SIGIRR:一个新的信号受体TIR超家族成员,机体炎症、免疫反应的“刹车”分子!
日期:2023-06-28 15:04:16
近期,Seminars in Immunology杂志发表了一篇题为"IL-1R8: A molecular brake of anti-tumor and anti-viral activity of NK cells and ILC"的文章 [1],该报道揭示IL-1R8/SIGIRR是调节NK细胞和ILC对肿瘤和病毒免疫反应的重要"刹车"分子。值得关注的是,SIGIRR是一种新发现的Toll-IL-1R(TIR)信号受体超家族成员。ILRs(Interleukin-1 receptors)和TLRs(Toll-like-receptors)亚家族均属于TIR家族。
大量研究已证实SIGIRR负调控ILRs和TLRs炎症信号通路,在感染性疾病、肿瘤及自身免疫疾病起调控相关炎症反应的作用。因此,SIGIRR作为一种新型的抗炎分子,可用来预测炎症和免疫相关的疾病的发展。在临床药物研究中,SIGIRR也被寄予厚望,有望展现出重要的价值。目前,SIGIRR作为TIR超家族成员,成为机体炎症和免疫反应研究的重要关注靶点!
1. 什么是Toll-IL-1R(TIR)超家族?
Toll-IL-1R(TIR)是一个新发现的信号受体超家族。1997年,Medazhitov等首次发现与果蝇同源的人的Toll样蛋白,命名为Toll样受体(Toll-like-receptors,TLRs)。由于它与白细胞介素1受体(Interleukin-1 receptors,IL-1Rs)在结构、功能、信号转导通路上的诸多相似,所以被归类为一个大的信号受体家族—Toll-IL-1R(TIR)家族 [2]。TLRs和IL-1Rs是重要的天然免疫受体,可以启动天然免疫反应,它们的共同特征是胞质区有个名为Toll/IL-1R(TIR)结构域的保守序列。目前的研究发现人TIR超家族至少包括3个不同的群体:Toll 样受体家族、IL-1R 家族、My D88(图1) [3]。
TLRs亚家族成员包括多种受体,如TLR1,TLR2,TLR3,TLR4,TLR5,TLR6,TLR7,TLR8和TLR9等。ILRs亚家族包括受体IL-1R1,IL-18R,T1/ST2,IL-1Rrp2和IL-1,IL-18,IL-33的辅助蛋白(Ac P)(IL-1RAcP,IL-18RAcP,IL-1RAcPb),还有其它的IL-1家族成员(IL-1F6,IL-1F8,IL-1F9)。许多研究均证实,TIR信号受体家族的成员在机体对抗外来病原体的天然免疫中起到了重要的作用。在TIR家族中都存在一些孤儿受体,它们的配体和功能仍然未知,如SIGIRR [1-3]。
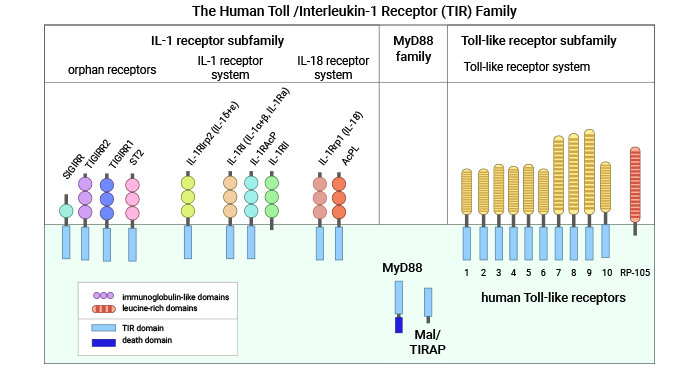
图1. 人Toll-IL-1R(TIR)超家族 [3]
2. 什么是SIGIRR?
2.1 SIGIRR的结构
单免疫球蛋白白细胞介素1受体相关蛋白(Single Ig IL-1-related receptor,SIGIRR),又称白细胞介素1受体8(Interleukin-1 receptor8,IL-1R8),于1999年由Thomassen等首次发现并命名,属于TIR超家族。SIGIRR基因位于11号染色体,该蛋白含有一个单一Ig胞外结构域(aa17-112),跨膜结构域(aa117-139),胞内TIR保守结构域(aa166-305)和一个95aa长度的胞内尾区(图2)[4-7]。
SIGIRR和IL-1R、TLRs结构相似,但SIGIRR结构特殊性表现为:SIGIRR只有1个Ig胞外结构域,而IL-1R有3个;SIGIRR胞内的TIR结构域缺乏传递信号所必须的氨基酸Ser447和Tyr536。由于SIGIRR独特的分子结构,所以SIGIRR在炎症反应中不能激活下游炎症信号通路 [4-7]。
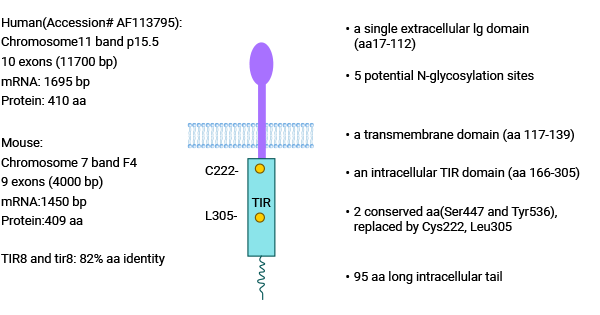
图2. SIGIRR的结构 [4]
2.2 SIGIRR的表达
SIGIRR广泛表达于多种上皮组织,包括肺脏、肝脏、甲状旁腺、胃肠道和肾脏等组织,其中以胃肠道和肾脏的上皮细胞中含量最为丰富。炎症状态下,SIGIRR表达水平的降低与p38活化增加和泛素化酶USP13表达降低有关。此外,当受到内毒素LPS刺激时,USP13表达下调,SIGIRR的泛素化水平增加,其稳定性降低。SIGIRR的结构和表达模式在人类的进化中都趋于保守。SIGIRR在机体大部分组织器官上的广泛性表达为其负性炎症调控机制的发挥奠定了组织基础 [8-10]。
2.3 SIGIRR的功能
SIGIRR是一种孤儿受体,其配体目前尚未完全阐明,但有报道称IL-1F5在神经胶质细胞中是其配体。SIGIRR具有抑制IL-1家族成员相关T细胞分化的信号传导及TLRs介导的激活作用的能力。这种对ILRs和TLRs家族成员信号通路的抑制能力,使得SIGIRR在炎症、肿瘤相关性炎症和自身免疫中起着至关重要的调节作用。SIGIRR的负性调节作用已在不同条件下的小鼠身上得到强有力的证明,并且支持SIGIRR与人类疾病相关的临床数据也在不断出现。因此,SIGIRR在炎症免疫反应中的调节作用具有重要的临床意义 [11-13]。
3. SIGIRR对TLRs和IL-1Rs信号通路的负向调节机制
SIGIRR具有独特的结构,与TIR超家族成员的功能完全相反。在许多炎性相关疾病中,SIGIRR表现出负向调控TLRs和IL-1Rs信号通路的作用,阻碍炎性信号传递。该调控机制复杂,影响多个下游靶点,包括IL-1R1、IL-1R5/IL-18Rα、IL-1R4/ST2、TLR4、TLR7、TLR9、TLR3和TLR1/2的活化,并抑制TIR结构域诱导的NF-κB和JNK活化。目前尚未完全阐明SIGIRR如何调节TLR/IL-1R信号通路的活化机制 [14-16]。
SIGIRR的抑制作用主要涉及IL-1诱导的信号传导、Pam3Cys诱导的TLR2信号通路、内毒素(1ipopolysacharride, LPS)与Cp G DNA诱导的TLR4和TLR9,以及TLR3和TLR1/2信号通路的活化。报道显示,SIGIRR可能通过两种机制实现其作用:一是胞外Ig样区可能干扰IL-1RI和IL-1RAcP形成二聚体;二是胞内TIR结构域干扰TLR/IL-1R与衔接蛋白结合如My D88、IRAK及TRAF6等,从而抑制核转录因子NF-κB和JNK等的激活(图3)[17-19] 。
三维模型表明,TIR结构域尤其是其BB-环可以与MyD88二聚体形成竞争,从而抑制信号。除了MyD88依赖的途径外,SIGIRR还可以通过阻断TRAM二聚化的方式来干扰TRIF的信号传导。这种作用机制可以影响TLR3的信号传导以及TLR4-TRAM和TRIF-TRAM的相互作用。此外,SIGIRR还可调节Th17细胞和NK细胞中的JNK和mTOR磷酸化以及肠上皮细胞中由IL-1或TLR激动剂驱动的mTOR磷酸化 [20-22]。
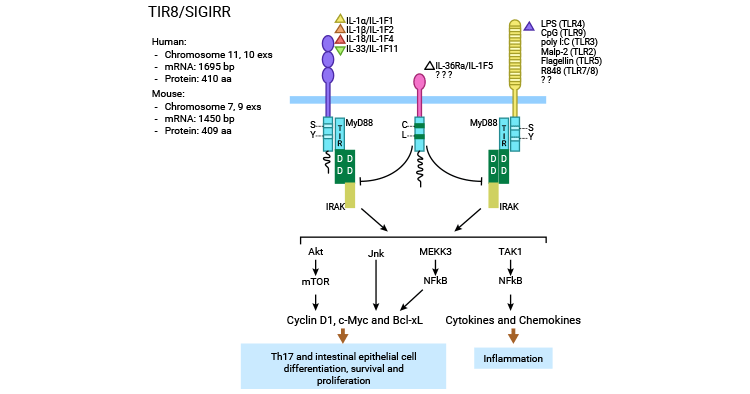
图3. SIGIRR的信号调节机制 [22]
4. SIGIRR在炎症免疫相关性疾病中的作用
近年来,SIGIRR的负性调控作用在炎症免疫相关性疾病的研究中取得了诸多进展。SIGIRR可在感染性疾病中,防止因过度的炎症反应而造成的组织损伤,促进感染性疾病的恢复;在自身免疫性疾病中,降低疾病的发生风险以及严重程度;在肿瘤中,通过控制肿瘤相关炎症反应,抑制肿瘤的发生和发展。此外,SIGIRR可能在协助肿瘤细胞扩散和转移时也发挥了一定的作用。
4.1 SIGIRR和感染性疾病
SIGIRR表达异常与机体组织炎症损伤的严重程度相关。例如,在结核分枝杆菌感染中,SIGIRR基因缺陷小鼠表现出过度的炎症反应和死亡率升高,这是由于SIGIRR缺乏导致其对IL-1和TNF-α抑制效应的解除 [23-24]。
在其他感染模型中,如铜绿假单胞菌、白色念珠菌或烟曲霉菌等引起的急性肺部感染,以及大肠杆菌引起的尿路感染,低表达或沉默的SIGIRR会导致机体易感性增加、促炎细胞因子过度释放和死亡率增加 [13]。此外,在SIGIRR缺陷小鼠中,β-淀粉样肽诱导的突触和认知功能障碍更为严重,但上调SIGIRR表达可以缓解Abeta介导的海马突触活动长时程增强(LTP)损伤 [17, 25]。
4.2 SIGIRR和自身免疫疾病与过敏反应
ILRs和TLRs参与了自身免疫性疾病和过敏性炎症的病理生理机制。其中,IL-1作为Th17分化和活化的关键因子,在多种自身免疫性疾病中发挥着重要作用。SIGIRR作为抑制剂,可控制IL-1依赖性Th17的分化、扩增和效应功能,并抑制T细胞中多种IL-1依赖的信号通路发挥作用,特别是Th17增殖相关的mTOR通路 [21, 25]。
缺乏SIGIRR会导致自身免疫性疾病风险增加,且与疾病严重程度呈正相关。在过敏性炎症中,SIGIRR的作用尚存在争议。在IL-33依赖的气道过敏性炎症中,缺乏SIGIRR的小鼠表现为肺炎症、脾肿大以及血清IL-5和IL-13水平升高和Th2细胞因子的产生增加 [26-27]。
4.3 SIGIRR和肿瘤
炎症微环境可以促进肿瘤的发展,而肿瘤和炎症之间的关联受到内源性恶性肿瘤遗传易感基因的激活和转录,以及外源性炎症或感染的影响。这些作用机制都与核转录因子NF-κB、信号转导与转录激活因子3(STAT3)和缺氧诱导因子-1α(HIF-1α)的激活有关。
SIGIRR是一种可以抑制肿瘤相关炎症反应的因子,其缺失会影响炎症相关肿瘤的发生和发展。在结肠癌模型中,SIGIRR缺陷小鼠的结肠组织中会大量激活NF-κB信号,并通过影响对细胞增殖和生存至关重要的靶基因(如Cyclin D1和Bcl-xL)的表达来促进肿瘤形成 [28-29]。
同时,在这些小鼠的结肠组织中还检测到了多种细胞因子(如TNF-α、IL-6和IFN-γ)和趋化因子(如MIP-2、MCP-1和CXCL1/KC)的表达增加。在肿瘤发展过程中,肿瘤细胞会采取多种方式来调节炎症反应以避免被机体免疫系统发现和消灭 [28-29]。
SIGIRR可通过抑制IL-18通路影响NK细胞分化和功能成熟,在二乙基亚硝胺诱导的肝癌模型和小鼠乳腺癌模型中,均显示了SIGIRR对于肿瘤发展的抑制作用 [1, 30-32]。SIGIRR作为免疫与炎症的负性调控因子,在肿瘤中的作用机制有待进一步阐明(图4) [1]。
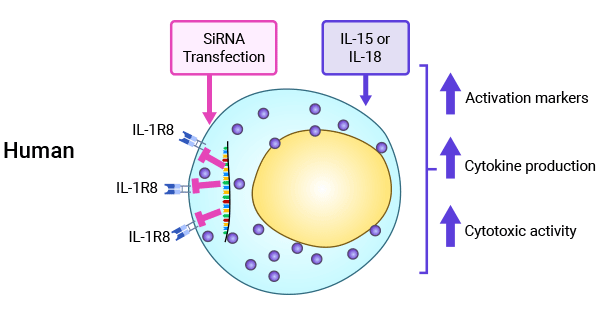
图4. SIGIRR(IL-1R8)在调控NK细胞功能中的重要性 [1]
5. SIGIRR的临床药物研究前景
近年来,SIGIRR作为TIR家族致炎信号通路中具有鲜明特点的负调控分子,在感染性疾病、自身免疫性疾病、肿瘤等多种炎症免疫相关疾病中取得了重要进展,展现出了重要的临床应用价值。TIRs介导的信号传导在抵抗病原微生物的固有免疫中具有重要作用,但其过度激活引起的炎性因子大量释放,则使机体的免疫稳态失衡。
SIGIRR在炎症免疫反应中的负性调控,可维持TIR超家族所介导下游信号通路平衡。ILRs和TLRs均属于TIR超家族。TIR成员在炎症或免疫反应相关疾病中的正性促进作用已被广泛认知,但其平衡调控研究却鲜见报道。因此,SIGIRR作为机体炎症、免疫反应的“刹车”分子,拥有巨大的临床研究价值!
为鼎力协助各药企针对SIGIRR在感染性疾病、自身免疫性疾病、肿瘤等多种炎症免疫相关疾病临床中的研究,CUSABIO推出SIGIRR蛋白产品(Code:CSB-MP743558HU),助力您在SIGIRR机制方面的研究或其潜在临床价值的探索。
Recombinant Human Single Ig IL-1-related receptor(SIGIRR),partial
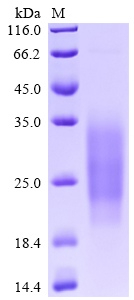
High purity was validated by SDS-PAGE. (Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
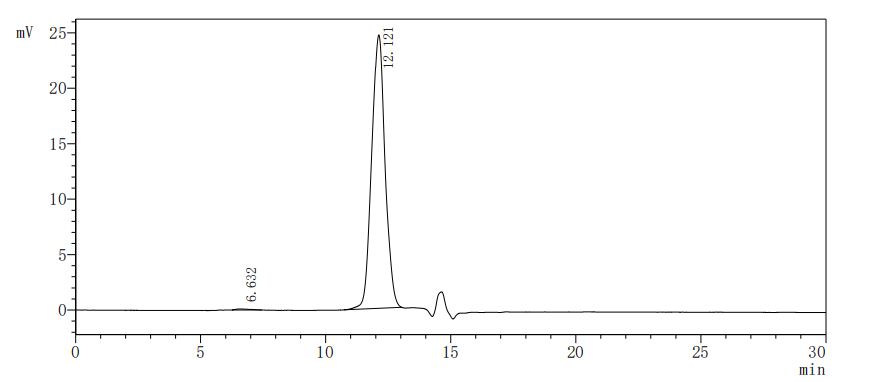
The purity of Human SIGIRR was greater than 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC.
参考文献:
[1] Mariotti F R, Supino D, Landolina N, et al. IL-1R8: A molecular brake of anti-tumor and anti-viral activity of NK cells and ILC[C]//Seminars in Immunology Academic Press, 2023, 66: 101712.
[2] Carty M, Kearney J, Shanahan K A, et al. Cell survival and cytokine release after inflammasome activation is regulated by the Toll-IL-1R protein SARM[J]. Immunity, 2019, 50(6): 1412-1424. e6.
[3] Martin M U, Wesche H. Summary and comparison of the signaling mechanisms of the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor family[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research, 2002, 1592(3): 265-280.
[4] Huang Xun. Experimental study of SIGIRR regulating HMGB1-induced inflammatory response of alveolar epithelial cells A549. Diss. Fourth Military Medical University, 2012.
[5] Thomassen E, Renshaw B R, Sims J E. Identification and characterization of SIGIRR, a molecule representing a novel subtype of the IL-1R superfamily[J]. Cytokine, 1999, 11(6): 389-399.
[6] Lech M, Skuginna V, Kulkarni O P, et al. Lack of SIGIRR/TIR8 aggravates hydrocarbon oil-induced lupus nephritis[J]. The Journal of Pathology: A Journal of the Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland, 2010, 220(5): 596-607.
[7] Drexler S K, Kong P, Inglis J, et al. SIGIRR/TIR-8 is an inhibitor of toll-like receptor signaling in primary human cells and regulates inflammation in models of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis & Rheumatism, 2010, 62(8): 2249-2261.
[8] Li L, Wei J, Li S, et al. The deubiquitinase USP13 stabilizes the anti-inflammatory receptor IL-1R8/Sigirr to suppress lung inflammation[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 45: 553-562.
[9] Li L, Wei J, Suber T L, et al. IL-37-induced activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β promotes IL-1R8/Sigirr phosphorylation, internalization, and degradation in lung epithelial cells[J]. Journal of cellular physiology, 2021, 236(8): 5676-5685.
[10] Wang Q, Sun Z, Xia W, et al. Role of USP13 in physiology and diseases[J]. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 2022, 9: 977122.
[11] Garlanda C, Anders H J, Mantovani A. TIR8/SIGIRR: an IL-1R/TLR family member with regulatory functions in inflammation and T cell polarization[J]. Trends in immunology, 2009, 30(9): 439-446.
[12] Bertilaccio M T S, Simonetti G, Dagklis A, et al. Lack of TIR8/SIGIRR triggers progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in mouse models[J]. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology, 2011, 118(3): 660-669.
[13] Riva F, Bonavita E, Barbati E, et al. TIR8/SIGIRR is an interleukin-1 receptor/toll like receptor family member with regulatory functions in inflammation and immunity[J]. Frontiers in immunology, 2012, 3: 322.
[14] Heinig K, Sperandio M. Interleukin-1R8: balancing inflammation and hemostasis in platelets[J]. Cardiovascular Research, 2016, 111(4): 307-309.
[15] Molgora M, Barajon I, Mantovani A, et al. Regulatory role of IL-1R8 in immunity and disease[J]. Frontiers in immunology, 2016, 7: 149.
[16] Giannoudaki E, Stefanska A M, Lawler H, et al. SIGIRR negatively regulates IL-36-driven psoriasiform inflammation and neutrophil infiltration in the skin[J]. The Journal of Immunology, 2021, 207(2): 651-660.
[17] Costello D A, Carney D G, Lynch M A. α-TLR2 antibody attenuates the Aβ-mediated inflammatory response in microglia through enhanced expression of SIGIRR [J]. Brain, behavior, and immunity, 2015, 46: 70-79.
[18] Qin J, Qian Y, Yao J, et al. SIGIRR inhibits interleukin-1 receptor- and toll-like receptor 4-mediated signaling through different mechanisms[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2005, 280(26): 25233-25241.
[19] Zhang C, Wu X, Zhao Y, et al. SIGIRR inhibits toll-like receptor 4, 5, 9-mediated immune responses in human airway epithelial cells[J]. Molecular biology reports, 2011, 38: 601-609.
[20] Zhao R, Song C, Liu L, et al. Single immunoglobulin and Toll-interleukin-1 receptor domain containing molecule protects against severe acute pancreatitis in vitro by negatively regulating the Toll-like receptor-4 signaling pathway: A clinical and experimental study[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports, 2020, 22(4): 2851-2859.
[21] Gulen M F, Kang Z, Bulek K, et al. The receptor SIGIRR suppresses Th17 cell proliferation via inhibition of the interleukin-1 receptor pathway and mTOR kinase activation[J]. Immunity, 2010, 32(1): 54-66.
[22] Jiang Keguo. The regulation of SIGIRR on the activation of NF-κB in human renal tubular epithelial cells, the feedback regulation of NF-κB on SIGIRR and the preliminary study on the mechanism of SIGIRR regulation of EMT. Diss. Anhui Medical University, 2015.
[23] Horne D J, Randhawa A K, Chau T T H, et al. Common polymorphisms in the PKP3-SIGIRR-TMEM16J gene region are associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis [J]. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 2012, 205(4): 586-594.
[24] Garlanda C, Di Liberto D, Vecchi A, et al. Damping excessive inflammation and tissue damage in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by Toll IL-1 receptor 8/single Ig IL-1-related receptor, a negative regulator of IL-1/TLR signaling[J]. The Journal of Immunology, 2007, 179(5): 3119-3125.
[25] Costello D A, Watson M B, Cowley T R, et al. Interleukin-1α and HMGB1 mediate hippocampal dysfunction in SIGIRR-deficient mice[J]. Journal of Neuroscience, 2011, 31(10): 3871-3879.
[26] Martin M U. Special aspects of interleukin-33 and the IL-33 receptor complex[C]//Seminars in immunology. Academic Press, 2013, 25(6): 449-457.
[27] Lunding L, Webering S, Vock C, et al. IL-37 requires IL-18Rα and SIGIRR/IL-1R8 to diminish allergic airway inflammation in mice[J]. Allergy, 2015, 70(4): 366-373.
[28] Xiao H, Gulen M F, Qin J, et al. The Toll-interleukin-1 receptor member SIGIRR regulates colonic epithelial homeostasis, inflammation and tumorigenesis[J]. Immunity, 2007, 26(4): 461-475.
[29] Liu J, Chen Y, Liu D, et al. Ectopic expression of SIGIRR in the colon ameliorates colitis in mice by downregulating TLR4/NF-κB overactivation[J]. Immunology letters, 2017, 183: 52-61.
[30] Che Y Y, Shi X, Zhong X D, et al. Resveratrol prevents liver damage in MCD-induced steatohepatitis mice by promoting SIGIRR gene transcription[J]. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 2020, 82: 108400.
[31] Molgora M, Bonavita E, Ponzetta A, et al. IL-1R8 is a checkpoint in NK cells regulating anti-tumour and anti-viral activity[J]. Nature, 2017, 551(7678): 110-114.
[32] Bodaszewska-Lubas M, Liao Y, Zegar A, et al. Dominant-Negative Form of SIGIRR: SIGIRRΔE8 Promotes Tumor Growth Through Regulation of Metabolic Pathways[J]. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research, 2022, 42(9): 482-492.











