Recombinant Human CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA)
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha(CEBPA),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-YP005180HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha(CEBPA),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP005180HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha(CEBPA),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP005180HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha(CEBPA),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-BP005180HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha(CEBPA),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-MP005180HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
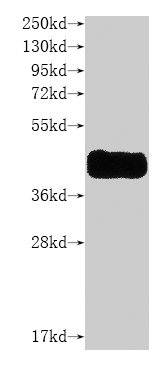
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:CEBPA
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Apoptotic cysteine protease; Apoptotic protease Mch 5; C/EBP alpha; C/ebpalpha; CAP4; Caspase 8 precursor; CBF-A; CCAAT Enhancer Binding Protein alpha; CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP); alpha; CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha; CEBP ; CEBP A; CEBP alpha; Cebpa; CEBPA_HUMAN; FADD homologous ICE/CED 3 like protease; FADD like ICE; FLICE; ICE like apoptotic protease 5; ICE8; MACH; MCH5; MORT1 associated CED 3 homolog
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-358
-
氨基酸序列MESADFYEAE PRPPMSSHLQ SPPHAPSSAA FGFPRGAGPA QPPAPPAAPE PLGGICEHET SIDISAYIDP AAFNDEFLAD LFQHSRQQEK AKAAVGPTGG GGGGDFDYPG APAGPGGAVM PGGAHGPPPG YGCAAAGYLD GRLEPLYERV GAPALRPLVI KQEPREEDEA KQLALAGLFP YQPPPPPPPS HPHPHPPPAH LAAPHLQFQI AHCGQTTMHL QPGHPTPPPT PVPSPHPAPA LGAAGLPGPG SALKGLGAAH PDLRASGGSG AGKAKKSVDK NSNEYRVRRE RNNIAVRKSR DKAKQRNVET QQKVLELTSD NDRLRKRVEQ LSRELDTLRG IFRQLPESSL VKAMGNCA
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor that coordinates proliferation arrest and the differentiation of myeloid progenitors, adipocytes, hepatocytes, and cells of the lung and the placenta. Binds directly to the consensus DNA sequence 5'-TCan act as dominant-negative. Binds DNA and have transctivation activity, even if much less efficiently than isoform 2. Does not inhibit cell proliferation.; Directly and specifically enhances ribosomal DNA transcription interacting with RNA polymerase I-specific cofactors and inducing histone acetylation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- during monocyte to macrophage differentiation, the endosomal/lysosomal proteolytic activity can be regulated by cystatin F whose expression is under the control of transcriptional factor C/EBP alpha. PMID: 30033148
- We found 6 frame shift mutations, 1 missense mutation, 3 synonymous variants. The most common mutation was the c.487del G resulting p.Glu163Ser in 5 cases. Three patients carried CEBPA double mutations. CONCLUSION: The detected variants in this article seemed to be the first screening results of genes studied by NGS in pediatric acute leukemia patients. PMID: 29947237
- The zinc finger, ZNF143, binds to the CCCAGCAG site in the CEBPA promoter. PMID: 28900037
- The earliest steps of adult hepatocellular carcinoma and aggressive pediatric liver cancer have identical features that include conversion of the tumor suppressor C/EBPalpha into an oncogenic isoform, which further creates preneoplastic foci where hepatocytes dedifferentiate into cancer cells, giving rise to liver cancer PMID: 29159818
- Data suggest that up-regulation of NPY inhibits proliferation of adipose-derived stem cells while promoting adipogenesis and up-regulating expression of white adipocyte biomarkers PPARG, CEBPA, CIDEC, and RIP140. (NPY = neuropeptide Y; PPARG = peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma; CIDEC = cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector C; RIP140 = nuclear receptor interacting protein 1) PMID: 28954935
- Study identified for the first time that HNF4alpha and C/EBPalpha are important transcriptional regulators for FBP1 expression in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. PMID: 29566023
- The presence of biallelic CEBPA mutations is a favourable prognostic feature in acute myeloid leukaemia. PMID: 29180507
- C/EBP-alpha mediates anti-inflammatory effects in podocytes PMID: 27644413
- proteogenomics profiling study reveals that an activation of C/EBPalpha, along with the upregulation of its lipogenesis targets, accounts for lipid storage and acts as a hallmark of ARVC ( Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy) PMID: 28665611
- Taken together, the s propose that the miR-939-Jmjd3 axis perturbs the accessibility of hepatitis B virus enhancer II/core promoter (En II) promoter to essential nuclear factors (C/EBPalpha and SWI/SNF complex) therefore leading to compromised viral RNA synthesis and hence restricted viral multiplication. PMID: 27779233
- Integration of WGS-based fine-mapping and complementary epigenomic datasets provided evidence for causal mechanisms at several loci, including at a previously undiscovered basophil count-associated locus near the master hematopoietic transcription factor CEBPA The fine-mapped variant at this basophil count association near CEBPA overlapped an enhancer active in common myeloid progenitors and influenced its activity. PMID: 28031487
- in our study on a large cohort of CEBPAmut AML patients, we found a high coincidence of GATA2mut, in particular within the subgroup of patients with CEBPAbi mutations PMID: 27375010
- a decision analysis comparing allo-HCT vs chemotherapy in first complete remission for patients with cytogenetically intermediate-risk acute myeloid leukemia, depending on the presence or absence of FLT3-ITD), NPM1, and CEBPA mutations showed that allo-HCT was a favored postremission strategy in patients with FLT3-ITD, and chemotherapy was favored in patients with biallelic CEBPA mutations. PMID: 27040395
- This is the first study providing evidence that the c.690G>T, p.(Thr230Thr) (rs34529039) polymorphism of the CEBPA gene, together with up-regulation of its mRNA expression, are negative factors worsening ovarian cancer outcome PMID: 27602952
- CSF3R mutations co-occur with CEBPA mutations in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. PMID: 27143256
- While much is known about how C/EBPalpha orchestrates granulopoiesis, our understanding of molecular transformation events, the role(s) of cooperating mutations and clonal evolution during C/EBPalpha deregulation in leukemia remains elusive. In this review, we will summarize the latest research addressing these topics with special emphasis on CEBPA mutations PMID: 28720765
- miR-182 is a strong regulator of C/EBPalpha. There is a regulatory loop between C/EBPalpha and miR-182. While C/EBPalpha blocks miR-182 expression by direct promoter binding during myeloid differentiation, enforced expression of miR-182 reduces C/EBPalpha protein level and impairs granulopoiesis in vitro and in vivo. PMID: 28663557
- CHOP negatively regulates Polo-like kinase 2 expression via recruiting C/EBPalpha to the upstream-promoter in human osteosarcoma cell line during ER stress PMID: 28652211
- C/EBPalpha overexpression suppressed the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) that was characterized by a gain of epithelial and loss of mesenchymal markers. Further study showed that C/EBPalpha suppressed the transcription of beta-catenin and downregulated the levels of its downstream targets. PMID: 28746919
- Binding of C/EBPalpha was associated with increased deacetylation near the transcription start site (TSS) of the PLK1 promoter. PMID: 28341486
- a MEF2C and CEBPA correlation in CML disease progression PMID: 27297623
- CEBPA gene expression is significantly associated with long-term changes in Blood Pressure, providing a link between gene expression and Blood Pressure. PMID: 28784648
- We provide evidence that CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha directly binds the miR-203 gene within its hairpin region and thereby induces miR-203 transcription PMID: 28640877
- High CEBP expression is associated with glioblastomas. PMID: 27591677
- identified high frequencies of mutations in CEBPA (32.7%), GATA2 (22.4%), NPM1 (15.5%), SETBP1 (12.1%) and U2AF1 PMID: 27389056
- our data show that excess p30 cooperated with TRIB2 only in the presence of p42 to accelerate acute myeloid leukaemia (AML), and the direct interaction and degradation of C/EBPa p42 is required for TRIB2-mediated AML. PMID: 26996668
- A single +42-kb enhancer is essential for CEBPA expression in myeloid cells only. PMID: 26966090
- Co-occurrence of mutations in CSF3R and CEBPA in a well-defined acute myeloid leukemia subset, which uniformly responds to JAK inhibitors; this paves the way to personalized clinical trials for this disease. PMID: 27034432
- we established a reliable and straightforward screening method, based simply on the multidimensional analysis of widely available phenotypic parameters, suitable for large-scale detection of CEBPA-dm status and potentially able to overcome technical issues related to molecular methods. PMID: 28250006
- This study of a large multi-generational pedigree reveals that a germline mutation in the C-terminal bZip domain can alter the ability of C/EBP-alpha to bind DNA and reduces transactivation, leading to acute myeloid leukemia. PMID: 26721895
- SBDS function is specifically required for efficient translation re-initiation into the protein isoforms C/EBPalpha-p30 and C/EBPbeta-LIP, which is controlled by a single cis-regulatory upstream open reading frame (uORF) in the 5' untranslated regions (5' UTRs) of both mRNAs. PMID: 26762974
- SHP2-ERK2 signaling acts upstream of C/EBPalpha as a regulator of cell surface I antigen synthesis. PMID: 27600951
- the importance of C/EBPalpha for neutrophil maturation, its role in myeloid priming of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, and its indispensable requirement for AML development. PMID: 28179278
- found significantly higher frequencies for NPM1-mutated 24.2 % and CEBPA-mutated 12.1 % PMID: 27436336
- results demonstrate that the low-level expression of human ACAT2 gene with specific CpG-hypomethylated promoter is regulated by the C/EBP transcription factors in monocytic cells, and imply that the lowly expressed ACAT2 catalyzes the synthesis of certain CE/SE that are assembled into lipoproteins for the secretion PMID: 27688151
- Our study highlighted two novel promoter KLF1 and 3'-region C/EBPalpha motifs in the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) gene which decrease transcription in vitro and, thus, could be considered as PAH expression modifiers. PMID: 27447460
- The QA repeat domain of TCERG1 is required for relocalization of CEBPalpha. PMID: 26264132
- In the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha gene, no mutations were detected but a known polymorphism (c.584_589dup ACCCGC) was observed in 26 (28.3%) patients. PMID: 25932436
- The p53-KLF4-CEBPA axis is deregulated in AML but can be functionally restored by conventional chemotherapy and novel p53 activating treatments. PMID: 26408402
- C/EBPalpha inhibited breast cancer cell growth via a novel miR-134/CREB signaling pathway. PMID: 26823765
- C/EBP-alpha was primarily expressed in hepatocytes in normal liver, but its expression decreased significantly in liver fibrosis PMID: 26722507
- The efficient repression of E2F dependent S-phase genes and the activation of differentiation genes reside in the balanced DNA binding capacity of C/EBP alpha. PMID: 27131901
- we are the first to identify that miR-381 suppresses C/EBPalpha-dependent Cx43 expression in breast cancer cells. The miR-381-C/EBPalpha-Cx43 axis might be a useful diagnostic and therapeutic target of metastatic breast cancer PMID: 26450928
- results suggested that C/EBPalpha-saRNA successfully inhibited HCC metastasis by inhibiting EGFR/beta-catenin signaling pathway mediated EMT in vitro and in vivo PMID: 27050434
- These results suggest that genetic predisposition to higher IL-6 production is associated with increased risk to HBV infection and hepatic inflammation, which might be due to C/EBPalpha-mediated regulatory effect on Th17 and Treg responses. PMID: 26447433
- the present study demonstrated that suppression of C/EBPa P42 induced by PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibition impaired the differentiation and ATRA sensitivity of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. PMID: 26397153
- Data uncover GCN5 as a negative regulator of C/EBPalpha and demonstrate the importance of C/EBPalpha acetylation in myeloid differentiation. PMID: 27005833
- younger age, presence of mirror repeats, and high CEBPA expression level in relation to potential topo II-sites, might affect the incidence of B-ZIP in-frame CNVs through aberrant recombination-mediated DNA repair mechanisms. PMID: 26460249
- Reprogramming human B cells into induced pluripotent stem cells and is enhanced by C/EBPa. PMID: 26500142
- this is the first report on the regulation mechanism of SIRT7 gene, in which, HDAC3 collaborated with C/EBPalpha to occupy its responding element in the upstream region of SIRT7 gene and repressed its expression in human cells. PMID: 26704017
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.; [Isoform 4]: Nucleus, nucleolus.
-
蛋白家族:BZIP family, C/EBP subfamily
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 1833
OMIM: 116897
KEGG: hsa:1050
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000427514
UniGene: Hs.76171
Most popular with customers
-
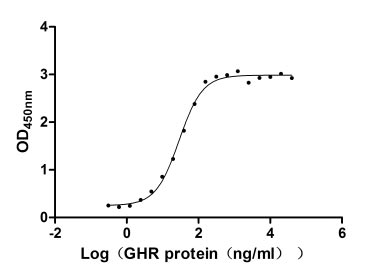
Recombinant Human Growth hormone receptor (GHR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
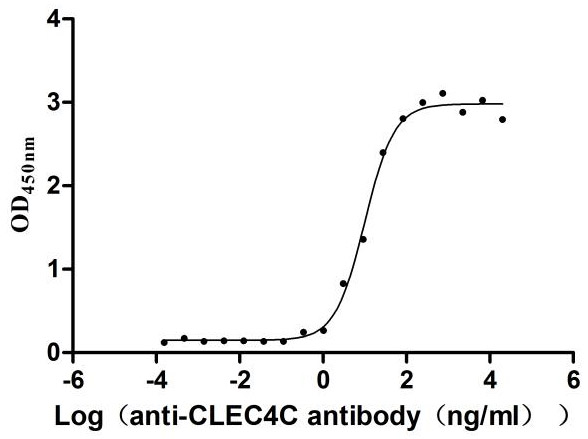
Recombinant Human C-type lectin domain family 4 member C (CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
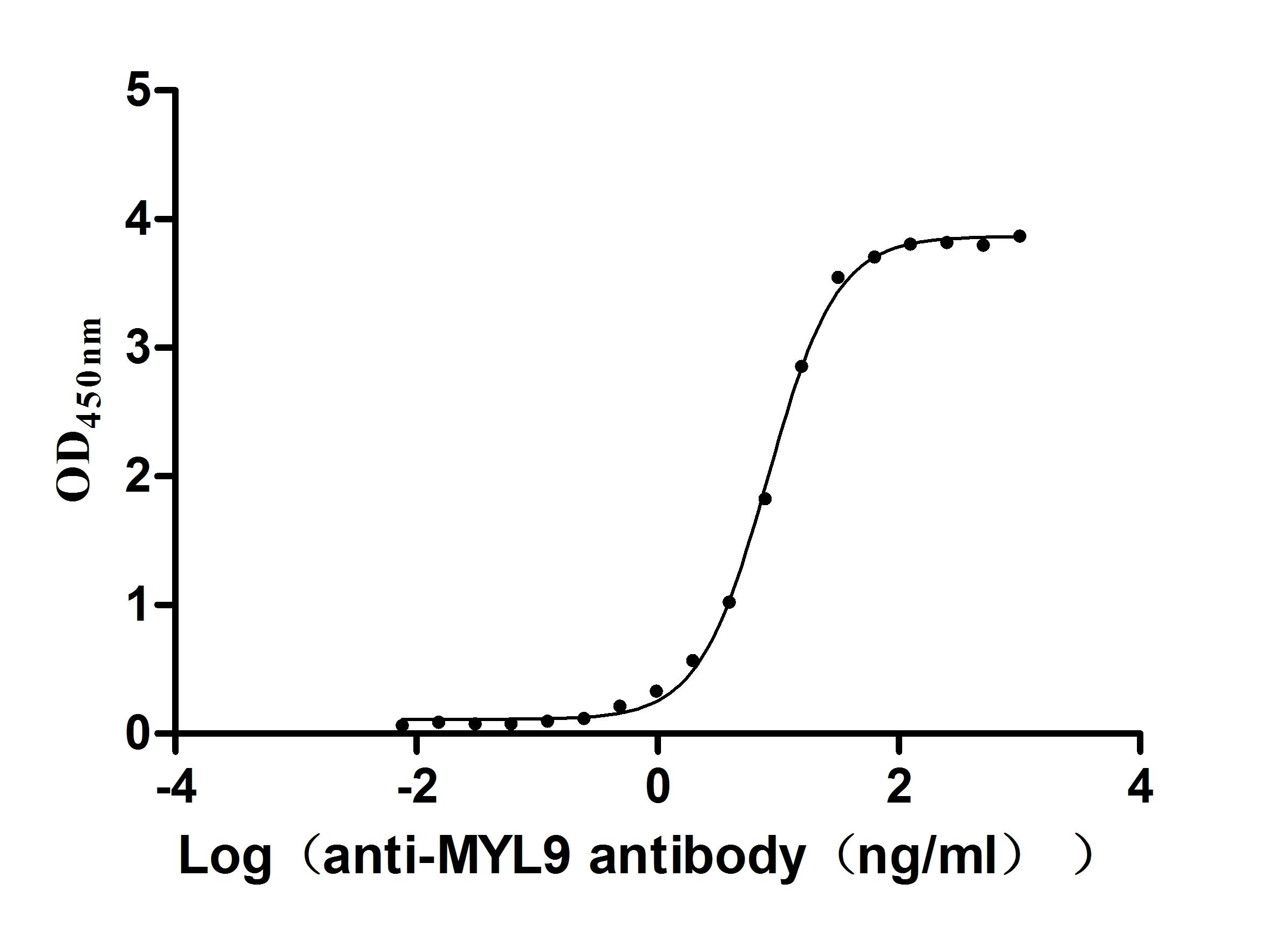
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B(MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
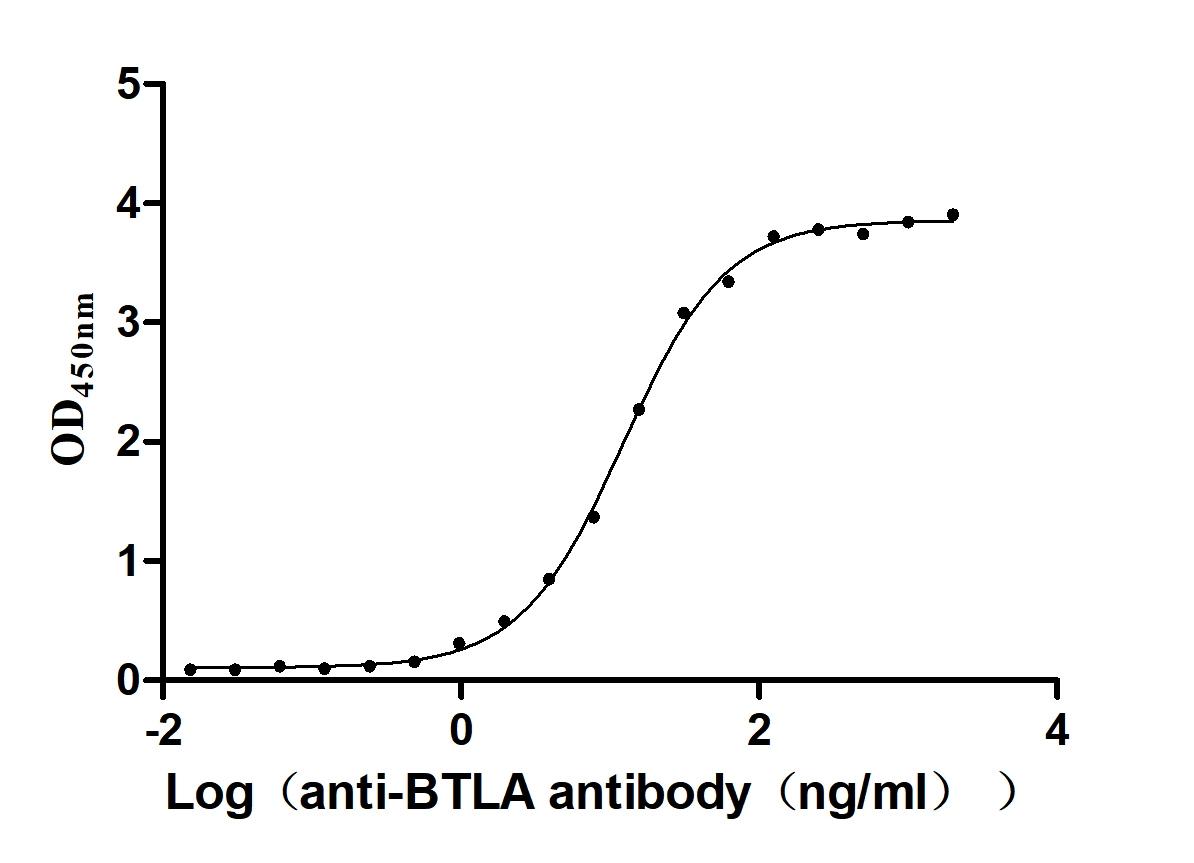
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(BTLA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
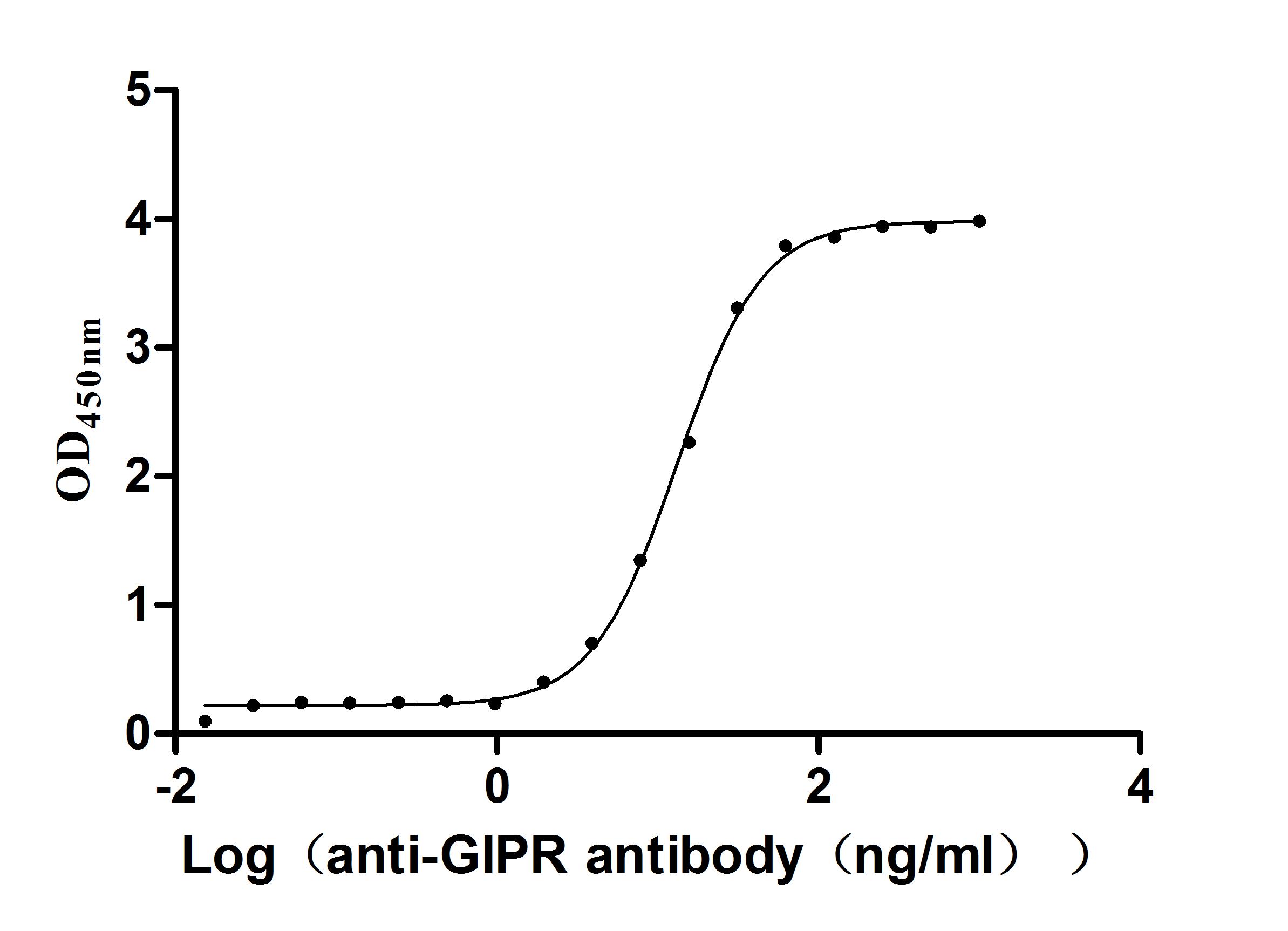
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIPR), partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)


-AC1.jpg)