Recombinant Mouse T-cell surface glycoprotein CD4 (Cd4), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP004935MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP004935MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP004935MO1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP004935MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP004935MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Cd4; T-cell surface glycoprotein CD4; T-cell differentiation antigen L3T4; T-cell surface antigen T4/Leu-3; CD antigen CD4
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Integral membrane glycoprotein that plays an essential role in the immune response and serves multiple functions in responses against both external and internal offenses. In T-cells, functions primarily as a coreceptor for MHC class II molecule:peptide complex. The antigens presented by class II peptides are derived from extracellular proteins while class I peptides are derived from cytosolic proteins. Interacts simultaneously with the T-cell receptor (TCR) and the MHC class II presented by antigen presenting cells (APCs). In turn, recruits the Src kinase LCK to the vicinity of the TCR-CD3 complex. LCK then initiates different intracellular signaling pathways by phosphorylating various substrates ultimately leading to lymphokine production, motility, adhesion and activation of T-helper cells. In other cells such as macrophages or NK cells, plays a role in differentiation/activation, cytokine expression and cell migration in a TCR/LCK-independent pathway. Participates in the development of T-helper cells in the thymus and triggers the differentiation of monocytes into functional mature macrophages.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- data showed the critical role of the first extracellular domain of CD4, by obtaining mice with a loss of function mutation from Ile to Asn at the position 99 of CD4 (I99N). PMID: 29028486
- results suggest that CD4 CD8 double knockout (DN)T cells can develop efficiently in vivo and chronic exposure to bacterial superantigens may precipitate a lupus-like autoimmune disease through activation of DNT cells PMID: 28468970
- TCF-1-deficient CD4+ CD8+ double positive thymocytes fail to undergo TCR alpha Valpha14-Jalpha18 rearrangement and produce significantly fewer Natural killer T cells. PMID: 25536344
- High-fat diet - induced type 2 diabetes decreases the number of ileum IL17/RORgammaT CD4 T cells. PMID: 26154056
- Results indicate that hypomethylation of Cd4 antigen correlates with stable CD4 expression. PMID: 26030024
- CD4 is expressed in distinct nanoclusters and does not colocalize with T-cell receptor and active protein tyrosine kinase p56lck PMID: 25829544
- This study establishes an important role of IgE in abdominal aortic aneurysms pathogenesis by activating CD4+ T cells, mast cells, and macrophages. PMID: 24963147
- 5-kb cis-element is required in postselection thymocytes for helper lineage commitment, presumably mediating the maintenance of CD4 expression, and suggest that inactivation of the cis-element by DNA methylation PMID: 24729613
- Both type I CD8+ cytotoxic (Tc1) cells and interleukin (IL)-17-producing CD8+ (Tc17) cells mediate effective antitumor immunity through distinct effector mechanisms, but Tc1 cells are superior to Tc17 cells in mediating tumor regression. PMID: 23315072
- Accumulation of CD4 positive effector T cells is a critical step in the progression from mild glomerulonephritis to severe crescentic glomerulonephritis accompanied by tubulointerstitial inflammation and loss of kidney function. PMID: 22437418
- Thymic selection does not appear to play an important role in CD4+CD8+ T cell receptor (TCR)beta repertoire overlap between individuals. PMID: 22826324
- CD4-positive cell deficiency impairs IFN-gamma production by CD8-positive effector cells at the site of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice. PMID: 22837486
- galectin-1 inhibition reduces murine lung metastasis with increased CD4(+) and CD8 (+) T cells and reduced cancer cell adherence PMID: 22484915
- Mice that lack the ability to make both CD8-positive and CD4-positive induced regulatory T (iTreg) cells have accelerated graft-vs-host-disease mortality compared with animals that are competent to make both iTreg populations. PMID: 22649199
- Danazol induced prolonged cardiac allograft survival and generation of regulatory CD4(+) cells. PMID: 22564626
- Hepatic stellate cells seem to act as liver-resident antigen-presenting cells instructing the generation of CD4/CD25/Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. PMID: 22564624
- Thymic or peripheral CD4+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells cells manifest prominent functional plasticity and readily reprogram into Th1 and Th17 effector cells, particularly in the gut microenvironment or sites of parasitic infection. PMID: 22545118
- Both CD4(+) and CD8(+) regulatory T cells appeared to be protective against Graft vs Host Disease - induced lethality and required IL-2 and TGF-beta receptor expression for their generation. PMID: 22496155
- SR-A knockout (SR-A(-/-)) mice developed a more robust Cd4(+) T cell response than wild-type mice after ovalbumin immunization. PMID: 22083206
- CD4+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells from Galphai2-/- mice are functionally active in vitro, but do not prevent colitis PMID: 21966415
- GITR is not required on the surface of CD4-positive T-cells to induce colitis in mice. Knockout mice develop aggravated chronic enterocolitis via an imbalance of colitogenic Th1 cells and Treg cells. PMID: 22155173
- leflunomide has an effect on CD4(+)CD25 (+)Foxp3 (+) T regulatory cells in mice receiving allogeneic bone marrow transplantation PMID: 22057872
- The average percentage of CD154 expression among CD4+ FoxP3+ T regulatory (Treg) cells was only about 4-9%. PMID: 21496498
- AP4 contributes to Cd4 silencing both in DN and CD8(+) T cells by enforcing checkpoints for appropriate timing of CD4 expression and its epigenetic silencing. PMID: 21873191
- HMGB1 has the ability to directly modulate the suppressive capacity of CD4(+)CD25(+)Tregs, and TLR4 might be a potential receptor essential for the negative effect of HMGB1 on CD4(+)CD25(+)Tregs activity PMID: 21419643
- aged CD4+ T cell function impairment is intimately related to multiple alterations in aged DCs, rather than being caused solely by intrinsic T cell defects PMID: 21453718
- Small intestine CD11c+ CD8+ T cells suppress CD4+ T cell-induced immune colitis. PMID: 21436315
- Data show that CD8(+) T cell tolerance established in the lung depends only partially on the function of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. PMID: 21518973
- anti-TIM3 requires IFN-gamma producing CD8(+) T cells and CD4(+) T cells, and a higher ratio of tumor infiltrating CD8(+):CD4(+) T cells correlating with therapeutic success PMID: 21430066
- Prolonged survival of allografts induced by mycobacterial Hsp70 is dependent on CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells PMID: 21170379
- Endogenous matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 regulate activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells PMID: 20639459
- Astragalus membranaceus injection prolonged allograft survival associated with promotion of CD4+ CD25+ Treg activities. PMID: 21094858
- Results suggest that CD4+CD25+ Treg cells directly affect cisplatin nephrotoxicity and their modulation represents an additional treatment strategy. PMID: 20463654
- Cotransfer of CD8-positiveCD122-positive regulatory T cells (Tregs) clearly suppresses development of colitis, a synergistic effect similar to that of CD4-positiveCD45RB(low) cells that are mostly CD4-positive Tregs. PMID: 21098236
- T-cell receptor stimulation of HTLV-1 LTR-Tax transgenic CD4+ T cells induced Tax expression, hyper-proliferation, and immortalization in culture. PMID: 20634377
- impairment of Lck-mediated CD4 coreceptor signaling by Nef is an important in vivo mechanism of HIV-1 pathogenesis PMID: 20826747
- Pulmonary CD11c+ cells are critical for NO2-promoted allergic sensitization via antigenspecifici CD4+ T-cell polarization. PMID: 20659336
- Data describe why ibalizumab has not had adverse immunological consequences in infected patients but also raise possible steric hindrance mechanisms by which this antibody blocks HIV-1 entry into a CD4-positive cell. PMID: 20463063
- This significant intracellular storage of LAG-3 appears to facilitate its rapid translocation to the cell surface following T-cell activation, which was much faster for LAG-3 than CD4 PMID: 20391435
- Immunosuppressive agents could be successfully combined with in vitro-expanded CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Treg cell therapy to prevent allograft rejection. PMID: 20305583
- the proximal enhancer (E4(P)) of Cd4 is essential for CD4 expression in immature CD4(+)8(+) thymocytes PMID: 20360383
- Flt3-L significantly inhibited the effect of cockroach antigen sensitization and challenge to increase GATA3 expression in lung CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells. PMID: 19448155
- CD4 modulates activity of T cells that express an intermediate affinity, histocompatibility class-I restricted T cell receptor. PMID: 19923452
- These results indicate that CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs modify innate immune responses during resolution of lung injury and suggest potential targets for treating acute lung injury. PMID: 19770521
- Glutamic acid decarboxylase-derived epitopes with specific domains expand CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells PMID: 19759824
- miR-155 is shown to be crucially involved in nTreg cell mediated tolerance by regulating the susceptibility of conventional human as well as murine CD4(+) Th cells to nTreg cell-mediated suppression PMID: 19777054
- the effects of Deletion of the CD4 silencer element on thymocyte lineage was examined PMID: 11694883
- An organic CD4 inhibitor reduces the clinical and pathological symptoms of acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. PMID: 11908949
- Relationship between CD34 expression and CD4 expression by hematpoietic stem cells and their long-term reconstitution capability. PMID: 11937272
- CD4 regulatory T cells prevent lethal autoimmunity in IL-2Rbeta-deficient mice: implications for the nonredundant function of IL-2 PMID: 12196288
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in T-helper cells. The presence of CD4 is a hallmark of T-helper cells which are specialized in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T-cells, regulation of B cells, or activation of phagocytes. CD4 is also present in other immune cells
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:12504
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000024044
UniGene: Mm.2209
Most popular with customers
-
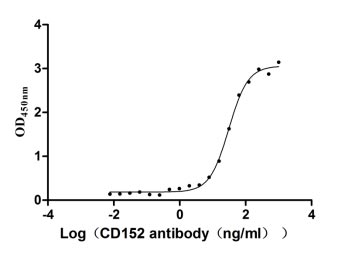
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4 (CTLA4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
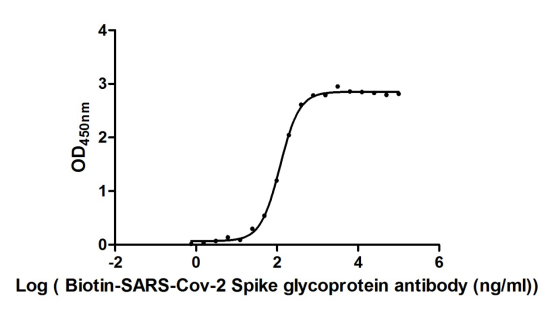
Recombinant Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Spike glycoprotein (S), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (2019-nCoV) (SARS-CoV-2)
-
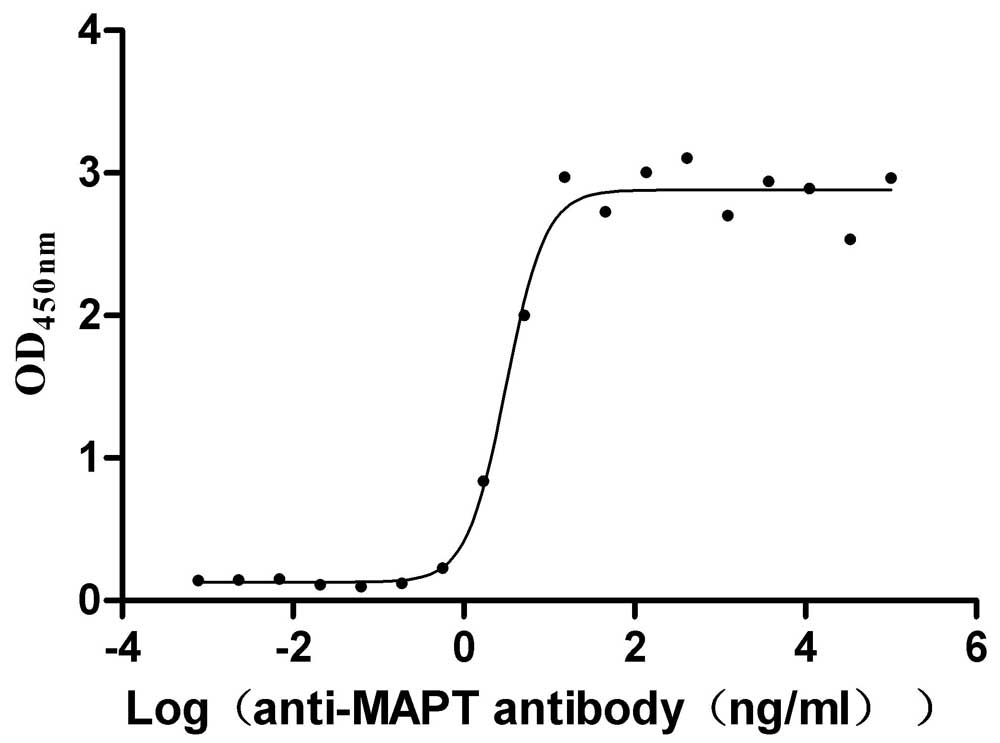
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
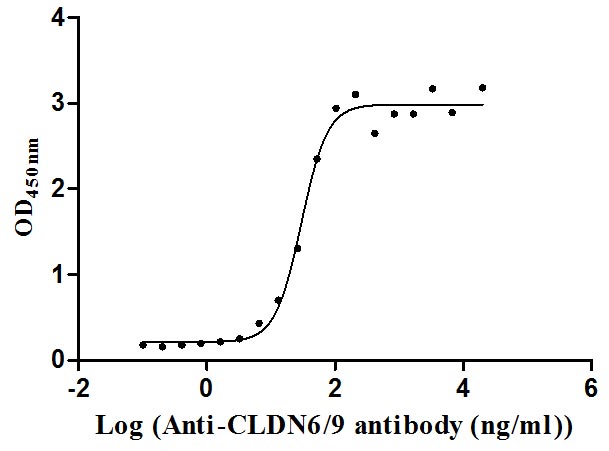
Recombinant Human Claudin-9 (CLDN9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
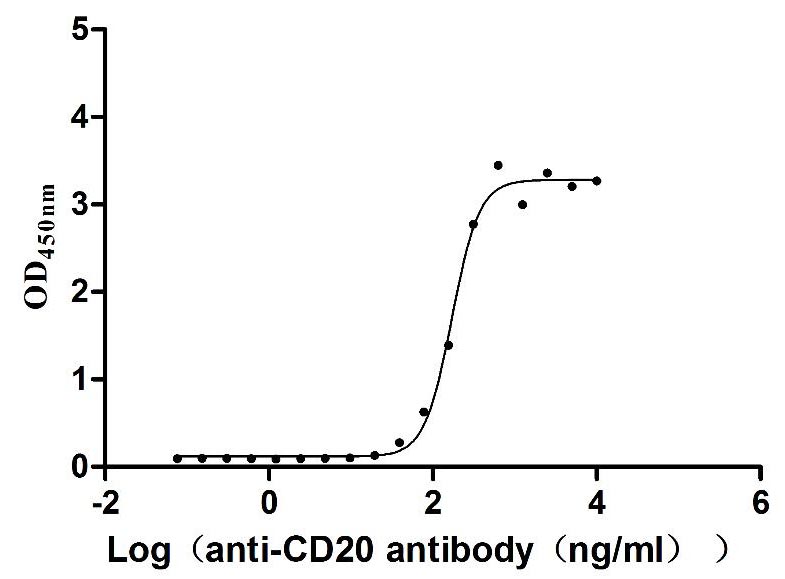
Recombinant Dog B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
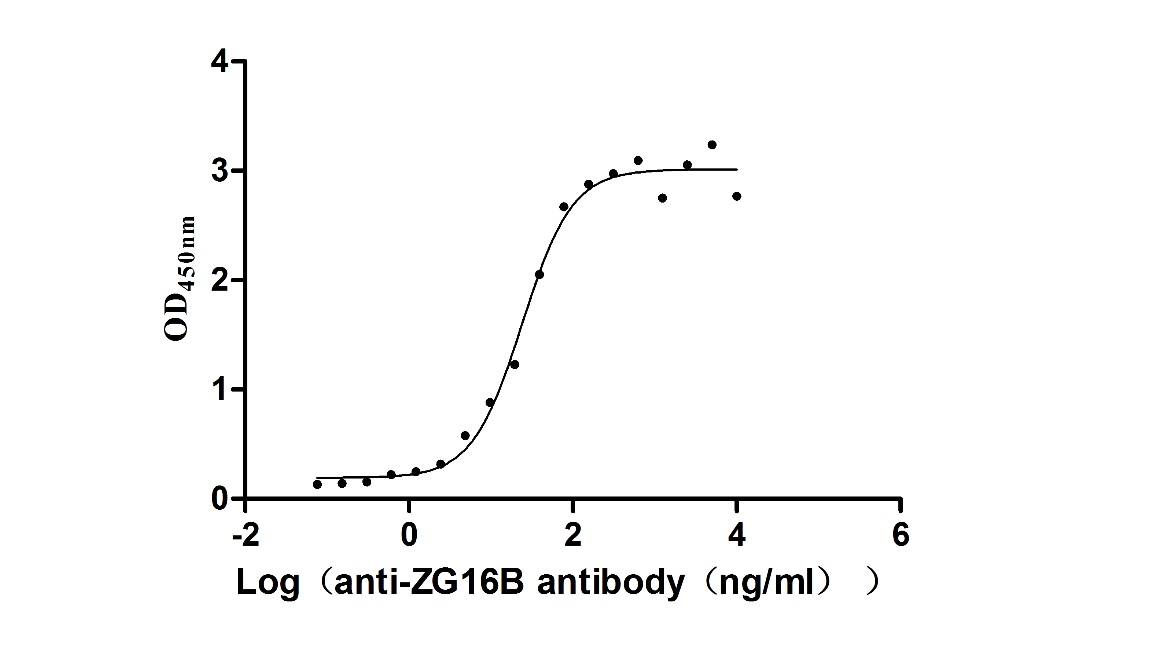
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
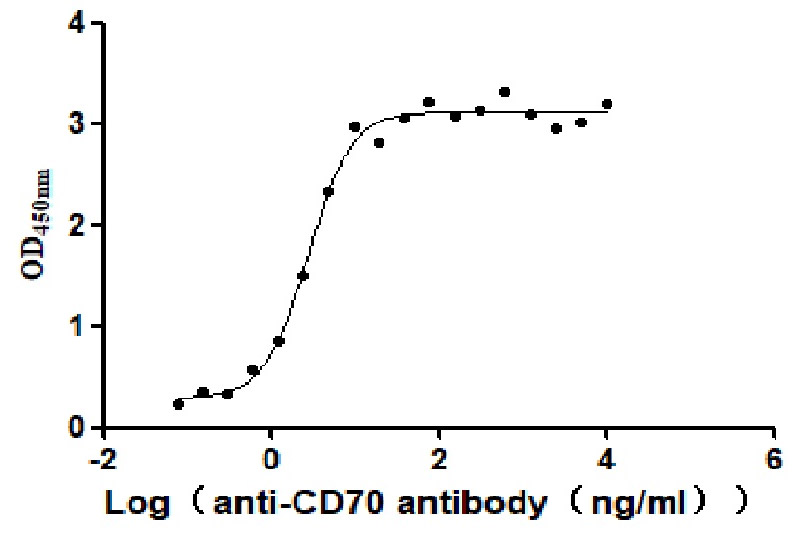
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)