ABCA4 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA217707
-
规格:¥1100
-
图片:
-
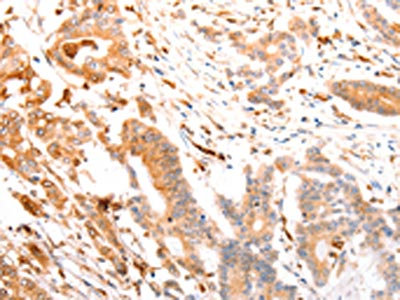
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human colon cancer tissue using CSB-PA217707(ABCA4 Antibody) at dilution 1/30, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
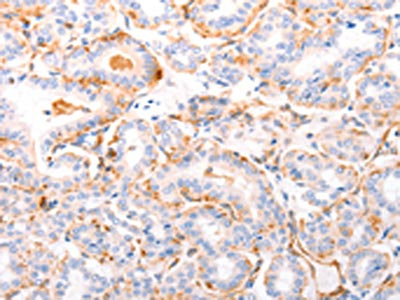
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human thyroid cancer tissue using CSB-PA217707(ABCA4 Antibody) at dilution 1/30, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P78363
-
基因名:
-
别名:ABC 10 antibody; ABC A4 antibody; ABC transporter; retinal-specific antibody; ABC10 antibody; ABCA 4 antibody; abcA4 antibody; ABCA4_HUMAN antibody; ABCR antibody; ARMD 2 antibody; ARMD2 antibody; ATP binding cassette 10 antibody; ATP binding cassette sub family A member 4 antibody; ATP binding cassette sub family A member4 antibody; ATP binding cassette transporter antibody; ATP binding cassette transporter retinal specific antibody; ATP binding cassette; sub family A (ABC1); member 4 antibody; ATP binding cassette; sub family A (ABC1); member4 antibody; ATP binding cassette10 antibody; ATP binding transporter; retina specific antibody; ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 4 antibody; CORD 3 antibody; CORD3 antibody; DKFZp781N1972 antibody; FFM antibody; FLJ17534 antibody; Photoreceptor rim protein antibody; Retina specific ABC transporter antibody; Retinal specific ATP binding cassette transporter antibody; Retinal-specific ATP-binding cassette transporter antibody; RIM ABC transporter antibody; RIM protein antibody; RmP antibody; RP 19 antibody; RP19 antibody; Stargardt disease protein antibody; STGD antibody; STGD1 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Synthetic peptide of Human ABCA4
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen affinity purification
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:-20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution ELISA 1:2000-1:5000 IHC 1:25-1:100 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Flippase that catalyzes in an ATP-dependent manner the transport of retinal-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugates like the 11-cis and all-trans isomers of N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine from the lumen to the cytoplasmic leaflet of photoreceptor outer segment disk membranes, where N-cis-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine (N-cis-R-PE) is then isomerized to its all-trans isomer (N-trans-R-PE) and reduced by RDH8 to produce all-trans-retinol (all-trans-rol) and therefore prevents the accumulation of excess of 11-cis-retinal and its schiff-base conjugate and the formation of toxic bisretinoid. May display both ATPase and GTPase activity that is strongly influenced by the lipid environment and the presence of retinoid compounds. Binds the unprotonated form of N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine with high affinity in the absence of ATP, and ATP binding and hydrolysis induce a protein conformational change that causes the dissociation of N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- neighboring deep-intronic ABCA4 variants (c.4539+2001G>A and c.4539+2028C>T) result in a retina-specific 345-nt pseudoexon insertion. PMID: 29526278
- Two intronic variants c.4773+3A>G and c.5461-10T>C, both predicted to affect splicing, are indeed disease-causing mutations due to skipping of exons 33, 34, 39 and 40 of ABCA4 gene. The experimental proof that ABCA4 mutations in STGD patients affect protein function is crucial for their inclusion to future clinical trials. PMID: 29461686
- The study broadens the spectrum of ABCA4 mutations with 60 likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants, all associated with Stargardt disease. PMID: 30060493
- Full-field electroretinography is a predictor of the natural course of ABCA4-associated retinal degeneration. PMID: 29386879
- Next-generation sequencing was effective for the molecular diagnosis of genetic diseases and specifically allowed a conclusive diagnosis in 80% (40/50) of the patients. As the ABCA4 gene does not show a preferential region for pathogenic variants, the diagnosis of Stargardt disease depends on broader analysis of the gene. The most common pathogenic variants in the ABCA4 gene described in the literature were also found. PMID: 30093795
- The results indicate that the p.Ala1773Val mutation in ABCA4 is associated with a severe retinal phenotype and thus, could be classified as null. PMID: 29422768
- The ROC phenotype is a unique classification of ABCA4 disease, which is caused by deleterious null biallelic ABCA4 mutations and is characterized by the rapid deterioration of retinal pigment epithelium and photoreceptor layers in the macula and significant choroidal thinning within the first 2 decades of life. PMID: 28947085
- ABCA4 midigenes reveal the full splice spectrum of all reported noncanonical splice site variants in Stargardt disease. PMID: 29162642
- These findings expand the mutation spectrums of ABCA4 and LRP5, and will be valuable for genetic counseling and development of therapeutic interventions for patients with Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. PMID: 29207047
- Our analyses allowed us to classify novel variants in ABCA4 as being clearly loss-of-function mutations, and thus pathogenic variants. PMID: 28885670
- High prevalence of p.L541P, p.A1038V, and p.G1961E mutations of the ABCA4 gene has been established in patients with Stargardt disease by performing massive parallel sequencing of all coding regions of the ABCA4 gene. PMID: 28980559
- Two novel pathogenic ABCA4 mutations were identified in Chinese families with Stargardt disease. PMID: 27739528
- We report an unusual phenotype in a child with a clinical diagnosis of recessive Stargardt disease (STGD1) and two pathogenic variants in the ABCA4 gene. PMID: 28726568
- Studies indicate that variants in ABCA4 are associated with a wide variety of inherited retinal diseases. PMID: 28044389
- Segregation analysis is important in order to confirm the molecular diagnosis of patients with Stargardt disease, given the frequency of complex alleles in the ABCA4 gene. The various pathogenic variation combinations observed in this study were associated with different phenotypes. PMID: 29114839
- The histopathology of the retina in this patient with Stargardt disease displayed a highly degenerated fovea. In all retinal locations studied, cones were more severely affected than rods. PMID: 25265374
- Thirty six SNP including 9 previously not described, were identified in juvenile-onset blindness patients of south Asian decent. PMID: 28327576
- This study describes the functional effect and the molecular mechanism of the pathogenic ABCA4 variant c.5461-10T>C. The variant is functionally important as it leads to splicing defects and a reduced level of ABCA4 protein. PMID: 27775217
- study to determine the effect of 15 individual ABCA4 mutations on retinal disease severity; in the hemizygous state, 2/15 ABCA4 alleles retain preserved peripheral retinal function; 7/15 are associated with either preserved or only mildly abnormal retinal function, worse in older patients; 6/15 behave like null mutations PMID: 27820952
- The ABCA4 variant c.5461-10T-->C is located on a founder haplotype lacking other disease-causing rare sequence variants. In vitro studies revealed that it leads to mRNA exon skipping and ABCA4 protein truncation. PMID: 26976702
- Genetic risk score estimates suggest that defined common ABCA4 variants influence disease risk in carriers of a single pathogenic ABCA4 allele. PMID: 28118664
- A combination of p.[(L541P; A1038V)] and/or a truncating ABCA4 mutation always resulted in an early disease onset. Identification of ABCA4 retinopathies provides a specific molecular diagnosis and justifies a prompt introduction of simple precautions that may slow disease progression. PMID: 26593885
- Nullizygosity for ABCA4 is associated with early onset cone-rod dysfunction with rapid progression shown by enlargement of central atrophy on FAF, decline of ERG amplitudes with age, and a high risk of reaching legal blindness by the fourth decade. PMID: 27583828
- Results identified nonsynonymous variants in MYH9 and ABCA4 to be the most frequent risk loci in nonsyndromic orofacial clefts in the Taiwanese population. PMID: 27527345
- 1268A>G missense variant of the ABCA4 gene has often been reported as causative of disease, and in other cases protective of disease, in our family case, the variant appears to reduce or delay the risk of onset of Stargardt disease. PMID: 28290600
- Of the 225 genetic tests performed, 150 were for recessive IRD, and 75 were for dominant IRD. A positive molecular diagnosis was made in 70 (59%) of probands with recessive IRD and 19 (26%) probands with dominant IRD. Thirty-two novel variants were identified; among these, 17 sequence changes in four genes were predicted to be possibly or probably damaging including: ABCA4 (14), BEST1 (2), PRPH2 (1), and TIMP3 PMID: 28005406
- A transient SD-OCT phenotype ascribed to patients with hydroxychloroquine retinopathy is associated with an early subtype of STGD1. PMID: 26311262
- Ten novel ABCA4 variations are detected of which 8 belongs to non-Slavonian population. Most of the detected known variations are found in European and American Stargardt disease populations PMID: 27939946
- seven out of 27 families, displaying mutations in the ABCA4, RP1, RP2 and USH2A genes, could be genetically or clinically reclassified. These results demonstrate the potential of our panel-based NGS strategy in RP diagnosis PMID: 26806561
- ABCA4 carriers demonstrated reduced macular function measured by mERG along with none to subtle and even extensive morphological retinal changes. The c.768 G>T, c.5461-10T>C, and c.319 C>T mutations were associated with the most deviant ERGs. PMID: 26261413
- 633C>A (CC+CA) genotype, 5646G>A and 6389T>A polymorphisms of ABCA4 gene and smoking are susceptible factors for age-related macular degeneration PMID: 26261643
- This family epitomizes the clinical and genetic complexity of ABCA4-associated diseases. It contained variants from all classes of mutations PMID: 26527198
- The mutation spectrum of the ABCA4 gene in Chinese patients is quite different from that for Caucasian patients. The establishment of the mutation profile will facilitate ABCA4 screening and risk evaluation for Chinese patients with STGD1. PMID: 26780318
- This study indicates that carriers of monoallelic ABCA4 mutations are phenotypically normal. PMID: 26720470
- With few exceptions, individuals heterozygous for ABCA4 mutations and between the ages of 9 and 60 years do not present with elevated qAF. PMID: 26551331
- The ABCA4 L541P;A1038V mutation causes severe retinal degenerations whereas the V mutation alone causes mild disease. PMID: 25712131
- Identification of Novel Mutations in ABCA4 Gene: Clinical and Genetic Analysis of Indian Patients with Stargardt Disease. PMID: 25922843
- Our findings demonstrate that minor alleles of common genetic variants in ABCA4 significantly reduce susceptibility to develop toxic maculopathy under chloroquine treatment. PMID: 25884411
- Stargardt eye disease ABCA4 R1108C and R1129C are both temperature-sensitive processing mutants that engage the cellular quality control mechanism and show a strong interaction with the chaperone Hsp 27. PMID: 26092729
- Two known disease-causing mutations in ABCA4 were identified in proband 1; c.4234C>T, p.(Gln1412*) in exon 28; and c.5882G>A, p.(Gly1961Glu) in exon 42. PMID: 25640233
- Our study provides further evidence regarding the roles of genetic markers in ABCA4 in NSCL/P development in this northern Chinese Han population. G allele of rs560426 may be a risk factor for developing NSCL/P. PMID: 25499508
- high qAF levels of ABCA4-positive patients are a hallmark of ABCA4-related disease PMID: 26024099
- Study reveals high frequency of the deep intronic variant c.4539+2001G>A (V4)in ABCA4 gene that has founder effect and moderate-to-severe impact in the phenotype of Autosomal-recessive Stargardt disease Belgian patients. PMID: 25346251
- Results show the presence of heterozygous deep-intronic and exonic variants and deletions in ABCA4 in patients with retinal dystrophies. PMID: 25363634
- Significant evidence was found for a relationship between the G1961E and D2177N variants in ABCA4 with increased susceptibility to AMD, specifically for Americans PMID: 25921964
- New mutations have been described in the ABCA4 genomic locus in Stargardt disease. PMID: 25082829
- The relatively high proportion of deleterious ABCA4 variants supports the hypothesis that earlier onset disease is often owing to more severe variants in ABCA4 than those found in adult-onset disease. PMID: 25312043
- Thus, early-onset Stargardt lies at the severe end of the spectrum of ABCA4-associated retinal phenotypes. PMID: 25444351
- The qAF method can differentiate between ABCA4-associated and non-ABCA4-associated BEM and may guide clinical diagnosis and genetic testing. PMID: 25283059
- The anatomy, metabolism, and biochemistry of the retina, as well as genetic variations in genes other than ABCA4, can influence the etiology of foveal sparing. PMID: 25324290
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Stargardt disease 1 (STGD1); Fundus flavimaculatus (FFM); Macular degeneration, age-related, 2 (ARMD2); Cone-rod dystrophy 3 (CORD3); Retinitis pigmentosa 19 (RP19)
-
亚细胞定位:Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum. Cytoplasmic vesicle. Cell projection, cilium, photoreceptor outer segment.
-
蛋白家族:ABC transporter superfamily, ABCA family
-
组织特异性:Retinal-specific. Seems to be exclusively found in the rims of rod photoreceptor cells.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 34
OMIM: 153800
KEGG: hsa:24
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000359245
UniGene: Hs.416707
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-