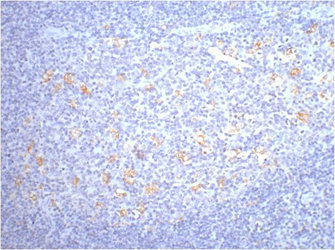
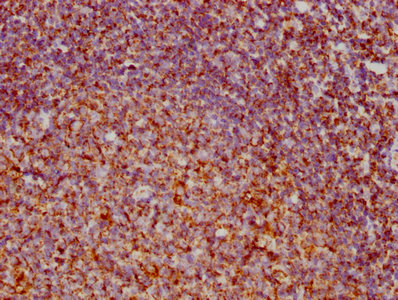
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P34810
-
基因名:
-
别名:CD68; Macrosialin; Gp110; CD antigen CD68
-
宿主:Mouse
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthetic Peptide
-
免疫原种属:H, M, R
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:PBS, pH 7.4, containing 0.02% sodium azide as Preservative and 50% Glycerol.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC 1:100-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
引用文献
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Could play a role in phagocytic activities of tissue macrophages, both in intracellular lysosomal metabolism and extracellular cell-cell and cell-pathogen interactions. Binds to tissue- and organ-specific lectins or selectins, allowing homing of macrophage subsets to particular sites. Rapid recirculation of CD68 from endosomes and lysosomes to the plasma membrane may allow macrophages to crawl over selectin-bearing substrates or other cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Combined detection of tumor-associated macrophages markers, CD68 and Sema4D, in gastric carcinoma tissue shows potential to predict the trend of gastric carcinoma progression. PMID: 29434448
- The study revealed that CD16-CD68-expressing macrophages appear to participate in ureteral neoplastic transformation. PMID: 29243545
- A combination of CD68/CD206 density and HBV-positivity improves further predictive value for post-operative recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) . Quantification of CD68/CD206 macrophages and their distribution can be exploited for better postsurgical management of HCC patients. PMID: 28656201
- Report CD68 over-expression in multinucleated giant cells and mononuclear cells in central and peripheral giant cell granuloma of jaw. PMID: 28832079
- This study shown the CD68 expression in Microglia and Astrocytes in stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and Lewy body dementia. PMID: 28398520
- The results of this study found that the expression levels of Cd68 and Atp5b were significantly correlated with the neurofibrillary tangle burden in the Alzheimer's Disease brain and with their cognition. PMID: 27911303
- Taken together, these results suggested that the changes, including ox-LDL/LDL ratio, CD68(+)/RANK(+) cells number, and the levels of RANKL and HMGB1 in AS patients, favored osteoclastogenesis. PMID: 29146189
- High expression of CD68 is associated with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. PMID: 28951310
- increased amount of CD68+TAM in gaps of ductal tumor structures is protective against metastatic spread in regional lymph nodes. PMID: 26391151
- Most cases of histiocytic sarcoma expressed histiocytic markers CD68 (6 of 7 cases), CD163 (5 of 5 cases), and PU.1 (3 of 4 cases). PMID: 28805986
- Renal expression of CD68 and the chronicity index are associated with progression to chronic kidney disease in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis. PMID: 26621103
- Results indicate that the expression of FoxP3 was not significantly associated with survival, and suggest prognostic significance of high CD68 expression in primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). PMID: 28508176
- Her-2 overexpression results in ICA were similar to previous reports, the finding of 28% in HGD was unexpected and may have clinical implications. Positive Her-2 DISH in 6% of LGD is novel, suggesting a role of Her-2 during BE progression PMID: 26469325
- CD68 may play key roles in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and its complications may be via induction of inflammation; CD68 may be considered as a risk factor for development of AD and also psychotic symptoms in the patients PMID: 28465247
- hCD68GFP/ApoE(-/-) mice provide a new approach to study macrophage accumulation in atherosclerotic plaque progression and to identify cells recruited from adoptively transferred monocytes. PMID: 27908893
- Findings indicate that human CD68 and its mouse ortholog macrosialin located in the lysosomal membrane and share many structural similarities. PMID: 27869795
- The strong CD68 and S100 co-expression in our case did not allow a clear-cut discrimination between the immunophenotype of histiocytic neoplasms and amelanotic melanoma, because of CD68 immunoreactivity occurring in 75% of metastatic malignant melanomas PMID: 26407839
- Using double labeling with Iba-1 and cd68 could determine the physiological state of microglia in brain contusion based on their morphology and immunoreactivity. PMID: 27442380
- we confirmed the similarities between epithelial ovarian cancer and fallopian tube, normal and adenocarcinoma using FOLR1, FOLR2, CD68 and CD11b markers PMID: 25971554
- Data indicate the prognostic value of CD68 antigen in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). PMID: 24766492
- This study does not support a prognostic role of CD68 positivity in predicting survival. PMID: 25204373
- we raised a possibility that the microlocalization of CD68(+) tumor-associated macrophages was an indispensable factor for the advance of oral squamous cell carcinoma. PMID: 25666753
- Data indicate that the high CD68/CD3 ratio identifies a bad prognosis group among muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma (UC). PMID: 24794251
- The human CD68 promoter drives green fluorescent protein expression in all CD115(+) monocytes of adult blood, spleen, and bone marrow. PMID: 25030063
- CD68 tumor-associated macrophage marker is not prognostic of clinical outcome in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. PMID: 24067108
- The CD68-positive cells (those that have not yet developed into foam cells) present in the intima of saphenous vein grafts might serve as a very early marker of graft occlusion. PMID: 23275124
- the distribution of CD68-positive cells during normal brain development may not reflect a supportive role of these microglia in axonogenesis of midterm human fetuses. PMID: 24459672
- The MRC1/CD68 ratio is positively associated with adipose tissue lipogenesis and with muscle mitochondrial gene expression in humans. PMID: 23951013
- CD68 has a role in poor recurrence-free survival of hepatocellular carcinoma, but CD163 is more related to active hepatitis PMID: 23555776
- Multivariate analysis identified the density of CD163-positive cells as well as the ratio of CD163/CD68 expression as negative predictors for survival of epithelial ovarian cancer patients. PMID: 23289476
- Follicular lymphoma patients with PSMB1 P11A (G allele) and low CD68 expression have significantly longer progression free survival with bortezomib-rituximab versus rituximab. PMID: 23549871
- Rhinovirus colocalizes with CD68- and CD11b-positive macrophages following experimental infection in humans. PMID: 23727038
- the marker CD68 might accurately predict early outcome of de novo cHL and could be used in combination with c-kit and TiA1 staining. PMID: 22667341
- Suggest that the proteins or mRNAs expressed by the proinflammatory CD68(+)MR(-) macrophages may contribute to abdominal aortic aneurysm pathology. PMID: 23241402
- After bed rest, CD68 expression was increased in LBW (P=0.03) but not in NBW individuals. PMID: 22968485
- Increased CD68 expression was associated with Hodgkin lymphoma PMID: 22948049
- CSF1R and cd68 gene expression is an independent predictor for progression-free survival of Hodgkin lymphoma patients. PMID: 22955918
- CD163 staining is lower than CD68, with less non-specific staining of background inflammatory cells and Hodgkin cells, therefore is a better marker for Hodgkin lymphoma associated macrophages. PMID: 22289504
- elderly subjects had twofold higher CD68 and CD206 gene expression (both P < 0.002) than young participants. In both studies, CD68(+) muscle macrophages were not associated with BMI. PMID: 22314623
- CD68 may have a role in atherosclerotic plaque PMID: 22395501
- Statins promote the beneficial remodeling of plaques in diseased mouse arteries through the stimulation of the CCR7 / CD68 emigration pathway in macrophages PMID: 22163030
- CD68 and CD163 are prognostic factors for Korean patients with Hodgkin lymphoma PMID: 22044760
- Data show that the number of TNF-alpha and CD68 positive cells in HIZ was significantly higher than that in the annulus fibrosus around HIZ and in the control. PMID: 21192298
- Fibrolamellar carcinomas are positive for CD68. PMID: 21113139
- Increased numbers of CD68-positive tumor macrophages indicate an adverse overall outcome in Hodgkin lymphoma. PMID: 21266828
- Significant co-localization of CD36 receptor with cells of the macrophage lineage, such as CD68 positive cells. PMID: 20333725
- Treatment with etanercept may be involved in vascular and cell proliferations with inhibition of the expression of CD68 and MMP-3 in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis patients. PMID: 20374310
- CD68 was expressed in beta-cells of NOD mice by 14-17 weeks of age, when a large proportion of these cells were infiltrated with lymphocytes and monocytes. PMID: 12397372
- CD68 expression is down-regulated in lymphoid cells by combinatorial interactions between PU.1 and IRF-4 PMID: 12676954
- study expands the immunophenotype of granular cell tumor (S100, CD68, protein gene product 9.5, and inhibin-alpha) regardless of location and supports a neural origin PMID: 15214825
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform Short]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Isoform Long]: Endosome membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Lysosome membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:LAMP family
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed by blood monocytes and tissue macrophages. Also expressed in lymphocytes, fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Expressed in many tumor cell lines which could allow them to attach to selectins on vascular endothelium, facilitating their diss
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 1693
OMIM: 153634
KEGG: hsa:968
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000250092
UniGene: Hs.647419
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
-
-
-
-
-
VDAC1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat