GIPR蛋白:糖和脂肪代谢的重要调控者,糖尿病、肥胖症“救星”?
日期:2023-06-15 10:33:53
最近,GIPR靶点备受关注。Pharmsnap发布的最新临床数据表明,GIPR靶点的药物Tirzepatide(替尔泊肽;2022年批准上市)在中国已处于申请上市阶段,主要用于治疗2型糖尿病、肥胖症及心血管疾病等。GIPR属于G蛋白耦联受体家族(GPCR)。多个GPCR分子已被报道在多种疾病调控中发挥重要功能(点击查看以往文章报道:如GCGR)。
目前,国内外对GIPR的研究着重于其与糖代谢及脂肪代谢的关系。大量数据表明GIPR有望成为临床治疗肥胖症和糖尿病的“救星”。最新研究揭示,GIPR还参与了胃肠道神经内分泌肿瘤(NETs)的发生和发展。那么,GIPR作为GPCR家族中的一员,在糖代谢和脂肪代谢中是如何发挥调控作用?今天,我们一起揭晓!
1. 什么是GIPR?
胃抑制肽受体(Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor,GIPR)是GIP的受体,亦是具有7个跨膜域的G蛋白耦联受体(点击查看专题报道:跨膜蛋白系列三:G蛋白偶联受体)[1]。人GIPR基因位于19号染色体的q 13.3,分子量约为50KD。结构上,GIPR的N端含一个连续糖基化序列(N-X-S/T)和一个第三细胞质环,C端富含苏氨酸和丝氨酸,为潜在的磷酸化位点(图1)[2-4]。
GIPR在胰腺细胞、胃、小肠、脂肪组织、肾上腺皮质、心脏、垂体、骨骼、肺和脾脏等组织均有表达。在胰岛中只有a和β细胞表达GIPR。GIPR通过激活G蛋白,活化的G蛋白使细胞内cAMP水平和Ca2+水平提高,通过PI3K、PAK、PKB等信号通路对下游基因进行表达调控 [2-4]。
当人体摄入食物后,GIPR信号能够促进胰岛素的分泌,从而使得血糖水平降低。同时,GIPR还能够影响脂肪细胞的存储和代谢,以及肝脏中的葡萄糖合成和释放。大量研究揭示,GIPR在调控胰岛素分泌、血糖和脂代谢方面扮演着重要的角色,对维持正常的代谢状态至关重要 [5]。
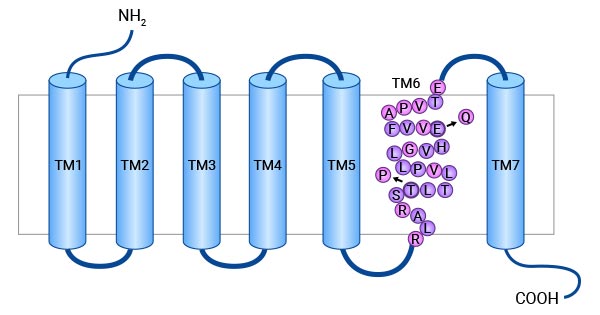
图1. GIPR的结构 [4]
2. GIPR的配体
GIPR的配体是葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素多肽(GIP,glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide)。GIP是由小肠上段的K细胞分泌的肠促胰岛素。肠促胰岛素主要包括GIP和胰高血糖素样肽-1(GLP-1,glucagon-likepeptide-1),它们分别通过作用于β细胞相应受体GIPR和GLP-1R,进而调控β细胞分化增殖、胰岛素合成与分泌等,发挥其主要作用(图2) [6]。GIP具有促进胰岛素分泌并改善其敏感性,增加GLP-1的分泌,上调p细胞相关基因的表达,促进胰岛细胞的增殖,延迟胰岛素清除,促进神经修复等功能。GIP的表达主要受RFX6,PDX1,GATA-4和ISL1等转录因子的调节 [6-10]。
GIP与GIPR结合,使G蛋白的构象改变,激活腺苷酸环化酶(AC),释放cAMP,使细胞内的cAMP浓度升高,并激活PAK信号通路,从而提高控制胰岛素合成分泌的关键蛋白质(如CREB)磷酸化程度,最终促进葡萄糖刺激后胰岛素的分泌。GIP需要与细胞表面相应的GIPR结合才能发挥生物学效应。因此,GIPR是GIP发挥作用的关键 [10]。
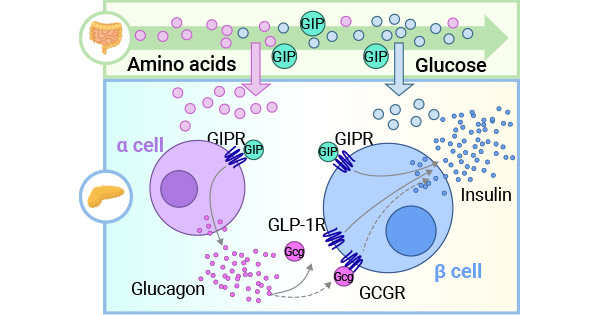
图2. GIP和GLP-1作用于β细胞相应受体GIPR和GLP-1R[6]
3. GIPR-GIP调控的相关信号通路
近年来,GIPR-GIP通路的重要性逐渐被重视。GIPR信号通路涉及许多生理过程,包括胰岛增殖、能量代谢调节、肠道功能调控,与脂肪组织中脂质积累、胰岛素抵抗等密切相关。目前,GIPR-GIP诱导的下游相关信号分子通路有待进一步阐明。
在脂肪等细胞中的研究显示,GIPR-GIP激活CREB、TORC2或胰岛素,协同促进PKB磷酸化等途径,促进脂蛋白脂肪酶LPL,从而促进脂肪堆积(图3) [11-12]。GIP还能促进脂肪组织中IL-6的表达,从而诱导胰岛素抵抗。GIPR-GIP还可通过MAPK、Akt和FoxO1通路降低caspase3和bax基因的活性,发挥促增殖和抗凋亡的作用 [11-13]。
另有报道,激动GIPR-GIP信号通路能驱动肥胖状态下瘦素(leptin)抵抗的发生。GIP通过激活下丘脑中Epac/Rapl信号通路,抑制瘦素受体信号通路分子的激活,促进瘦素信号通路负性调节因子的表达,抑制瘦素诱导的阿片黑素促皮质素原(proopiomelanocortin,POMC)神经元激活,从而诱导中枢瘦素抵抗的发生。因此,抑制GIPR-GIP信号通路可作为减肥的新靶点 [14-15]。
此外,GIPR-GIP经Akt信号通路上调TCF4进而增强GIPR表达,形成正反馈加强GIP信号,提高β细胞增殖和胰岛素分泌的功能,维持血糖稳态。因此,在胰岛素抵抗阻断Akt及上游信号通路时,GIPR有望作为改善胰岛β细胞功能障碍的靶点 [16-17]。
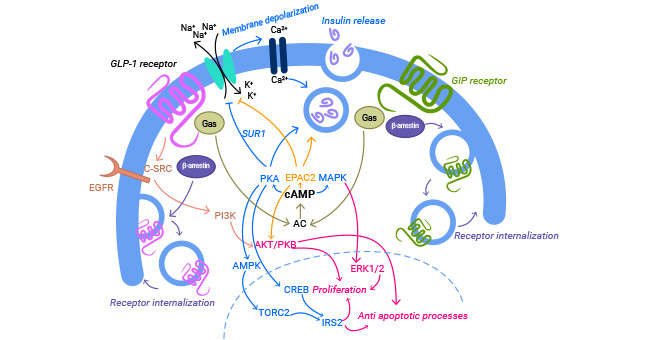
图3. GIPR-GIP调控的相关信号通路 [12]
4. GIPR在糖尿病、肥胖症等疾病中的作用
GIPR在血糖调节和能量代谢方面扮演着关键角色。另外,GIPR与GLP-1R相似,在控制食欲和体重方面具有潜在的效果。GLP-1R受体是目前糖尿病治疗中广泛使用的靶点之一,它能够减少食欲,从而帮助糖尿病患者减轻体重和控制血糖水平。因此,GIPR作为GLP-1R的近亲,GIPR成为了一个非常重要的治疗靶点,有望帮助控制肥胖、糖尿病等代谢性疾病的发生和发展。
4.1 GIPR和糖尿病
糖尿病是一种常见的代谢性疾病,主要分为1型糖尿病(T1DM)、2型糖尿病(T2DM)、特异型和妊娠型糖尿病4种。糖尿病患者中,90%以上为2型糖尿病。研究发现,高脂膳食诱导肥胖(diet-induced obesity,DIO)小鼠血清GIP水平较对照组小鼠相比显著升高。肥胖和糖耐量受损患者的GIP水平较健康人群也显著高 [18-20]。
另外,健康人血浆GEP(Gene Expression Profile)水平与BMI(Body Mass Index)、胰岛素抵抗等指标呈正相关。采用多种途径阻断GIR-GIPR信号通路后,包括基因敲除、注射单克隆抗体、使用拮抗剂以及疫苗接种等方法,均能显著减轻DIO小鼠的体重,减少脂肪含量,改善胰岛素抵抗等代谢相关异常 [18-20]。
4.2 GIPR和肥胖
越来越多的研究表明,在肥胖者体内观察到GIPR-GIP轴功能的受损。进一步的研究提示,GIPR-GIP能促进人皮下脂肪细胞和小鼠脂肪细胞中IL-1beta的合成和分泌 [21-23]。
相反,阻断GIPR-GIP的信号通路,包括给小鼠侧脑室注射GIPR抑制剂或者采用GIPR敲除小鼠,小鼠摄食减少,体重减轻,脂肪含量减少,血清和脂肪组织中瘦素和IL-6等炎症因子水平降低,同时脂肪组织的脂质氧化增强 [21-23]。
4.3 GIPR和其它疾病
在食物成瘾、肢端肥大症和胃肠道神经内分泌肿瘤(gastrointestinal neuroendocrine neoplasm,GINEN)等情况中,GIPR-GIP通路的异常激活特别常见。在进行糖耐量试验时,GIPR-GIP异常激活与生长激素(GH)反常升高有关。GIP与肾上腺皮质腺瘤及垂体GH腺瘤异位表达的GIPR结合后,促进相应激素分泌增加及细胞增殖;部分生长抑素受体阴性的GINEN高表达GIPR [24-27]。
此外,在GINEN肿瘤组织中,GIPR和SSTR2的表达显著高于正常对照组织。GINEN与正常组织中,GIPR表达量的比值即GIPR相对表达量显著高于SSTR2相对表达量。这些发现提示,GIPR可以作为一个候选的肿瘤标记物应用于GINEN的诊断 [24-27]。
5. GIPR的临床在研药物
目前,国内外高达40多款GIPR靶点药物临床研究正在进行中(表1),包括礼来(Ei Lilly)、安进(Amgen)、浙江道尔生物、华东医药、杭州先为达生物等。药物形式更是包括了单抗、双抗、多肽偶联药物(PDC)、融合蛋白等。这些药物的作用机制大多是激动或拮抗GIPR,同时有些还具有GLP-1R激动剂、GCGR激动剂和NPY受体调节剂等作用。如前所述,已有1款GIPR靶点药物获批上市。当前,GIPR作为糖代谢和脂肪代谢的重要调控者,有望在糖尿病、肥胖、代谢综合征、心血管疾病等多个领域展现出广泛的应用前景,对神经内分泌肿瘤也有潜在的治疗作用。总之,GIPR是一个值得关注的重要靶点,相信未来还将有更多的药物涌现。
| 药物 | 靶点 | 作用机制 | 在研适应症 | 药物最高研发状态(全球) | 药物类型 | 在研机构 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tirzepatide替尔泊肽 | GIPR+GLP-1R | GIPR激动剂;GLP-1R激动剂 | 2型糖尿病;超重;阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征;心血管疾病;肥胖 | 批准上市 | 合成多肽 | Ei Lilly & Co;Ei Lily Japan KK;礼来苏州制药有限公司 |
| Retatrutide | GCGR +GIPR | GCGR激动剂;GLP-1R激动剂 | 心血管疾病;肥胖;超重;2型糖尿病 | 临床3期 | 合成多肽 | Ei Lilly & Co;礼来苏州制药有限公司 |
| Maridebart Cafraglutide | GIPR+GLP-1R | GIPR拮抗剂;GLP-1R激动剂 | 2型糖尿病;肥胖;超重 | 临床2期 | 多肽偶联药物(PDC) | Amgen, Inc. |
| LY-3537031 | GIPR+GlP-1R | GIPR激动剂、GLP-1R激动剂 | / | 临床1期 | 合成多肽 | Ei Lilly & Co |
| CT-388 | GIPR+GlP-1R | GIPR激动剂、GLP-1R调节剂 | 糖尿病;2型糖尿病;肥胖;非酒精性脂肪性肝炎 | 临床1期 | 合成多肽 | 卡默療法股份有限公司 Carmot Therapeutics, Inc. |
| DR10627 | GIPR+GlP-1R | GIPR激动剂、GLP-1R调节剂 | 糖尿病;非酒精性脂肪性肝炎 | 临床1期 | 合成多肽 | 浙江道尔生物科技有限公司 Zhejiang Doer Biologics Co.,Ltd. |
| GMA-106 | GIPR+GlP-1R | GIPR拮抗剂、GLP-1R拮抗剂 | 肺沉着症;2型糖尿病;非酒精性脂肪性肝炎;肥胖;超重 | 临床1期 | 双特异性抗体 | 鸿运华宁(杭州)生物医药有限公司 Gmax Biopharm LLC |
| Maridebart | GIPR | GIPR拮抗剂 | 肿瘤 | 临床阶段不 | 单克隆抗体 | / |
| Efocipegtrutide | GIPR+GlP-1R | GIPR激动剂、GLP-1R激动剂 | / | 临床阶段不 | 融合蛋白 | / |
| DR10628 | GIPR+GlP-1R | GIPR激动剂、GLP-1R激动剂 | 糖尿病;非酒精性脂肪性肝炎 | 临床前 | 融合蛋白 | 浙江道尔生物科技有限公司 Zhejiang Doer Biologics Co.,Ltd. |
| HDM-1005 | GIPR+GlP-1R | GIPR激动剂、GLP-1R激动剂 | 糖尿病;肥胖 | 临床前 | 双特异性抗体 | 华东医药股份有限公司 Huadong Medicine Co., Ltd. |
| 111In-3BP tracer | GIPR | GIPR拮抗剂 | 神经内分泌肿瘤 | 临床前 | 合成多肽 | 3B Pharmaceuticals GmbH |
| DR10625 | FGF21 + GIPR + GLP-1R | FGF21 调节剂、GIPR激动剂、GLP-1R激动剂 | 肥胖;2型糖尿病;非酒精性脂肪性肝炎 | 临床前 | 融合蛋白 | 浙江道尔生物科技有限公司 Zhejiang Doer Biologics Co.,Ltd. |
| XW-017 | GIPR | GIPR激动剂 | 肥胖;2型糖尿病;非酒精性脂肪性肝炎 | 临床前 | 合成多肽 | 杭州先为达生物科技有限公司 Hangzhou Sciwind Biosciences Co., Ltd. |
| LBT-6030 | GIPR+GlP-1R | GIPR激动剂、GLP-1R激动剂 | 糖尿病 | 临床前 | 生物药 | Longevity Biotech, Inc. |
| 3B-402 | GIPR | GIPR调节剂 | 神经内分泌肿瘤 | 药物发现 | 合成多肽 | 3B Pharmaceuticals GmbH |
| 3B-401 | GIPR | GIPR调节剂 | 神经内分泌肿瘤 | 药物发现 | 合成多肽 | 3B Pharmaceuticals GmbH |
| ZP-3022(Zealand Pharma A/S) | GCGR + GIPR + GLP-1R + NPY receptor | GCGR调节剂、GIPR激动剂、GLP-1R激动剂 | / | 临床前 | 生物药 | / |
| ZP-1-98(Zealand Pharma A/S) | GIPR | GIPR激动剂 | / | 临床前 | 生物药 | / |
| CYT-014-GIPQb | GIPR | GIPR调节剂 | / | 药物发现 | 生物药 | / |
表1:GIPR的临床在研药物(部分)
为鼎力协助科研和药企人员针对GIPR在糖尿病、肥胖症、肿瘤临床应用中的研究,CUSABIO推出GIPR活性蛋白(Code: CSB-MP009438MO1; Code: CSB-MP009438RA1)产品,助力您在GIPR机制方面的研究或其潜在临床价值的探索。
j9九游会登录入口首页CUSABIO蛋白GIPR
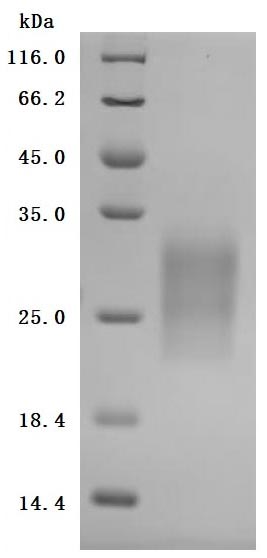
High specificity was validated by SDS-PAGE. SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
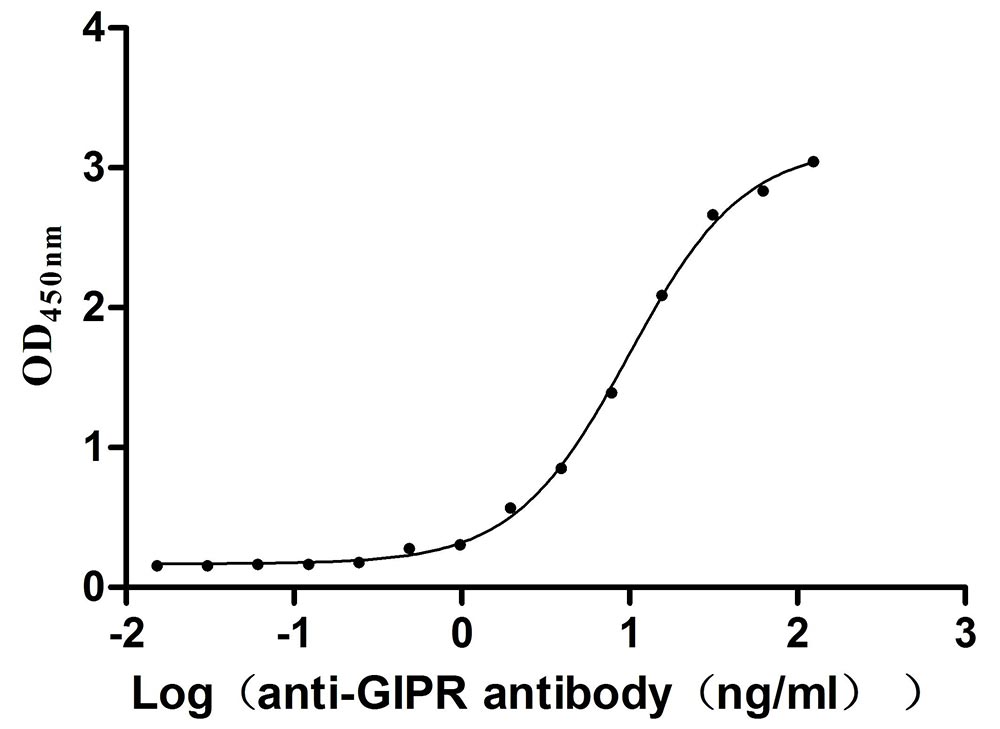
Immobilized Mouse Gipr at 2μg/mL can bind Anti-Mouse Gipr recombinant antibody (CSB-RA009438MA1MO), the EC50 is 8.622-11.36 ng/mL.
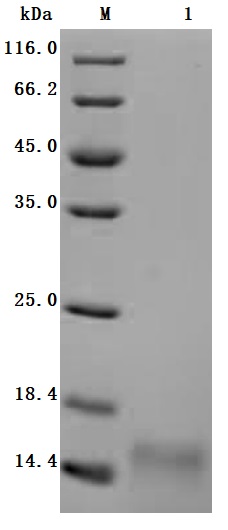
High specificity was validated by SDS-PAGE. SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
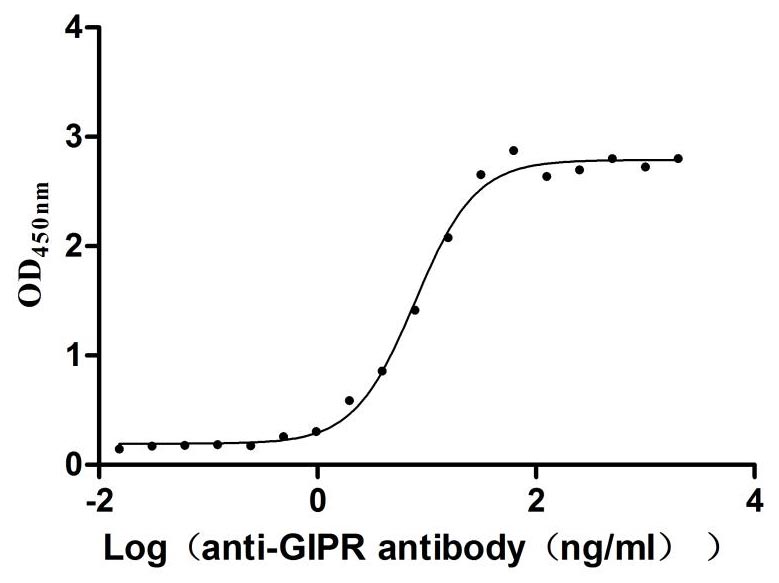
Immobilized Rat Gipr at 2μg/mL can bind Anti-Mouse Gipr recombinant antibody (CSB-RA009438MA1MO), the EC50 is 6.946-8.740 ng/mL.
High specificity was validated by SDS-PAGE. SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
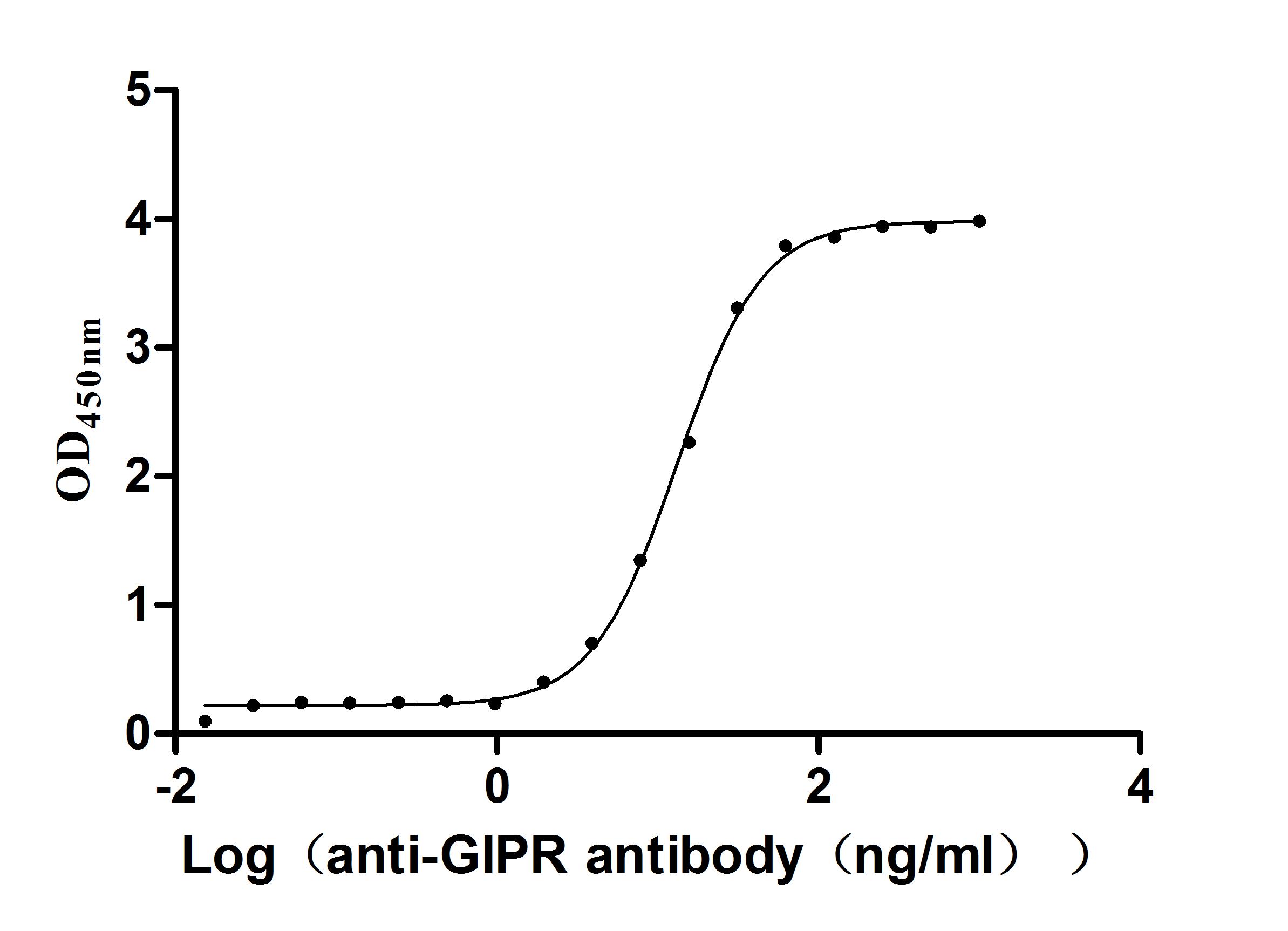
Immobilized Macaca fascicularis GIPR at 2μg/mL can bind Anti-GIPR recombinant antibody (CSB-RA009438MA1HU),the EC50 is 12.66-13.86 ng/mL.
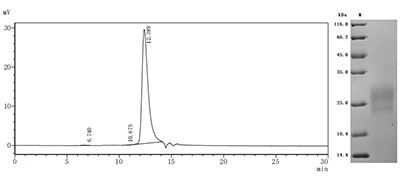
High specificity was validated by SDS-PAGE and SEC-HPLC. SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
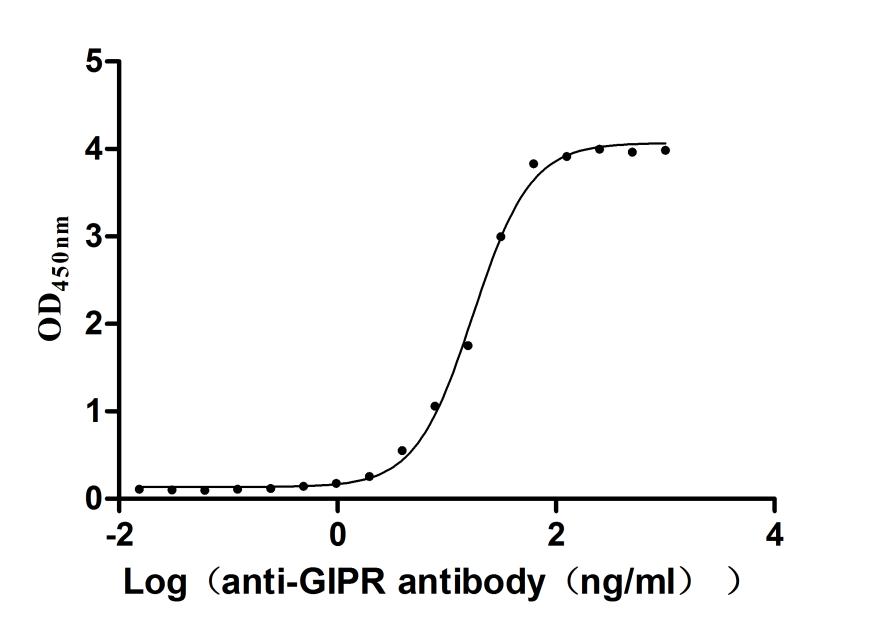
Immobilized Human GIPR at 2μg/mL can bind Anti-GIPR recombinant antibody (CSB-MP009438HU1d7),the EC50 is 16.18-18.70 ng/mL.
j9九游会登录入口首页CUSABIO抗体GIPR
参考文献:
[1] Saxena, Richa, et al. "Genetic variation in GIPR influences the glucose and insulin responses to an oral glucose challenge." Nature genetics 42.2 (2010): 142-148.
[2] Canivell Fusté, Silvia. "The association of DNA methylation patterns in TCF7L2 and GIPR genes with Type 2 Diabetes." (2014).
[3] Sauber, Jeannine, et al. "Association of variants in gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor gene with impaired glucose homeostasis in obese children and adolescents from Berlin." European journal of endocrinology 163.2 (2010): 259-264.
[4] Sauber, Jeannine, et al. "Association of variants in gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor gene with impaired glucose homeostasis in obese children and adolescents from Berlin." European journal of endocrinology 163.2 (2010): 259-264.
[5] Erfanian, Saiedeh, et al. "Association of gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIPR) gene polymorphism with type 2 diabetes mellitus in iranian patients." BMC Medical Genomics 16.1 (2023): 44.
[6] El, K., et al. "GIP mediates the incretin effect and glucose tolerance by dual actions on α cells and β cells." Science advances 7.11 (2021): eabf1948.
[7] Suzuki, Kazuyo, et al. "Transcriptional regulatory factor X6 (Rfx6) increases gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) expression in enteroendocrine K-cells and is involved in GIP hypersecretion in high fat diet-induced obesity." Journal of Biological Chemistry 288.3 (2013): 1929-1938.
[8] Ikeguchi, Eri, et al. "Transcriptional factor Pdx1 is involved in age-related GIP hypersecretion in mice." American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 315.2 (2018): G272-G282.
[9] Jepeal, Lisa I., Michael O. Boylan, and M. Michael Wolfe. "Cell-specific expression of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide gene functions through a GATA and an ISL-1 motif in a mouse neuroendocrine tumor cell line." Regulatory peptides 113.1-3 (2003): 139-147.
[10] Kim, Su-Jin, Cuilan Nian, and Christopher HS McIntosh. "GIP increases human adipocyte LPL expression through CREB and TORC2-mediated trans-activation of the LPL gene." Journal of lipid research 51.11 (2010): 3145-3157.
[11] Ast, Julia, Johannes Broichhagen, and David J. Hodson. "Reagents and models for detecting endogenous GLP1R and GIPR." EBioMedicine 74 (2021): 103739.
[12] Mayendraraj, Ashok, Mette M. Rosenkilde, and Laerke S. Gasbjerg. "GLP-1 and GIP receptor signaling in beta cells–A review of receptor interactions and co-stimulation." Peptides (2022): 170749.
[13] Lavine, Jeremy A., and Alan D. Attie. "Gastrointestinal hormones and the regulation of β‐cell mass." Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1212.1 (2010): 41-58.
[14] Lyu, Xiaorui, et al. "Safflower yellow and its main component hydroxysafflor yellow A alleviate hyperleptinemia in diet‐induced obesity mice through a dual inhibition of the GIP‐GIPR signaling axis." Phytotherapy Research (2023).
[15] Dowsett, Georgina KC, et al. "A survey of the mouse hindbrain in the fed and fasted states using single-nucleus RNA sequencing." Molecular metabolism 53 (2021): 101240.
[16] Campbell, Jonathan E., et al. "TCF1 links GIPR signaling to the control of beta cell function and survival." Nature medicine 22.1 (2016): 84-90.
[17] Erfanian, Saiedeh, et al. "Association of gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIPR) gene polymorphism with type 2 diabetes mellitus in iranian patients." BMC Medical Genomics 16.1 (2023): 44.
[18] Zhang, Qian, et al. "The glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) regulates body weight and food intake via CNS-GIPR signaling." Cell metabolism 33.4 (2021): 833-844.
[19] Kee, Vanessa Ting Zhen. Dual incretin agonism in the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. Diss. Monash University, 2022.
[20] Bastin, Marie, and Fabrizio Andreelli. "Dual GIP–GLP1-receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a short review on emerging data and therapeutic potential." Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy (2019): 1973-1985.
[21] Davies, Iona, and Tricia MM Tan. "Design of novel therapeutics targeting the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) to aid weight loss." Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery (2023): 1-11.
[22] Dekker, Mark J., et al. "Exercise prior to fat ingestion lowers fasting and postprandial VLDL and decreases adipose tissue IL-6 and GIP receptor mRNA in hypertriacylglycerolemic men." The Journal of nutritional biochemistry 21.10 (2010): 983-990.
[23] Campbell, Jonathan E. "Targeting the GIPR for obesity: to agonize or antagonize? Potential mechanisms." Molecular metabolism 46 (2021): 101139.
[24] Dalle Nogare, Mattia, et al. "The Methylation Analysis of the Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptor (GIPR) Locus in GH-Secreting Pituitary Adenomas." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.11 (2023): 9264.
[25] Sherman, Scott K., et al. "Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIPR) is a promising target for imaging and therapy in neuroendocrine tumors." Surgery 154.6 (2013): 1206-1214.
[26] Sherman, S. K., et al. "High Expression of Somatostatin Type 2 Receptor (SSTR2) and Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide Receptor (GIPR) in Stomach and Duodenal Neuroendocrine Tumors (NETs)." The Journal of surgical research 186.2 (2014): 506-506.
[27] Wang, Donghong, et al. "GIPR Expression in Gastric and Duodenal Neuroendocrine Tumors." (2014).











