Phospho-CEBPA (Thr230) Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA599746
-
规格:¥2454
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) CEBPA Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:P49715
-
基因名:CEBPA
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
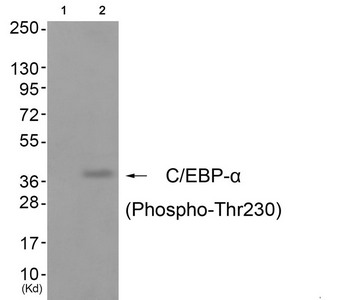
免疫原:Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of threonine 230 (P-P-T(p)-P-V) derived from Human C/EBP-α.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic phosphopeptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific phosphopeptide. Non-phospho specific antibodies were removed by chromatogramphy usi
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:1000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor that coordinates proliferation arrest and the differentiation of myeloid progenitors, adipocytes, hepatocytes, and cells of the lung and the placenta. Binds directly to the consensus DNA sequence 5'-TCan act as dominant-negative. Binds DNA and have transctivation activity, even if much less efficiently than isoform 2. Does not inhibit cell proliferation.; Directly and specifically enhances ribosomal DNA transcription interacting with RNA polymerase I-specific cofactors and inducing histone acetylation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- during monocyte to macrophage differentiation, the endosomal/lysosomal proteolytic activity can be regulated by cystatin F whose expression is under the control of transcriptional factor C/EBP alpha. PMID: 30033148
- We found 6 frame shift mutations, 1 missense mutation, 3 synonymous variants. The most common mutation was the c.487del G resulting p.Glu163Ser in 5 cases. Three patients carried CEBPA double mutations. CONCLUSION: The detected variants in this article seemed to be the first screening results of genes studied by NGS in pediatric acute leukemia patients. PMID: 29947237
- The zinc finger, ZNF143, binds to the CCCAGCAG site in the CEBPA promoter. PMID: 28900037
- The earliest steps of adult hepatocellular carcinoma and aggressive pediatric liver cancer have identical features that include conversion of the tumor suppressor C/EBPalpha into an oncogenic isoform, which further creates preneoplastic foci where hepatocytes dedifferentiate into cancer cells, giving rise to liver cancer PMID: 29159818
- Data suggest that up-regulation of NPY inhibits proliferation of adipose-derived stem cells while promoting adipogenesis and up-regulating expression of white adipocyte biomarkers PPARG, CEBPA, CIDEC, and RIP140. (NPY = neuropeptide Y; PPARG = peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma; CIDEC = cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector C; RIP140 = nuclear receptor interacting protein 1) PMID: 28954935
- Study identified for the first time that HNF4alpha and C/EBPalpha are important transcriptional regulators for FBP1 expression in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. PMID: 29566023
- The presence of biallelic CEBPA mutations is a favourable prognostic feature in acute myeloid leukaemia. PMID: 29180507
- C/EBP-alpha mediates anti-inflammatory effects in podocytes PMID: 27644413
- proteogenomics profiling study reveals that an activation of C/EBPalpha, along with the upregulation of its lipogenesis targets, accounts for lipid storage and acts as a hallmark of ARVC ( Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy) PMID: 28665611
- Taken together, the s propose that the miR-939-Jmjd3 axis perturbs the accessibility of hepatitis B virus enhancer II/core promoter (En II) promoter to essential nuclear factors (C/EBPalpha and SWI/SNF complex) therefore leading to compromised viral RNA synthesis and hence restricted viral multiplication. PMID: 27779233
- Integration of WGS-based fine-mapping and complementary epigenomic datasets provided evidence for causal mechanisms at several loci, including at a previously undiscovered basophil count-associated locus near the master hematopoietic transcription factor CEBPA The fine-mapped variant at this basophil count association near CEBPA overlapped an enhancer active in common myeloid progenitors and influenced its activity. PMID: 28031487
- in our study on a large cohort of CEBPAmut AML patients, we found a high coincidence of GATA2mut, in particular within the subgroup of patients with CEBPAbi mutations PMID: 27375010
- a decision analysis comparing allo-HCT vs chemotherapy in first complete remission for patients with cytogenetically intermediate-risk acute myeloid leukemia, depending on the presence or absence of FLT3-ITD), NPM1, and CEBPA mutations showed that allo-HCT was a favored postremission strategy in patients with FLT3-ITD, and chemotherapy was favored in patients with biallelic CEBPA mutations. PMID: 27040395
- This is the first study providing evidence that the c.690G>T, p.(Thr230Thr) (rs34529039) polymorphism of the CEBPA gene, together with up-regulation of its mRNA expression, are negative factors worsening ovarian cancer outcome PMID: 27602952
- CSF3R mutations co-occur with CEBPA mutations in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. PMID: 27143256
- While much is known about how C/EBPalpha orchestrates granulopoiesis, our understanding of molecular transformation events, the role(s) of cooperating mutations and clonal evolution during C/EBPalpha deregulation in leukemia remains elusive. In this review, we will summarize the latest research addressing these topics with special emphasis on CEBPA mutations PMID: 28720765
- miR-182 is a strong regulator of C/EBPalpha. There is a regulatory loop between C/EBPalpha and miR-182. While C/EBPalpha blocks miR-182 expression by direct promoter binding during myeloid differentiation, enforced expression of miR-182 reduces C/EBPalpha protein level and impairs granulopoiesis in vitro and in vivo. PMID: 28663557
- CHOP negatively regulates Polo-like kinase 2 expression via recruiting C/EBPalpha to the upstream-promoter in human osteosarcoma cell line during ER stress PMID: 28652211
- C/EBPalpha overexpression suppressed the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) that was characterized by a gain of epithelial and loss of mesenchymal markers. Further study showed that C/EBPalpha suppressed the transcription of beta-catenin and downregulated the levels of its downstream targets. PMID: 28746919
- Binding of C/EBPalpha was associated with increased deacetylation near the transcription start site (TSS) of the PLK1 promoter. PMID: 28341486
- a MEF2C and CEBPA correlation in CML disease progression PMID: 27297623
- CEBPA gene expression is significantly associated with long-term changes in Blood Pressure, providing a link between gene expression and Blood Pressure. PMID: 28784648
- We provide evidence that CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha directly binds the miR-203 gene within its hairpin region and thereby induces miR-203 transcription PMID: 28640877
- High CEBP expression is associated with glioblastomas. PMID: 27591677
- identified high frequencies of mutations in CEBPA (32.7%), GATA2 (22.4%), NPM1 (15.5%), SETBP1 (12.1%) and U2AF1 PMID: 27389056
- our data show that excess p30 cooperated with TRIB2 only in the presence of p42 to accelerate acute myeloid leukaemia (AML), and the direct interaction and degradation of C/EBPa p42 is required for TRIB2-mediated AML. PMID: 26996668
- A single +42-kb enhancer is essential for CEBPA expression in myeloid cells only. PMID: 26966090
- Co-occurrence of mutations in CSF3R and CEBPA in a well-defined acute myeloid leukemia subset, which uniformly responds to JAK inhibitors; this paves the way to personalized clinical trials for this disease. PMID: 27034432
- we established a reliable and straightforward screening method, based simply on the multidimensional analysis of widely available phenotypic parameters, suitable for large-scale detection of CEBPA-dm status and potentially able to overcome technical issues related to molecular methods. PMID: 28250006
- This study of a large multi-generational pedigree reveals that a germline mutation in the C-terminal bZip domain can alter the ability of C/EBP-alpha to bind DNA and reduces transactivation, leading to acute myeloid leukemia. PMID: 26721895
- SBDS function is specifically required for efficient translation re-initiation into the protein isoforms C/EBPalpha-p30 and C/EBPbeta-LIP, which is controlled by a single cis-regulatory upstream open reading frame (uORF) in the 5' untranslated regions (5' UTRs) of both mRNAs. PMID: 26762974
- SHP2-ERK2 signaling acts upstream of C/EBPalpha as a regulator of cell surface I antigen synthesis. PMID: 27600951
- the importance of C/EBPalpha for neutrophil maturation, its role in myeloid priming of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, and its indispensable requirement for AML development. PMID: 28179278
- found significantly higher frequencies for NPM1-mutated 24.2 % and CEBPA-mutated 12.1 % PMID: 27436336
- results demonstrate that the low-level expression of human ACAT2 gene with specific CpG-hypomethylated promoter is regulated by the C/EBP transcription factors in monocytic cells, and imply that the lowly expressed ACAT2 catalyzes the synthesis of certain CE/SE that are assembled into lipoproteins for the secretion PMID: 27688151
- Our study highlighted two novel promoter KLF1 and 3'-region C/EBPalpha motifs in the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) gene which decrease transcription in vitro and, thus, could be considered as PAH expression modifiers. PMID: 27447460
- The QA repeat domain of TCERG1 is required for relocalization of CEBPalpha. PMID: 26264132
- In the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha gene, no mutations were detected but a known polymorphism (c.584_589dup ACCCGC) was observed in 26 (28.3%) patients. PMID: 25932436
- The p53-KLF4-CEBPA axis is deregulated in AML but can be functionally restored by conventional chemotherapy and novel p53 activating treatments. PMID: 26408402
- C/EBPalpha inhibited breast cancer cell growth via a novel miR-134/CREB signaling pathway. PMID: 26823765
- C/EBP-alpha was primarily expressed in hepatocytes in normal liver, but its expression decreased significantly in liver fibrosis PMID: 26722507
- The efficient repression of E2F dependent S-phase genes and the activation of differentiation genes reside in the balanced DNA binding capacity of C/EBP alpha. PMID: 27131901
- we are the first to identify that miR-381 suppresses C/EBPalpha-dependent Cx43 expression in breast cancer cells. The miR-381-C/EBPalpha-Cx43 axis might be a useful diagnostic and therapeutic target of metastatic breast cancer PMID: 26450928
- results suggested that C/EBPalpha-saRNA successfully inhibited HCC metastasis by inhibiting EGFR/beta-catenin signaling pathway mediated EMT in vitro and in vivo PMID: 27050434
- These results suggest that genetic predisposition to higher IL-6 production is associated with increased risk to HBV infection and hepatic inflammation, which might be due to C/EBPalpha-mediated regulatory effect on Th17 and Treg responses. PMID: 26447433
- the present study demonstrated that suppression of C/EBPa P42 induced by PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibition impaired the differentiation and ATRA sensitivity of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. PMID: 26397153
- Data uncover GCN5 as a negative regulator of C/EBPalpha and demonstrate the importance of C/EBPalpha acetylation in myeloid differentiation. PMID: 27005833
- younger age, presence of mirror repeats, and high CEBPA expression level in relation to potential topo II-sites, might affect the incidence of B-ZIP in-frame CNVs through aberrant recombination-mediated DNA repair mechanisms. PMID: 26460249
- Reprogramming human B cells into induced pluripotent stem cells and is enhanced by C/EBPa. PMID: 26500142
- this is the first report on the regulation mechanism of SIRT7 gene, in which, HDAC3 collaborated with C/EBPalpha to occupy its responding element in the upstream region of SIRT7 gene and repressed its expression in human cells. PMID: 26704017
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.; [Isoform 4]: Nucleus, nucleolus.
-
蛋白家族:BZIP family, C/EBP subfamily
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 1833
OMIM: 116897
KEGG: hsa:1050
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000427514
UniGene: Hs.76171
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-