组蛋白去甲基化酶:LSD和JmjC家族
日期:2024-02-05 14:28:27
在真核细胞核中,组蛋白H2A和H2B紧密相互作用形成二聚体,H3和H4形成四聚体,两个H2A、H2B二聚体和一个H3、H4四聚体形成核心组蛋白八聚体。DNA与核心组蛋白八聚体纠缠在一起,形成核小体,这是染色体的基本单位。组蛋白是 DNA 压缩的有力工具。组蛋白翻译后修饰是调节核小体结构的常见途径。四种常见的组蛋白修饰包括甲基化、乙酰化、磷酸化和泛素化。
组蛋白的甲基化与基因转录激活、转录沉默、X染色体失活和异染色质致密状态密切相关。长期以来,组蛋白甲基化被认为是一个不可逆的过程。随着2004年第一个组蛋白去甲基化酶的发现 [1],组蛋白甲基化显然是一个动态调控的过程。组蛋白甲基化受组蛋白甲基转移酶(HMTs)和组蛋白去甲基化酶(HDMs)的调控。组蛋白去甲基化是甲基化过程的对立过程。
1. 什么是组蛋白去甲基化?
组蛋白去甲基化是组蛋白去甲基化酶(HDMs)催化去除组蛋白N端尾部特定氨基酸上甲基的过程。组蛋白去甲基化酶主要作用于组蛋白H3上的赖氨酸(K)残基,包括K4、K9、K27和 K36。组蛋白去甲基化酶也称为组蛋白赖氨酸去甲基化酶(KDMs)。
2. 两个组蛋白去甲基化酶家族:LSD和JmjC
目前已发现两个进化保守的组蛋白去甲基化酶家族:赖氨酸特异性去甲基化酶(LSD)和含Jumonji C(JmjC)结构域的去甲基化酶(JHDM)[1][2]。它们利用不同的机制去除甲基。
2.1 LSD去甲基化酶
LSD家族由LSD1和LSD2组成,它们通过黄素腺嘌呤二核苷酸(FAD)依赖性胺氧化酶反应,使单甲基化和二甲基化赖氨酸残基去甲基化。LSD1又称KDM1A或AOF2,是第一个被发现的组蛋白赖氨酸去甲基化酶,它能去除组蛋白H3中赖氨酸4(H3K4me1/2)或组蛋白H3中赖氨酸9(H3K9me1/2)上的单甲基和二甲基基团,分别作为基因表达的抑制因子或激活因子。
LSD1去甲基化机制:
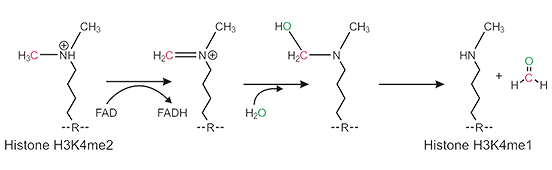
图1. LSD1去甲基化机制
图片来源:https://journals.biologists.com/dev/article/136/6/879/43849/Developmental-roles-of-the-histone-lysine
LSD1与CoREST和组蛋白去乙酰化酶1/2(HDAC1/2)相互作用,从而赋予H3K4me1/2更多的特异性,导致其去甲基化,从而促进异染色质的形成和靶基因的转录失活 [1][4]。然而,当LSD1与活化的雄激素受体(如雌激素受体(ER)或雄激素受体(AR))复合时,它作为转录激活剂会使H3K9me1/2去甲基化 [5][6]。
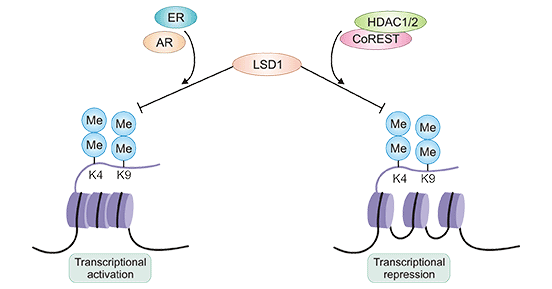
图2. LSD1同时充当转录激活剂或抑制剂
图片来源:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5691370/
通过使H3K4去甲基化,LSD1可使DNA甲基转移酶(DNMTs)的正调控因子DNMT3L与未甲基化的K4位点结合,从而促进DNMTs的表达,引起DNA的再甲基化,从而导致基因转录抑制。
此外,LSD1 还能使非组蛋白去甲基化,如p53上的K370me1和K370me2、DNMT1上的Lys1096以及E2F1上的Lys185。
LSD2也称为KDM1B或AOF2,是另一种FAD依赖性胺氧化酶同源物,含有SWIRM结构域,专门靶向H3K4me1/2 [7]。然而,由于KDM1B缺乏塔状结构域,因此无法与CoREST形成复合物。
2.2 JmjC去甲基化酶
Tsukada等人于2006年首次发现了含JmjC域的蛋白JHDM1A/KDM2A是一种H3K36me1/2去甲基化酶 [2]。根据序列信息,含JmjC的蛋白质可分为7个家族,即JHDM1、JHDM2、JHDM3、JARID1、UTX/UTY、PHF8和仅含 JmjC结构域的蛋白质。JmjC家族由30个成员组成,迄今已有近20个成员被证明具有组蛋白去甲基化酶活性。
JmjC去甲基化机制:
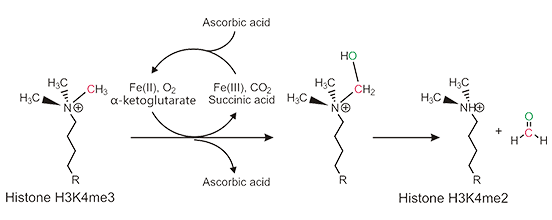
图1. JmjC去甲基化机理
图片来源:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5691370/
表1. HDM家族成员
| 家族 | HDM名称 | 结构域 | Histone亚结构 | 功能 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSD | LSD1 | KDM1A | SWIRM, AOL, Tower domains | H3K4me1/2, H3K9me1/2 | 转录抑制或激活;DNA 甲基化;早期胚胎发育 |
| LSD2 | KDM1B | AOL and SWIRM domains | H3K4me1/2 | 与基因中的转录编码区相关,对优化基因转录非常重要 | |
| JmjC domain-containing protein | JHDM1 | JHDM1A/KDM2A | JmjC, LRRS, F-box, CXXX zinc finger, and DNA-binding domains | H3K36me1/2 | 转录延伸 |
| JHDM1AB/KDM2B | H3K36me1/2; H3K4me3 | 转录延伸;抗癌基因 | |||
| JHDM2 | JHDM2A/KDM3A | JmjC, Zinc-like finger domain | H3K9me1/2 | 雄激素受体激活;精子发生;糖尿病 | |
| JHDM2B/KDM3B | H3K9me1/2 | 抗癌基因 | |||
| JHDM3 | JHDM3A/JMJD2A/KDM4A | JmjN domain, the JmjC domain, the C-terminal domain, and a zinc-finger motif | H3K9me2/3; H3K36me2/3 | 转录抑制;基因组完整性维护 | |
| JHDM3B/JMJD2B/KDM4B | H3K9me2/3; H3K36me 2/3 | 异染色质形成 | |||
| JHDM3C/JMJD2C/KDM4C | H3K9me2/3; H3K36me2/3 | 癌基因;维持干细胞的全能性 | |||
| JHDM3D/JMJD2D/KDM4D | H3K9me2/3; H3K36me2/3 | 雄激素受体激活 | |||
| JARID1 | JARID1A/KDM5A | JmjC, JmjN, AT rich interactive, C5HC2 zinc finger, and PHD domains | H3K4me2/3 | RB 结合蛋白 | |
| JARID1B/KDM5B | H3K4me1/2/3 | 转录抑制;癌基因 | |||
| JARID1C/KDM5C | H3K4me2/3 | 与 X 染色体有关的智力障碍 | |||
| JARID1D/KDM5D | H3K4me2/3 | 雄性特异抗原 | |||
| KDM6A | UTX | JmjC, six tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domains | H3K27me2/3 | 调节 HOX 基因表达;抗癌基因 | |
| KDM6B | JMJD3 | JmjC domain, a C-terminal segment embedded with a GATAL domain | H3K27me2/3 | 神经和表皮细胞产生免疫力 | |
| JMJD6 | JmjC domain, three apparent nuclear localization signals (NLS), a DNA binding domain (AT-hook domain), a putative sumoylation site, and a polyserine (polyS) domain | H3K2me2, H4K3me2 | 转录激活;胚胎发育 | ||
3. 组蛋白去甲基化酶的功能是什么?
自2004年发现第一个组蛋白去甲基化酶以来,研究人员已对已发现的组蛋白去甲基化酶的活性进行了全面鉴定,发现这些组蛋白去甲基化酶不仅可以靶向组蛋白和非组蛋白底物,而且在癌症、发育、代谢性疾病(糖尿病)等过程中发挥着重要作用。
3.1 组蛋白去甲基化酶与癌症
LSD1在许多癌症中异常表达,阻碍癌细胞分化,促进癌细胞增殖、转移和侵袭,并与预后不良有关。在造血和淋巴肿瘤中,包括急性髓性白血病(AML)、急性淋巴细胞白血病、T细胞非霍奇金淋巴瘤和霍奇金淋巴瘤,都发现了LSD1的过表达。LSD1还与多种实体瘤有关,包括非小细胞肺癌、神经母细胞瘤、胰腺癌、前列腺癌和乳腺癌。抑制LSD1的作用可能会减少或阻止这些肿瘤的细胞生长。
Wan,W.等发现,JMJD1A与HIF-1α的关联影响了膀胱肿瘤细胞糖代谢通路中PGK1启动子HRE区的H3K9me2水平,从而影响PGK1的表达,进一步调控膀胱肿瘤细胞的糖代谢通路,最终对膀胱肿瘤细胞的生长和增殖起到调控作用 [8]。
3.2 组蛋白去甲基化酶与发育
大量研究表明,组蛋白去甲基化酶在不同物种的发育过程中发挥着特定的生物学作用,包括在种系维持和减数分裂、早期胚胎发育和分化以及激素受体介导的转录调控中的作用。
在后生动物中,LSD1作用于 H3K4me1/2,并在生殖系中发挥重要作用。在发育过程中,几种去甲基化酶参与了多能祖细胞类型向分化细胞系的进展。在胚泡阶段,LSD1 既是母体储存的,也在胚胎发生过程中表达 [9]。在体外受精的小鼠胚胎中使用LSD1去甲基化酶抑制剂Bisguanidine 1c,会导致小鼠胚胎中 H3K4me2 整体增加并诱导不可逆的停滞 [10]。这证明了LSD1在胚胎中的作用,并且对早期分化事件至关重要 [10]。在苍蝇中,LSD1的缺失会导致胚胎死亡。
最近,JMJD2C和JHDM2A都与小鼠胚胎干(ES)细胞多能性的维持有关。这两种去甲基化酶在未分化的ES细胞中表达,似乎通过激活多能性维持蛋白(如OCT4、NANOG和TCL1)的转录来保持多能性 [11][12]。
Jepsen等人发现,当小鼠胚胎神经干细胞(NSCs)暴露于维甲酸(RA)诱导分化时,JMJD3成为维甲酸和甲状腺激素受体沉默介质(SMRT)的转录靶标[13]。他们还发现,JMJD3在NSC培养物中的过表达刺激了Dlx5等神经元亚型基因的表达,为JMJD3在驱动神经元分化中的作用提供了证据。
Yamane等人的研究表明,LSD1和JHDM2A共同调控了编码前列腺特异性抗原(PSA)和NKX3.1的雄激素受体(AR)反应基因 [6][14]。
3.3 组蛋白去甲基化酶与糖尿病
Tateishi 等人发现,JHDM2A 基因敲除小鼠表现出肥胖和高脂血症的症状。详细研究表明,β-肾上腺素的刺激可诱导JHDM2A基因的表达,JHDM2A可与Ppara和Ucp1基因结合,直接调控其表达。因此,JHDM2A基因的缺乏会影响棕色脂肪组织的甘油释放和氧代谢,降低骨胳脂肪氧化和甘油释放,最终导致肥胖和高血压。
j9九游会登录入口首页生物提供用于研究的各种重组组蛋白去甲基化酶:
参考文献:
[1] Shi Y, Lan F, et al. (2004) Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1 [J]. Cell 119: 941–953.
[2] Tsukada Y, Zhang Y, et al. (2006) Histone demethylation by a family of JmjC domain-containing proteins [J]. Nature 439: 811–816.
[3] Hojfeldt JW, Agger K, Helin K. Histone lysine demethylases as targets for anticancer therapy [J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12:917–930.
[4] Lee MG, Wynder C, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R. An essential role for CoREST in nucleosomal histone 3 lysine 4 demethylation [J]. Nature. 2005;437:432–5.
[5] Wissmann M. Cooperative demethylation by JMJD2C and LSD1 promotes androgen receptor-dependent gene expression [J]. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:347–353.
[6] Metzger E, Wissmann M, Yin N, et al. LSD1 demethylates repressive histone marks to promote androgen-receptor-dependent transcription [J]. Nature. 2005;437(7057):436–9.
[7] Ciccone DN. KDM1B is a histone H3K4 demethylase required to establish maternal genomic imprints [J]. Nature. 2009;461:415–418.
[8] Wan, W., Peng, K., et al. Histone demethylase JMJD1A promotes urinary bladder cancer progression by enhancing glycolysis through coactivation of hypoxia inducible factor 1α [J]. Oncogene 36, 3868–3877 (2017).
[9] McGraw, S., Vigneault, C. and Sirard, M. A. (2007). Temporal expression of factors involved in chromatin remodeling and in gene regulation during early bovine in vitro embryo development [J]. Reproduction 133, 597-608.
[10] Shao, G. B., Ding, H. M. and Gong, A. H. (2008). Role of histone methylation in zygotic genome activation in the preimplantation mouse embryo [J]. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 44, 115-120.
[11] Katoh, Y. and Katoh, M. (2007). Comparative integromics on JMJD2A, JMJD2B and JMJD2C: preferential expression of JMJD2C in undifferentiated ES cells [J]. Int. J. Mol. Med. 20, 269-273.
[12] Loh, Y. H., Zhang, W., et al. (2007). Jmjd1a and Jmjd2c histone H3 Lys 9 demethylases regulate self-renewal in embryonic stem cells. Genes Dev. 21, 2545-2557.
[13] Jepsen, K., Solum, et al. (2007). SMRT-mediated repression of an H3K27 demethylase in progression from neural stem cell to neuron [J]. Nature 450, 415-419.
[14] Yamane, K., Toumazou, C., et al. (2006). JHDM2A, a JmjC-containing H3K9 demethylase, facilitates transcription activation by androgen receptor [J]. Cell 125, 483-495.
下一篇: 组蛋白修饰:基因调控和疾病发病机制的意义











