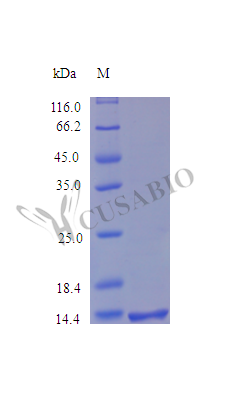
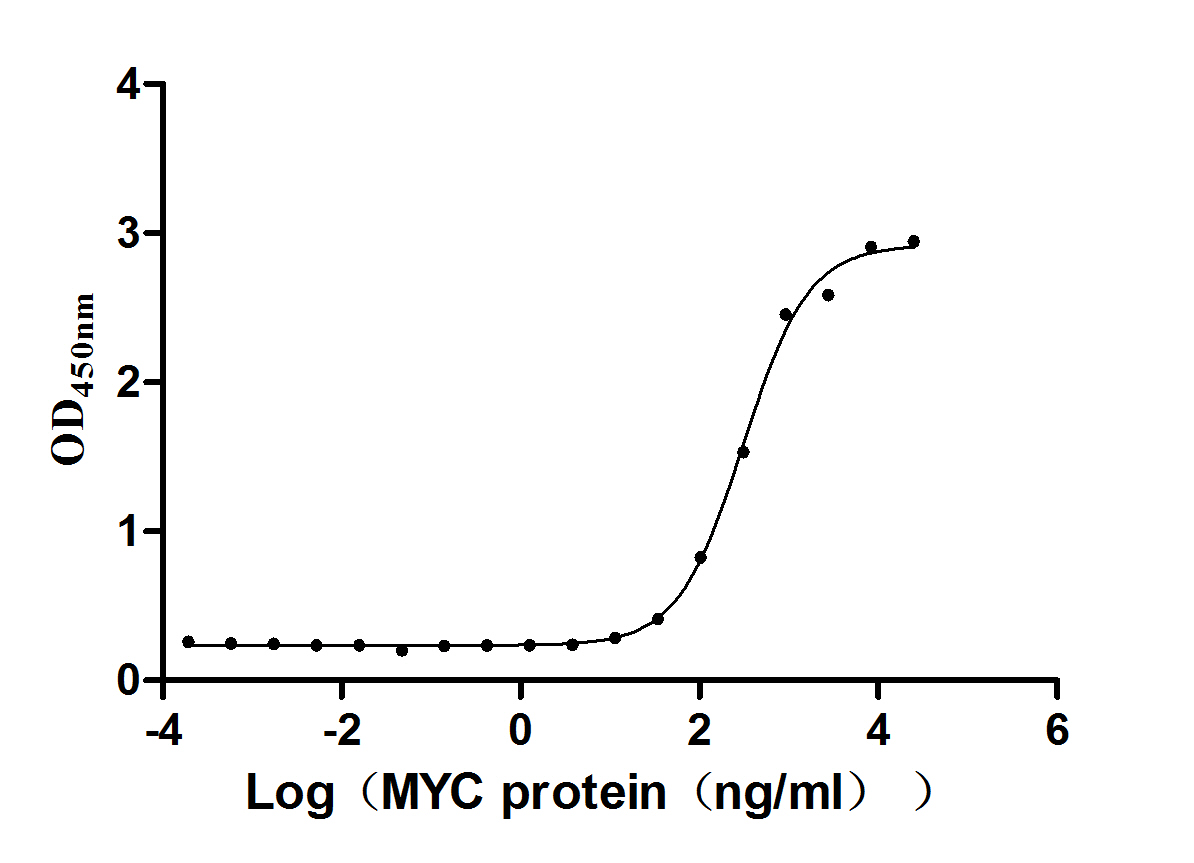
Recombinant Human Syndecan-4 (SDC4), partial (Active)
In Stock产品详情
-
纯度:>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
内毒素:Less than 1.0 EU/μg as determined by LAL method.
-
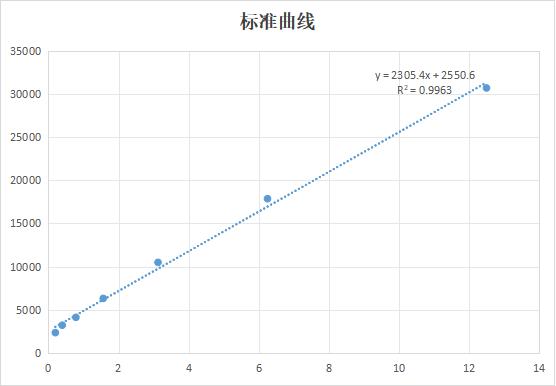
生物活性:Fully biologically active when compared to standard. The specific activity is determined by binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized rHuSYND4 at 500 ng/ml (100 μl/well) can bind rHubFGF with a linear range of 0.1-10 ng/ml.
-
基因名:SDC4
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Amphiglycan; MGC22217; OTTHUMP00000031788; ryudocan amphiglycan; Ryudocan; Ryudocan core protein; SDC 4; Sdc4; SDC4_HUMAN; SYND 4; SYND4; syndecan 4; syndecan 4 (amphiglycan, ryudocan); syndecan proteoglycan 4; Syndecan-4; Syndecan4
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:E.Coli
-
分子量:13.9 kDa
-
表达区域:19-145aa
-
氨基酸序列ESIRETEVID PQDLLEGRYF SGALPDDEDV VGPGQESDDF ELSGSGDLDD LEDSMIGPEV VHPLVPLDNH IPERAGSGSQ VPTEPKKLEE NEVIPKRISP VEESEDVSNK VSMSSTVQGS NIFERTE
-
蛋白标签:Tag-Free
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:0.2 μm filtered PBS, pH 7.4 ,lyophilized
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:5-10 business days
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Cell surface proteoglycan that bears heparan sulfate. Regulates exosome biogenesis in concert with SDCBP and PDCD6IP.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- SDC4 gene silencing affects cell Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition and apoptosis of papillary thyroid cancer through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. PMID: 30165731
- Downregulation of SDC-4 inhibited FGF signaling through the blockade of ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR activation, thus suppressing cell proliferation and migration. PMID: 28703800
- studies are required to show if syndecan-4 concentrations can be marker for prognosis assessment or disease progression PMID: 29232393
- Data provide evidence that SDC4 plays important roles in normal physiology of intervertebral disc and cartilage through controlling growth factor signaling and matrix homeostasis. However, several studies to date clearly show that in diseased joints, SDC4 and inflammatory cytokines IL-1beta and TNF-alpha form a positive feedback loop, wherein they control each other's expression and/or activity. [review] PMID: 26796346
- This study demonstrates that the shedding of synd4 from Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) plays a key role in advanced glycation end products-mediated dysfunction of EPC migration and homing. PMID: 27662820
- the Ser179Glu mutant of SDC-4 binds strongly Tiam1, a Rac1-GEF reducing Rac1-GTP by 3-fold in MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cells. PMID: 29121646
- Syndecan 4 is the biomarker independently distinguishing Heart Failure with preserved ejection fraction and Heart Failure with reduced ejection fraction. PMID: 27448535
- The upregulation of syndecan-4 in the eutopic endometrium of endometriosis patients may facilitate the pathogenetic process by promoting invasive cell growth via Rac1, MMP3, and ATF-2. PMID: 27041028
- Sdc4 has been identified as a mycobacterial attachment receptor on alveolar epithelial cells. PMID: 27279134
- Study has demonstrated that SDC-4 expression was increased in sera and skin of atopic dermatitis (AD) patients, suggesting that SDC-4 may contribute to the development of AD. PMID: 27591995
- the present study demonstrated that synd4 was involved in the chemotactic migration of ECs in vitro and in vivo. PMID: 27541034
- results suggest that SDC4 alleles affect lipid profile in elderly subjects and may in part mediate the link between LDL-C and longevity. PMID: 26254886
- Synd4 shedding is a molecular pathological alteration in the development and maintenance of inflammation-associated atrial fibrillation. PMID: 26261514
- Dynamic catch of a Thy-1-integrin alpha5beta1+syndecan-4 trimolecular complex explains extraordinary cancer cell adhesion to the vascular endothelium. PMID: 25216363
- Syndecan-4 polymorphisms were associated with essential hypertension, body mass index, and coronary artery disease prevalence in the Tampere adult population cardiovascular risk study. PMID: 25410619
- No association was found with SDC4 and breast cancer. PMID: 25361632
- Data indicate that depletion of syndecan 4 (S4) in umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) using shRNA inhibited flow-induced alignment in vitro, which was rescued by re-expression of S4. PMID: 25404299
- define a role for TG2 activity at the surface of human macrophages in multiple stages of AC clearance and we propose that TG2, in association with heparan sulphates may exert its effect on AC clearance via a mechanism involving the crosslinking of CD44 PMID: 25449226
- syndecan 4 is the predominant heparan sulfate proteoglycan in the glomerular endothelial cells glycocalyx PMID: 25122554
- TGM2 up-regulation along with ITGB1 and SDC4 plays an important role in the development of RCC tumors and advanced RCC with metastasis PMID: 23499501
- Sdc4 is necessary for activation of the integrin during chemokinesis induced by EGF. PMID: 25202019
- in healthy discs, SDC4, through its heparan sulfate side chains, contributes to maintenance of the hypoxic tissue niche by controlling baseline expression of Sox9. PMID: 24558194
- High glucose modifies TRPC6 channels and ROS production via SDC-4 in human podocytes. PMID: 24942878
- The cytoplasmic V domain of syndecan-4 made a significant contribution to the cellular uptake of octaarginine, whereas the cytoplasmic C1 and C2 domains were not involved in the process. PMID: 24632200
- syndecan-4 is differentially expressed in seminomas and nonseminomatous germ cell tumours and might be a useful marker. PMID: 23844358
- The more upgraded the NYHA grading, the higher level of serum syndecan-4 protein. PMID: 23948417
- Syndecan-4 expression and shedding were increased in failing human myocardium. PMID: 23374111
- EGFR are the key mediators of SDC-4 expression in MCF-7 cells. PMID: 23374155
- Increased expression of SDC4 and FN may be underlying molecular alteration of osteo-sarcoma which accounts for more aggressive clinical behaviour. PMID: 22531343
- studies identify S4 as a regulator of MAPK signaling and address the question of how distinct classes of FGFRs individually contribute to signal transduction in endothelial cells PMID: 22569333
- By accruing more syndecan-4 on their surface and also shedding it during Th1 cytokine-driven inflammation, asthmatic airway smooth muscle cells may regulate inflammation and remodeling locally and alter the responsiveness of the airways in asthma. PMID: 22268118
- in nucleus pulposus, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta regulate SDC4 expression, which plays a key role in pathogenesis of degenerative disc disease by promoting aggrecan degradation by ADAMTS-5. PMID: 21949132
- SD-4 bearing distinct heparan sulfate moieties plays a pathogenic role in Sezary syndrome and may be targeted for treatment. PMID: 21252093
- Expression of syndecan 4 in healthy human breast tissue during menstrual cycle. PMID: 20398359
- In dendritic cells, lysophosphatidylcholine-induced phosphorylation of SDC4 by PKCdelta results in a functional inactivation of SDC4 and decreases adhesion and motility. PMID: 20607801
- Data found that Wnt5a reduces cell surface levels and promotes ubiquitination and degradation of SDC4. PMID: 20639201
- SDC4 promotes cytokinesis in a phosphorylation-dependent manner in MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cells. The serine179-phosphorylation and the ectodomain shedding of SDC4 changed periodically in a cell cycle-dependent way. PMID: 20229236
- The expression of syndecan-4 protein was significantly enhanced by TNF-alpha in HUVECs. PMID: 17545042
- The down-regulation of syndecan-4, a heparan sulfate proteoglycan, decreased SDF-1/CXCL12-mediated HeLa cell invasion. PMID: 19695308
- Study identified an overrepresentation of focal amplifications of known (FGFR3, CCND1, MYC, MDM2) and novel candidate genes (MYBL2, YWHAB and SDC4) in stage Ta bladder carcinoma. PMID: 19821490
- Syndecan-4 may be a sensor of tension exerted on the matrix [review] PMID: 19538537
- Syndecan-4 mediates antithrombin-induced chemotaxis of human peripheral blood lymphocytes and monocytes PMID: 11801740
- Clustering induces redistribution of syndecan-4 core protein into raft membrane domains PMID: 11889131
- Syndecan-4 core protein mediates the effects of fibroblast growth factor (FGF)2 on cell function. PKCalpha activation and PDZ-mediated formation of a serine/threonine phosphatase-containing complex by syndecan-4 are downstream events of FGF2 signaling. PMID: 12011116
- SDC4 regulates inositol phospholipid binding and signaling PMID: 12377772
- the focal adhesion component alpha-actinin interacts with syndecan-4 in a beta-integrin-independent manner PMID: 12493766
- Syndecan-4 can promote cell spreading in a beta(1) integrin-dependent fashion through PKCalpha and RhoA PMID: 12509413
- endotoxin-induced adhesion of leukocytes to endothelium can be reversed by ligation of syndecan-4 with antithrombin's heparin-binding site PMID: 14652650
- syndecan-4/CXCR4 complex is likely a functional unit involved in SDF-1 binding PMID: 15033938
- human trabecular meshwork cells express only syndecan-1, and not syndecan-4, at the cell surface, and focal adhesion and stress fiber formation occur independent of syndecan-4 PMID: 15572366
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform 1]: Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Secreted.; [Isoform 2]: Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Syndecan proteoglycan family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in epithelial and fibroblastic cells.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 10661
OMIM: 600017
KEGG: hsa:6385
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000361818
UniGene: Hs.632267
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human papillomavirus type 16 Protein E7 (E7) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Human papillomavirus type 16
-
Recombinant Mouse Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Oncostatin-M (OSM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
Recombinant Human Urokinase-type plasminogen activator(PLAU) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Mucin-13(MUC13),partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)