因子β(TGF-β)可以负性调解CLDN4表达,且高表达CLDN4可抑制胰腺癌细胞的侵袭 [12]。在乳腺癌中,CLDN4通过PAK4-CEBPB-CLDN4轴,促进肿瘤细胞迁移和侵袭 [13]。
另外,在人喉癌Hep-2细胞中,CLDN4低表达,并初步证实CLDN4通过JAK2/STAT3信号通路,可抑制细胞增殖 [14]。另有研究认为,在喉癌Hep-2细胞中,DNA甲基化可下调CLDN4基因,其与MeCP2募集HDAC1有关,进一步发现,CLDN4上调可抑制Hep-2细胞增殖,并增加细胞间紧密连接数目 [15]。
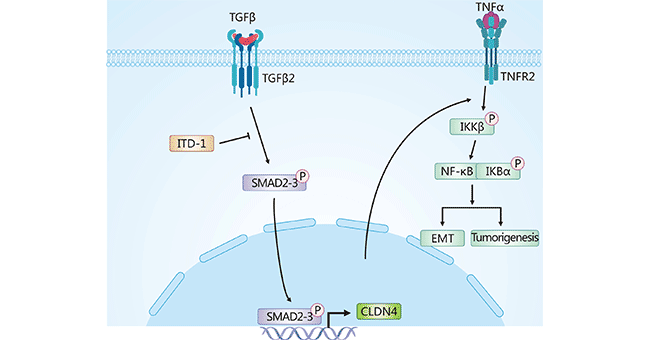
图2. CLDN4诱导胶质瘤细胞EMT途径 [1]
3. CLDN4在肿瘤中的作用
很多学者研究发现,CLDN4在多种肿瘤中存在异常表达现象。尤其在消化道肿瘤,包括食管肿瘤、胃癌、结肠癌、肝癌、胰腺癌、喉鳞状细胞癌等等;以及在生殖系统肿瘤,如卵巢癌、宫颈癌,均有研究显示CLDN4在这些肿瘤组织中的异常高表达或低表达。因此,CLDN4作为常见的肿瘤异常表达基因,将有着非常重要的潜在应用价值。
3.1 CLDN4与消化道肿瘤
在胰腺癌中,有研究表明,罗格列酮(Rosiglitazone)可通过抑制MEK-ERK信号通路,增加CLDN4的表达,从而抑制胰腺癌细胞的侵袭,认为CLDN4是胰腺癌细胞侵袭和转移表型的潜在抑制剂 [17]。然而,使用cDNA微阵列分析胰腺导管内乳头状黏液性肿瘤,显示CLDN4基因上调,提示CLDN4可能参与到早期胰腺癌的形成 [18]。在胃癌中,CLDN4异常高表达,采用CLDN4 siRNA 转染SGC7901胃癌细胞,发现细胞的侵袭能力显著下降,进一步研究发现,敲低CLDN4可增强PI3K和Akt的磷酸化,促进胃癌细胞的增殖、迁移、侵袭,以及降低胃癌细胞对化疗的敏感性 [19, 20]。
在肝癌中,锌指蛋白703(ZNF703)能够与CLDN4启动子结合,激活CLDN4的表达,诱导EMT从而促进肿瘤转移和索拉非尼耐药 [21]。在喉鳞状细胞癌中,CLDN4表达下调,研究证实喉癌组织中CLDN4的表达与MECP-2的表达相关,进一步的研究发现,DNA甲基化转移酶抑制剂(5-aza-dc)作用喉鳞癌细胞系hep-2后,可上调CLDN4的表达,并使hep-2细胞的迁移和侵袭能力下降 [22]。因此,CLDN4或可成为消化道相关肿瘤诊断的分子标志物。
3.2 CLDN4与生殖系统肿瘤
在卵巢癌中,过表达CLDN4可促进卵巢癌细胞的EMT进程,且高表达的CLDN4与患者的不良预后相关 [10, 11]。近期,另有研究揭示CLDN4缺失,可抑制DNA修复,并增加对PARP抑制剂的敏感性。而高表达CLDN4的卵巢癌肿瘤细胞,其对PARP抑制剂的敏感性降低 [23]。
在宫颈癌中,当细胞连接破坏后,与正常鱗状上皮相比,宫颈癌组织中CLDN4表达明显上调。当宫颈癌前病变越严重,组织表达的CLDN4水平则随之上升。CLDN4蛋白表达强度与宫颈癌前病变的程度密切相关,提示CLDN4的高表达可能会促进宫颈癌的发生 [24]。此外,高危型人乳头瘤病毒(HR-HPV)联合CLDN4检测能够提高宫颈癌前病变诊断的特异性。HR-HPV已被证实为宫颈癌及宫颈癌前病变的重要治病因素。因此,CLDN4或可作为诊断卵巢癌和宫颈癌前病变的重要手段。
3.3 CLDN4与其它肿瘤
在前列腺癌中,在表达CLDN4的小鼠前列腺癌异种移植模型中,注射产气荚膜梭菌肠毒素(clostridium perfringens enterotoxin, CPE)可显著抑制肿瘤的生长。CPE是人食物中毒及胃肠疾病的重要致病因子。CLDN3和CLDN4作为CPE的受体,CPE与受体特异性结合后,可通过胞膜穿透作用使细胞溶解坏死。研究表明,CPE的细胞毒性仅限于CLDN3和CLDN4高表达的癌细胞,并呈剂量依赖性 [25--27]。因此,在CLDN3和CLDN4高表达的癌组织中,整合CPE治疗,使其能结合特异CLDN受体,将使化疗药物具有肿瘤特异性,从而增强化疗效果。
在胶质瘤中,基于TCGA数据集进行Kaplan-Meier的分析表明,CLDN4的表达与OS和DFS呈负相关。进一步发现,CLDN4能够调节TNF-α诱导的NF-κB活性。破坏CLDN4/TNFα/NF-κB信号轴的功能,可能是治疗恶性胶质瘤患者的一种新策略 [1]。在三阴性乳腺癌中,CLDN4表达高于非三阴性乳腺癌,通过小鼠模型,使用CLDN4细胞外结构域抗体(4D3)可削弱乳腺癌细胞紧密连接的屏障功能,增强紫杉醇(Paclitaxel)的抗癌作用 [28]。在膀胱癌中,在皮下肿瘤和肺转移的小鼠模型中,联合CLDN4抗体(4D3)治疗可增强顺铂(Cisplatin)抑制肿瘤生长的效果 [29]。
4. CLDN4的临床研究前景
大量研究已证明CLDN家族是一类具有重要研究价值的细胞表面蛋白质分子,发挥着重要的屏障作用。CLDN蛋白在肿瘤细胞表面存在的异常表达,和多种肿瘤的发生发展有关。当前,CLDN4蛋白在细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭中的作用有了越来越多的新见解,大量证据显示CLDN4的异常表达能影响肿瘤的侵袭和转移能力。尤其是在高表达CLDN4的肿瘤中,CLDN4有望作为肿瘤的标志物和治疗靶点。日益增多的证据表明,联合抗CLDN4抗体治疗,具有潜在的应用前景,能增强现有药物的作用效果。随着CLDN家族领域研究的不断深入,相信越来越多CLDN蛋白作用将为更多疾病的诊断治疗提供新思路。
为鼎力协助科研和药企人员针对CLDN4在机体功能调节方面,以及CLDN4在肿瘤中的临床应用研究,CUSABIO推出CLDN4活性蛋白(Code: CSB-MP005506HU)产品,助力您在CLDN4机制方面的研究或其潜在临床价值的探索。
Recombinant Human Claudin-4(CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)

The high specifity was validated by western blot. CSB-MP005506HU is detected by Mouse anti-6*His monoclonal antibody.
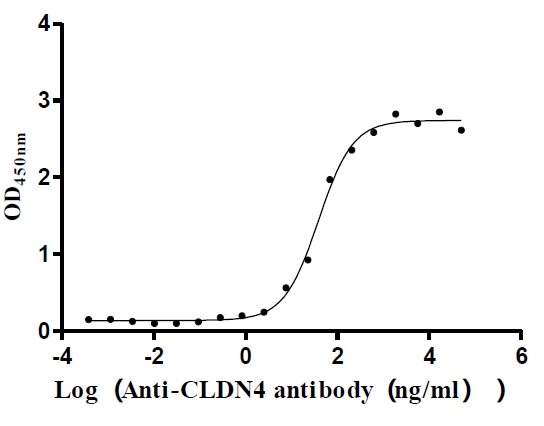
Immobilized Human CLDN4 at 5 μg/ml can bind Anti-CLDN4 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA005506MA1HU), the EC50 is 29.56-50.75 ng/mL.
参考文献:
[1] Yan, Tengfeng, et al. "TGF-β induces GBM mesenchymal transition through upregulation of CLDN4 and nuclear translocation to activate TNF-α/NF-κB signal pathway." Cell death & disease 13.4 (2022): 1-11.
[2] Uthayanan, Leshanth, and Mona El-Bahrawy. "Potential roles of claudin-3 and claudin-4 in ovarian cancer management. "Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute 34.1 (2022): 1-9.
[3] Yao, Qing-Ting, et al. "Pilocarpine improves submandibular gland dysfunction in irradiated rats by downregulating the tight junction protein claudin-4." Oral Diseases 28.6 (2022): 1528-1538.
[4] Liu, Hong, et al. "Claudin-1/4 as directly target gene of HIF-1α can feedback regulating HIF-1α by PI3K-AKT-mTOR and impact the proliferation of esophageal squamous cell though Rho GTPase and p-JNK pathway." Cancer Gene Therapy 29.6 (2022): 665-682.
[5] Maesaka, Fumisato, et al. "Hypomethylation of CLDN4 Gene Promoter Is Associated with Malignant Phenotype in Urinary Bladder Cancer." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.12 (2022): 6516.
[6] Kim, Won Shik, et al. "High Expression of Claudin-4 Is Associated with Synchronous Tumors in Patients with Early Gastric Cancer." journal of clinical medicine 11.12 (2022): 3550.
[7] Swisshelm, Karen, Robert Macek, and Manfred Kubbies. "Role of claudins in tumorigenesis." advanced drug delivery reviews 57.6 (2005): 919-928.
[8] Kage, Hidenori, et al. "Dichotomous roles of claudins as tumor promoters or suppressors: lessons from knockout mice." Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 76.23 (2019): 4663-4672.
[9] Li, Jian. "Context-dependent roles of claudins in tumorigenesis." Frontiers in oncology 11 (2021): 676781.
[10] Hicks, Douglas A., et al. "Claudin-4 activity in ovarian tumor cell apoptosis resistance and migration." bmc cancer 16.1 (2016): 1-11.
[11] English, Diana P., and Alessandro D. Santin. "Claudins overexpression in ovarian cancer: potential targets for Clostridium Perfringens Enterotoxin ( CPE) based diagnosis and therapy." international journal of molecular sciences 14.5 (2013): 10412-10437.
[12] Michl, Patrick, et al. "Claudin-4 expression decreases invasiveness and metastatic potential of pancreatic cancer." Cancer research 63.19 (2003): 6265-6271.
[13] Wang, Fei, et al. "A novel PAK4-CEBPB-CLDN4 axis involving in breast cancer cell migration and invasion." biochemical and biophysical research communications 511.2 (2019): 404-408.
[14] Shi, Hailian, et al. "SP1 affects the migration and invasion of laryngeal cancer cells by regulating methylation of claudin 4 promoter region through the p-JNK pathway." bioRxiv (2022).
[15] Liu, Yafang, et al. "DNA demethylation of claudin-4 suppresses migration and invasion in laryngeal squamous carcinoma cells." Human Pathology 75 (2018 ): 71-80.
[16] Okumura, Toshikatsu. "Mechanisms by which thiazolidinediones induce anti-cancer effects in cancers in digestive organs." journal of gastroenterology 45.11 (2010): 1097-1102.
[17] Kumei, Shima, et al. "Troglitazone increases expression of E-cadherin and claudin 4 in human pancreatic cancer cells." Biochemical and biophysical research communications 380.3 (2009): 614-619.
[18] Terris B, Blaveri E, Crnogorac-Jurcevic T, et al. Characterization of gene expression profiles in intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas[J]. The American journal of pathology, 2002, 160(5): 1745-1754.
[19] Liang Z Y, Kang X, Chen H, et al. Effect of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin on gastric cancer cells SGC7901 which highly expressed claudin-4 protein[. J]. World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology, 2017, 9(4): 153.
[20] Luo, Jie, et al. "CLDN4 silencing promotes proliferation and reduces chemotherapy sensitivity of gastric cancer cells through activation of the PI3K/ Akt signalling pathway." Experimental Physiology 105.6 (2020): 979-988.
[21] Wang, Hao, et al. "Zinc finger protein 703 induces EMT and sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by transactivating CLDN4 expression." Cell death & disease 11.4 (2020): 1-15.
[22] Liu, Yafang, et al. "DNA demethylation of claudin-4 suppresses migration and invasion in laryngeal squamous carcinoma cells." Human Pathology 75 (2018 ): 71-80.
[23] Yamamoto, Tomomi M., et al. "Loss of Claudin-4 Reduces DNA Damage Repair and Increases Sensitivity to PARP Inhibitors." Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 21.4 (2022): 647-657.
[24] Di, Chenhong, and Fan Jin. "Value of combined detection of claudin 4 and high-risk human papilloma virus in high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion and cervix squamous cell carcinoma." Zhejiang da xue xue bao. yi xue ban Journal of Zhejiang University. medical Sciences 47.4 (2018): 344-350.
[25] Maeda, Toshihiro, et al. "Claudin-4-targeted therapy using Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin for prostate cancer." The Prostate 72.4 (2012): 351-360.
[26] Takahashi, Azusa, et al. "Mutated C-terminal fragments of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin have increased affinity to claudin-4 and reversibly modulate tight junctions in vitro." Biochemical and biophysical research communications 410.3 (2011): 466-470.
[27] Saeki, Rie, et al. "A novel tumor-targeted therapy using a claudin-4-targeting molecule." Molecular Pharmacology 76.4 (2009): 918-926.
[28] Luo, Yi, et al. "Targeting claudin-4 enhances chemosensitivity in breast cancer." Cancer science 111.5 (2020): 1840-1850.
[29] Kuwada, Masaomi, et al. "Pro-chemotherapeutic effects of antibody against extracellular domain of claudin-4 in bladder cancer." Cancer letters 369.1 (2015): 212-221.
上一篇: ALPi——肠粘膜屏障保镖
下一篇: 结核病--卷土重来的“白色瘟疫”











