Recombinant Mouse Interleukin-1 alpha protein (Il1a)
In Stock产品详情
-
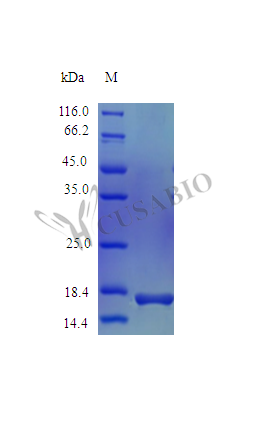
纯度:>97% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
内毒素:Less than 1.0 EU/μg as determined by LAL method.
-
生物活性:Fully biologically active when compared to standard. The ED50 as determined by a cell proliferation assay using murine D10S cells is less than 2 pg/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of >5.0x108 IU/mg.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Il1aInterleukin-1 alpha; IL-1 alpha
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
来源:E.Coli
-
分子量:17.9 kDa
-
表达区域:115-270aa
-
氨基酸序列SAPYTYQSDL RYKLMKLVRQ KFVMNDSLNQ TIYQDVDKHY LSTTWLNDLQ QEVKFDMYAY SSGGDDSKYP VTLKISDSQL FVSAQGEDQP VLLKELPETP KLITGSETDL IFFWKSINSK NYFTSAAYPE LFIATKEQSR VHLARGLPSM TDFQIS
-
蛋白标签:Tag-Free
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:0.2 μm filtered PBS, pH 7.4 ,lyophilized
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:5-10 business days
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Produced by activated macrophages, IL-1 stimulates thymocyte proliferation by inducing IL-2 release, B-cell maturation and proliferation, and fibroblast growth factor activity. IL-1 proteins are involved in the inflammatory response, being identified as endogenous pyrogens, and are reported to stimulate the release of prostaglandin and collagenase from synovial cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Infection with Mycobacterium bovis results in increase in interleukin-1alpha, TGF-beta1, and MMP1 in multinucleated macrophages. PMID: 29504104
- Together, these data suggest that caspase-11/IL-1alpha pathway plays an important role in defending against Klebsiella pneumoniae by recruiting neutrophils in the early stage of infection. PMID: 28939441
- These data highlight an important interdependency between the potent pro-inflammatory cytokine IL1A and Fshr expression. PMID: 28337831
- Since neither IL-1alpha nor IL-1beta depletions completely rescued the phenotype, we believe that IL-1alpha and IL-1beta have a similar and probably complementary role in FHF progression PMID: 28953903
- These results suggested that Streptococcus pneuomoniae PLY induces the influx of calcium in Streptococcus pneumoniae-infected macrophages, followed by calpain activation and subsequent IL-1alpha maturation and secretion. PMID: 28630064
- In response to chemically induced colitis, this microbial landscape promoted the release of IL-1alpha, which acted as a critical driver of colitis and colitis-associated cancer. PMID: 27775548
- our results suggest that mature IL-1alpha induced by hS100A7 is via RAGE-p38 MAPK and calpain-1 pathway in keratinocyte and this mechanism may play an important role during psoriasis. PMID: 28060905
- Il-1 signaling pathway has a key role in abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in mouse model of Kawasaki disease. PMID: 26941015
- endothelial cells were identified as the primary cellular source of G-CSF during OPC, which responded to IL-1alpha that was released from keratinocytes in the infected tissue. PMID: 27632536
- Key aspects of IL-1alpha biology and regulation especially with regard to inflammation are reviewed. Review. PMID: 27434011
- data suggested that pINSd needs IL-1R1 for inflammatory cytokine induction. Mouse embryo fibroblast cells of IL-1R1-deficient mice further confirmed that pINSd promotes immune responses through IL-1R1 PMID: 27226621
- IL-1alpha signaling and DNA damage is important for triggering a sterile inflammatory cascade . PMID: 26439902
- As a dual function cytokine, IL-1alpha may contribute to the induction of CHOP intracellularly, while IL-1alpha released from necrotic cells accelerates steatohepatitis via induction of inflammatory cytokines by neighboring cells. PMID: 26022690
- These data demonstrate that DC and macrophages display distinct patterns of cytokine regulation, particularly with respect to IL-1, as a consequence of cell-type specific differences in the physicochemical properties of the P2X(7)R PMID: 26068648
- Data suggest the role of stromal cell IL-1alpha and IL-1beta in Kawasaki disease vasculitis model. PMID: 26515418
- IL-1alpha and IL-36alpha form a self-amplifying inflammatory loop in vivo that in patients with insufficient counter regulatory mechanisms may become hyper-engaged and/or chronic PMID: 26203636
- IL-1alpha-positive cells were identified in the epithelium in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis. IL-1alpha was detected in the stool of colitic mice before IL-1beta. PMID: 25864926
- IL-1alpha acts as an alarmin essential for leukocyte recruitment and protective immunity against HSV-1 PMID: 25323745
- The aim of this study was to characterize the role of IL-1 in cellular responses of carbon nanotubes in cells from IL-1alpha/beta wild type (IL1-WT) mice. PMID: 25748835
- These findings do not support the previously suggested role of nuclear IL-1alpha in gene regulation of IL-1beta. PMID: 25748836
- the underlying mechanism by which AR influences AAA development is through IL-1alpha and transforming growth factor-beta1, and provides a potential new therapy to suppress/prevent AAA by targeting AR with ASC-J9. PMID: 26324502
- inhibition of this potentially important source of chronic inflammation in atherosclerosis requires blockade of interleukin-1alpha and not interleukin-1beta. PMID: 26139463
- The frustrated host response to Legionella pneumophila is bypassed by MyD88-dependent translation of pro-inflammatory cytokines. PMID: 25058342
- data suggest that central inhibition of IL-1alpha or Tox3 overexpression during the acute phase of a CNS insult may be an effective means for preventing the loss of neurological function PMID: 26224856
- Data (including date from studies in knockout mice) suggest that neutralization/deletion of Il1a reduces Il1b production and neutrophil infiltration in lung after inhalation exposure to silica nanoparticles. PMID: 25497724
- The controlled release of IL-1alpha could be a critical regulator during acute liver inflammation PMID: 25870999
- it appears the balance between TPO and IL-1alpha determines the MK cellular programming for thrombopoiesis in response to acute and chronic platelet needs. PMID: 25963822
- In acute lung injury, lipopolysaccharide induced alveolar macrophage necrosis via CD14 and the P2X7 receptor leading to interleukin-1alpha release. PMID: 25862090
- IL-1alpha induced the proliferation of CD11b(low) alveolar macrophages and differentiated these cells into CD11b(high) macrophages which perform critical phagocytic functions and organize granuloma. PMID: 25421226
- Data indicate that interleukin-1 cytokines IL-1alpha and IL-1beta are regulated by polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. PMID: 25371210
- IL-1 is a key mediator driving an innate immune response to inflammatory challenge in the mouse brain but is dispensable in extracerebral tissues including the lung and peritoneum. PMID: 25367678
- findings identify IL-1alpha as a crucial early danger signal triggering post-MI inflammation. PMID: 25505286
- Immune complexes inhibit IL-1 secretion and inflammasome activation. PMID: 25320279
- Selective deficiency of IL-1alpha in Kupffer cells reduces liver inflammation and expression of inflammatory cytokines, which may implicate Kupffer cell-derived IL-1alpha in steatohepatitis development. PMID: 24582082
- cigarette smoke-induced neutrophilia was dependent on IL-1alpha produced by alveolar macrophages and alveolar macrophages isolated from smoke-exposed mice were primed for excessive IL-1alpha production in response to bacterial ligands. PMID: 25092891
- tested the possible role of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1 in the age-related exhaustion of ovarian reserve using IL-1alpha and IL-1beta-KO mice PMID: 25114230
- This study documents distinct roles for IL-1alpha and IL-1beta in the response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection as a function of the type 3 secretion system effectors produced by the infecting strain. PMID: 25069982
- necroptosis caused the processing and release of IL-1alpha, and this was independent of IL-1beta processing and release PMID: 24790078
- IL-1 induces systemic inflammation and augments Streptococcal pneumoniae infection, atherosclerosis, and ischemic brain injury via platelet activation and microvascular coagulation. PMID: 24644058
- IL-1alpha was not released upon inflammasome activation unless significant cell damage occurred. PMID: 23684408
- haematopoietic-derived IL-1 is a key driver of ischaemic brain injury. PMID: 23519030
- In severe S. aureus bacteraemia in mice, TNF-alpha, IL-1alpha, and KC are biomarkers predicting fatal outcome of infection. PMID: 23520553
- Our results establish IL-1alpha as a critical initiator of the inflammatory response to L. pneumophila PMID: 23686480
- discovery of a novel inflammatory circuit in which RIP1-mediated IL-1alpha secretion in response to deregulated SHP-1 activity triggers an inflammatory destructive disease that proceeds independently of inflammasomes and programmed necrosis PMID: 23708968
- Results suggest importance of IL-1R1/IL-1alpha to the recruitment and activation of dendritic cells in response to cigarette smoke exposure. PMID: 22992200
- ERalpha-regulated repression of TNFalpha and IL1alpha is important for lumen formation and maintenance. PMID: 22328525
- Allergic sensitization to HDM was abolished in vivo when IL-1alpha, GM-CSF, or IL-33 was neutralized. PMID: 22802353
- Autophagy has a potentially pivotal role to play in the induction and regulation of inflammatory responses by innate immune cells, largely driven by IL-1 and its consequential effects on IL-23 secretion. PMID: 22972933
- Vascular wall resident cells are the main targets for the pro-atherogenic effects of bone marrow-derived IL-1 through IL-1R1, partly by induction of adhesion and chemotactic molecules in endothelial cells. PMID: 22236482
- This study demonstrated here in in vivo experiments that IL-1 exacerbates the effects of SCI by accentuating the impact of the inflammatory responses. PMID: 22483094
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:IL-1 family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:16175
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000028882
UniGene: Mm.15534
Most popular with customers
-
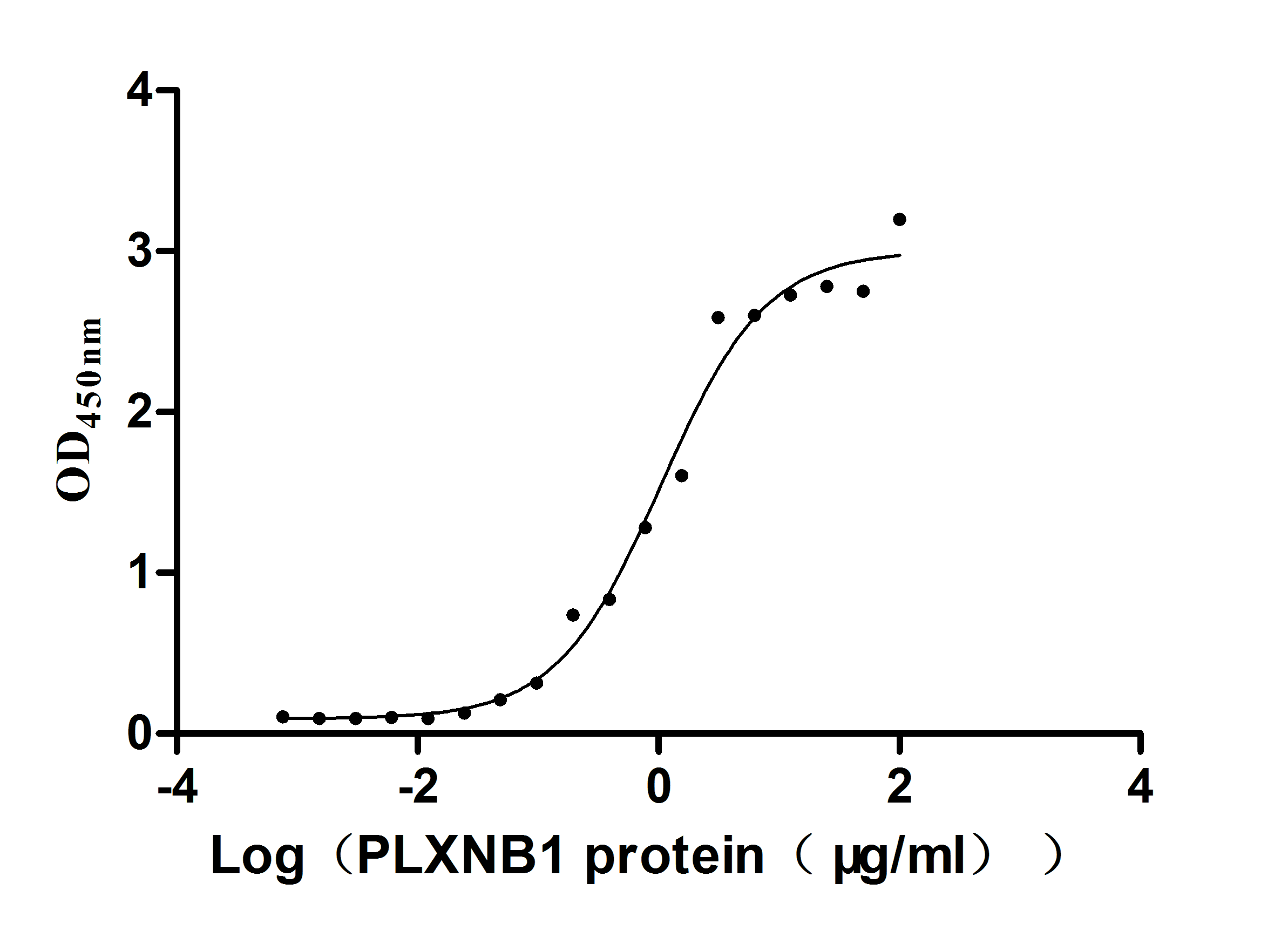
Recombinant Human Plexin-B1 (PLXNB1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
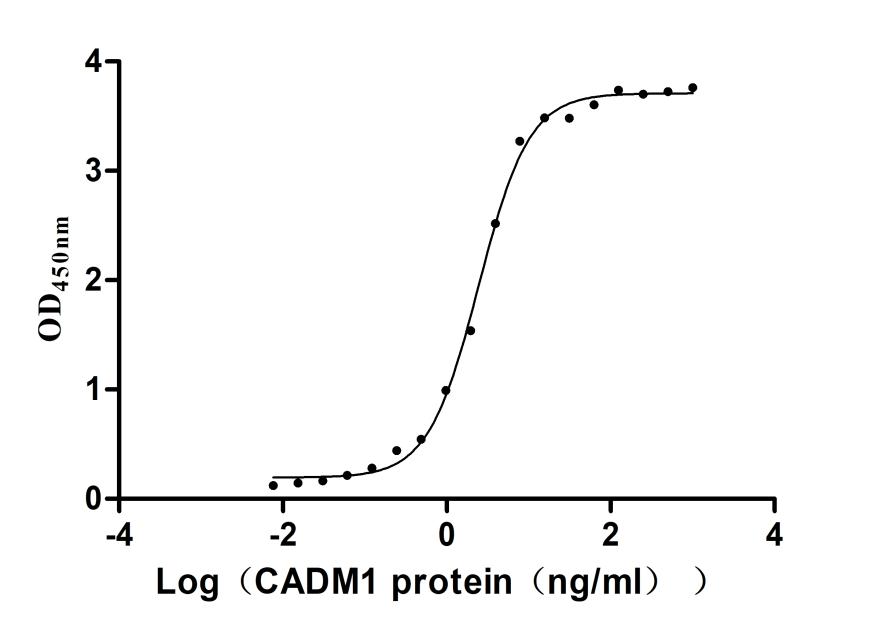
Recombinant Mouse Cell adhesion molecule 1 (Cadm1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
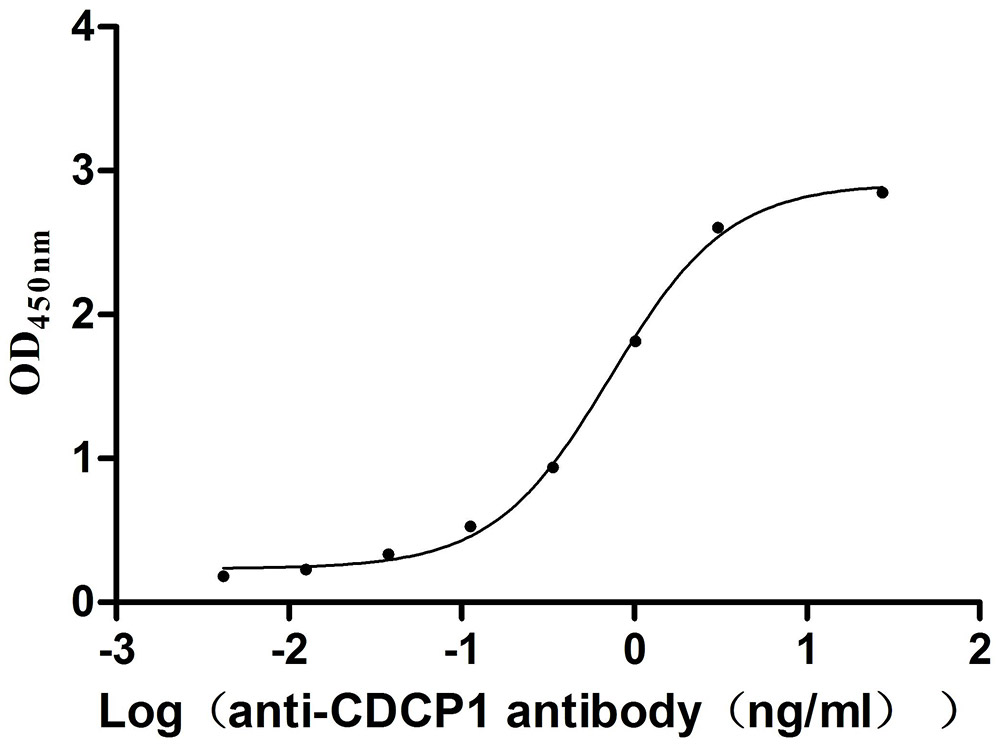
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
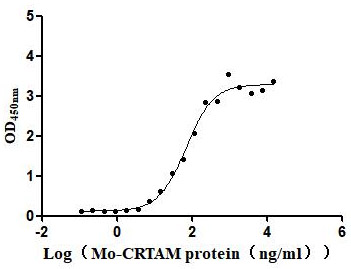
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
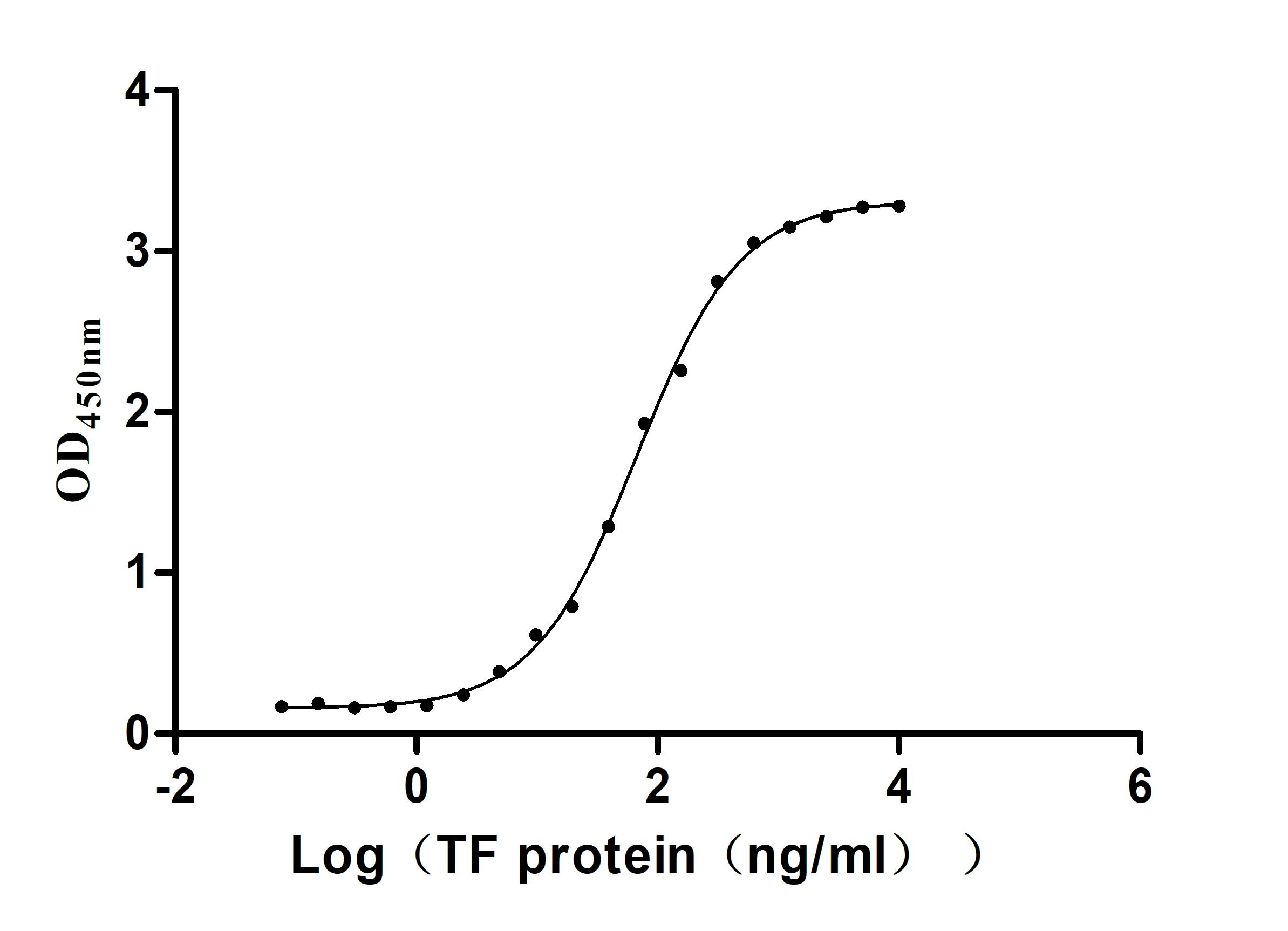
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
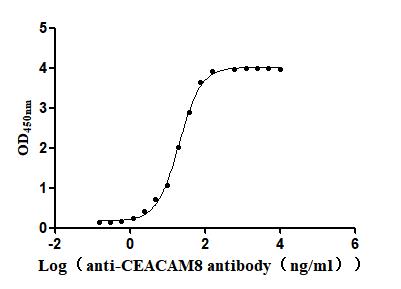
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)