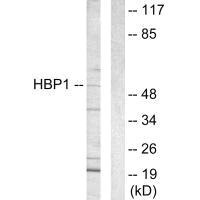
HBP1 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA097019
-
规格:¥2024
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) HBP1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:O60381
-
基因名:HBP1
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from Internal of Human HBP1.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:3000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcriptional repressor that binds to the promoter region of target genes. Plays a role in the regulation of the cell cycle and of the Wnt pathway. Binds preferentially to the sequence 5'-TTCATTCATTCA-3'. Binding to the histone H1.0 promoter is enhanced by interaction with RB1. Disrupts the interaction between DNA and TCF4.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Study shows that RORbeta is a transcriptional enhancer of inhibitor HBP1 of the Wnt pathway. NRIP2 prevents RORbeta to bind with downstream HBP1 promoter regions and reduces the transcription of HBP1. These results provide evidence that interactions between NRIP2, RORbeta, and HBP1 mediate a new mechanism for CCIC self-renewal via the Wnt activity. PMID: 28137278
- Low HBP1 expression is associated with invasive oral cancer. PMID: 28099936
- induced premature senescence and apoptosis. Furthermore, the Pim-1-HBP1 positive feedback loop exerts its effect by regulating the senescence markers DNMT1 and p16 and the apoptosis marker Bax. The Pim-1-HBP1 axis thus constitutes a novel checkpoint pathway critical for the inhibition of tumorigenesis. PMID: 28348080
- miR155 may contribute to the progression and growth of Colorectal carcinomaby enhancing the Wnt/betacatenin pathway in an HBP1associated mechanism. PMID: 26780942
- Data suggest HMG-box transcription factor (HBP1) as a target in prostate cancer radiotherapy. PMID: 26942107
- Data show that HMG-box transcription factor 1 protein HBP1-mediated elevation of CDK inhibitor p21 through the Mdm2/p53 and TCF4/EZH2 pathways contributes to both cellular senescence and tumor inhibition. PMID: 27129219
- All trans-retinoic acid can reverse the suppressive effect of MED28 on HBP1 and E-cadherin and inactivate the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in colorectal cancer, suggesting a protective effect of ATRA against colorectal cancer. PMID: 26660958
- HBP1-mediated Wnt signaling is involved with the role of miR-155 in osteosarcoma progression. PMID: 25666090
- Hbp1 plays a crucial role in regulating the timing of cortical neurogenesis by elongating the cell cycle and that it is essential for normal cortical development. PMID: 26041766
- HBP1 is a suppressor of cancer progression and a regulator of CTNNB1 gene transcription. PMID: 24895061
- miR-96/HBP1/Wnt/beta-catenin regulatory circuitry promotes the proliferation of glioma cell PMID: 24931370
- HBP1 is a novel target of the PI3K/FOXO pathway and controls cell proliferation in response to growth factors. PMID: 24762137
- acetylation of TCF4E is a novel regulatory mechanism that diversifies the transcriptional output of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling PMID: 23613959
- HBP1 represses the DNMT1 gene through binding a high-affinity site in the DNMT1 promoter. PMID: 23249948
- Cis-acting regulatory polymorphisms acting on HBP1 contribute to the osteoarthritis association signal at chromosome 7q22. PMID: 22586168
- miR-17-5p plays an important role in breast cancer cell invasion and migration by suppressing HBP1 and subsequent activation of Wnt/beta-catenin PMID: 20505989
- HBP1 targets P16(INK4A), upregulating its expression and consequently is involved in Ras-induced premature senescence. PMID: 20581871
- HBP1 directly inhibits MIF gene transcription, which is overexpressed in prostatic cancer. PMID: 20383199
- HBP1 binds c-Myc in cells, and expression of HBP1 inhibits c-Myc transactivational activity at least partly by preventing c-Myc binding to target gene promoters. PMID: 20008325
- NMR study of the AXH domain PMID: 14872137
- Results indicate that HBP1 may contribute to the regulation of NADPH oxidase-dependent superoxide production through transcriptional repression of the p47phox gene. PMID: 15024088
- HBP1 and Mad1 repressors bind the Sin3 corepressor PAH2 domain with opposite helical orientations PMID: 15235594
- in myeloid cells HBP1 may serve as a tumor suppressor and a general differentiation inducer and may synergize with chemical differentiating agents to enhance lineage-specific differentiation PMID: 16179914
- Transgenic mice overexpressing HBP1 exhibit altered thymus cellularity and decreased thymocyte development. PMID: 16210625
- EGCG blocks Wnt signaling by inducing the HBP1 transcriptional repressor and inhibits aspects of invasive breast cancer PMID: 16495219
- these studies highlight p38 MAPK, HBP1, and RB as important components for a premature-senescence pathway with possible clinical relevance to breast cancer. PMID: 16966377
- HBP1 transcriptional repressor alterations are associated with invasive breast cancer PMID: 17616670
- HBP1 regulates the cell cycle in liver regeneration and provides evidence for a role in tissue maintenance. PMID: 11486012
- HBP1 is a suppressor of Wnt signalling and lies in a region that is mutated in cancer. PMID: 11500377
- HBP1 was isolated as a cell cycle inhibitor and HMG-box transcriptional repressor. PMID: 9030690
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 23200
KEGG: hsa:26959
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000222574
UniGene: Hs.162032
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-