Recombinant Mouse Apolipoprotein C-I (Apoc1)
In Stock-
货号:CSB-CF001930MO
-
规格:¥5028
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Apoc1; Apolipoprotein C-I; Apo-CI; ApoC-I; Apolipoprotein C1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
来源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
分子量:12.5 kDa
-
表达区域:27-88aa
-
氨基酸序列APDLSGTLESIPDKLKEFGNTLEDKARAAIEHIKQKEILTKTRAWFSEAFGKVKEKLKTTFS
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
问答及客户评论
靶点详情
-
功能:Inhibitor of lipoprotein binding to the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor, LDL receptor-related protein, and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) receptor. Associates with high density lipoproteins (HDL) and the triacylglycerol-rich lipoproteins in the plasma and makes up about 10% of the protein of the VLDL and 2% of that of HDL. Appears to interfere directly with fatty acid uptake and is also the major plasma inhibitor of cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP). Modulates the interaction of APOE with beta-migrating VLDL and inhibits binding of beta-VLDL to the LDL receptor-related protein. Binds free fatty acids and reduces their intracellular esterification.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- APOC1 expression induces glomerulosclerosis, potentially by increasing the cytokine response in macrophages. PMID: 27976371
- Apolipoprotein C-I was significantly increased in obese mice plasma. PMID: 22404376
- The absence of ApoC-I results in impaired memory functions, which is, together with previous data, suggestive of an important, bell-shaped gene-dose dependent role for ApoC-I in appropriate brain functioning PMID: 21157034
- Data show that the stimulating effect of apoCI on the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)response resembles that of LPS-binding protein (LBP) and depends on CD14/ Toll-like receptor 4 signaling. PMID: 20335569
- regulated expression of gene cluster in macrophages PMID: 12032151
- present observations provide direct support for a potent specific inhibition of CETP by plasma apoCI in vivo PMID: 12070157
- The apoC-I content of lipoprotein remnants may serve as an early marker of coronary artery disease risk. PMID: 12231568
- TR4 can also regulate apolipoprotein E, C-I, and C-II gene expression via the TR4 response element within the hepatic control region PMID: 12954636
- apoC-I is a potent inhibitor of LPL-mediated triglyceride lipolysis PMID: 15576844
- irrespective of receptor-mediated remnant clearance by the liver, liver-specific expression of recombinant human apoCI causes hypertriglyceridemia in the absence of the VLDLr and apoCIII in mice PMID: 16478678
- Endogenous apoC-I increases hyperlipidemia in apoE-knockout mice by stimulating VLDL production and inhibiting LPL. PMID: 16537968
- Knockout mice show significant increases in the hepatic content of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides and in biliary cholesterol concentration. PMID: 17053273
- Systemic apoCI increases atherosclerosis, probably by inducing hyperlipidemia, in the absence of ApoE PMID: 17320883
- Data suggest that apoC-I binds free fatty acids (FFA), thereby reducing the blood FFA for uptake by cells, and this mechanism can serve as an additional mechanism for the resistance to obesity and the cutaneous abnormalities of APOC1(+/+) mice. PMID: 17339654
- apoCI is crucially involved in lipopolysaccharide(LPS)-induced atherosclerosis in apoe-/- mice, which mainly relates to an increased inflammatory response toward LPS PMID: 17967778
- apoCI is a novel inhibitor of the scavenger receptor BI -mediated uptake of HDL cholesterol by hepatocytes; apoCI is a determinant for the plasma levels and size of HDL in vivo. PMID: 18992221
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Apolipoprotein C1 family
-
组织特异性:Adult and fetal liver.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:11812
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000045571
UniGene: Mm.182440
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-18.2 (CLDN18.2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant DT3C (Diphtheria toxin & spg 3C domain) for Antibody Internalization Assay (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: N/A

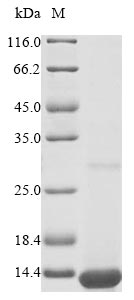

-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)