Recombinant Mouse Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 10 (Tnfsf10)
-
货号:CSB-YP023985MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP023985MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP023985MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP023985MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP023985MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Tnfsf10; Trail; Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 10; TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; Protein TRAIL; CD antigen CD253
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Extracellular domain
-
表达区域:39-291
-
氨基酸序列YMYFTNEMKQLQDNYSKIGLACFSKTDEDFWDSTDGEILNRPCLQVKRQLYQLIEEVTLR TFQDTISTVPEKQLSTPPLPRGGRPQKVAAHITGITRRSNSALIPISKDGKTLGQKIESW ESSRKGHSFLNHVLFRNGELVIEQEGLYYIYSQTYFRFQEAEDASKMVSKDKVRTKQLVQ YIYKYTSYPDPIVLMKSARNSCWSRDAEYGLYSIYQGGLFELKKNDRIFVSVTNEHLMDL DQEASFFGAFLIN
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF10A/TRAILR1, TNFRSF10B/TRAILR2, TNFRSF10C/TRAILR3, TNFRSF10D/TRAILR4 and possibly also to TNFRSF11B/OPG. Induces apoptosis. Its activity may be modulated by binding to the decoy receptors TNFRSF10C/TRAILR3, TNFRSF10D/TRAILR4 and TNFRSF11B/OPG that cannot induce apoptosis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- TRAIL protects against insulin resistance, NAFLD and vascular inflammation. Increasing TRAIL levels may be an attractive therapeutic strategy, to reduce features of diabetes, as well as liver and vascular injury, so commonly observed in individuals with NAFLD. PMID: 28507343
- Isolated highly-pure population of DcR2-positive renal tubular epithelial cells was isolated by MACS, which was confirmed to comprise of active senescent RTECs based on the cell cycle phase. PMID: 28461078
- Data suggest that the CXCL9-CXCR3 axis plays a pivotal role in the liver-specific distribution of TRAIL+ NK cells in mice. PMID: 29088306
- this study shows pathogenic role for TRAIL in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease PMID: 26555706
- pCLE results indicated that endomicroscopy could effectively quantify injected MSCs that homed to subcutaneous xenograft tumor sites in vivo and correlated well with the therapeutic effects of the TRAIL gene PMID: 27617958
- the aim of this study is to elucidate the role of TRAIL during rhinovirus (RV) infection in vivo. PMID: 27836899
- Tnfsf10 expression is increased in eosinophilic esophagitis. Tnfsf10(-/-) mice were largely protected from esophageal fibrosis and eosinophilic inflammation. PMID: 27742702
- Diabetes significantly increased OPG and the OPG/TRAIL ratio expression in the aorta, while dyslipidemia was the major determinant of the changes observed in the heart, where it significantly increased OPG and reduced TRAIL expression, thus increasing cardiac OPG/TRAIL ratio. PMID: 28070143
- Membrane-proximal TRAIL species are incapable of inducing short circuit apoptosis signaling: Implications for drug development and basic cytokine biology.( PMID: 26935795
- TRAIL can promote angiogenesis following hindlimb ischemia in vivo via NOX4/eNOS/nitric oxide signaling. PMID: 26572549
- PARP1 acts as a prominent upstream regulator of high mobility group box 1-mediated autophagy and maintains a homeostatic balance between apoptosis and autophagy, which provides new insight into the mechanism of TNFSF10 resistance PMID: 25607248
- Data suggest that Socs3 (suppressor of cytokine signaling 3) plays critical negative role in regulation of Trail expression in endoplasmic reticulum stress in macrophages via Jun N-terminal kinase/AP-1 transcription factor signaling. PMID: 25827060
- These findings indicate that acute fasting enhances TRAIL-mediated liver natural killer cell activity against neoplastic cells through upregulation of heat shock protein 70. PMID: 25356750
- These results demonstrated that TRAIL plays a deleterious role in acute kidney injury pathogenesis induced by scald burns PMID: 25031778
- TRAIL-deficiency in ApoE(-/-) mice exacerbates nephropathy and insulin resistance PMID: 24667560
- TRAIL induces apoptosis in tissue-infiltrating neutrophils thereby protecting organs from sepsis-induced injury. PMID: 24887152
- Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand translates neonatal respiratory infection into chronic lung disease. PMID: 24045576
- These results suggest that TRAIL inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis by increasing caspase-8 activity and subsequently decreasing non-apoptotic signaling functions of procaspase-8, without inducing caspase-3 activation and endothelial cell cytotoxicity. PMID: 24097299
- expression of TRAIL on natural killer cells is protective in a murine model of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury through modulation of natural killer cell cytotoxicity and NK cell differentiation PMID: 24804996
- TRAIL signaling and cell death in the immature central nervous system after hypoxia-ischemia and inflammation PMID: 24509861
- The extracellular domain of Fn14 fused to the extracellular domain of the TRAIL ligand is designed to modulate the immune system as an anti-inflammatory agent. PMID: 23497038
- oncogene metadherin modulates the apoptotic pathway based on the tumor necrosis factor superfamily member TRAIL (Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand) in breast cancer PMID: 23408429
- Data indicate that TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand knockout mice (TRAIL -/-) showed significantly decreased lung bacterial clearance and survival in response to Streptococcus pneumoniae. PMID: 23071253
- Data indicate the importance of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) pathogenesis and suggest its potential as a therapeutic target to direct future translational therapies PMID: 23071256
- data demonstrate that TRAIL induces osteoclastic differentiation via a TRAF-6 dependent signaling pathway PMID: 22719861
- CD8+ T cells use TRAIL to restrict West Nile virus pathogenesis by controlling infection in neurons. PMID: 22740407
- findings shed light on the possible anti-adipogenic and anti-inflammatory effects of TRAIL and open new therapeutic possibilities against obesity, systemic inflammation and T2DM PMID: 22616837
- Epirubicin enhances the antiarthritic effect of rAAV2/5-TRAIL and that combination treatment might be an important therapeutic alternative, with practical significance for rheumatoid arthritis. PMID: 22131069
- It was shown for the first time that TRAIL deficiency promotes numerous features of diabetes typical of human disease, and are associated with reduced insulin and pancreatic inflammation/apoptosis. PMID: 21965021
- TRAIL strongly synergizes with APAP in inducing cell death in hepatocyte-like cells lines and primary hepatocyte. PMID: 21654829
- the tumoricidal activity of CnB-activated peritoneal macrophages is partially dependent on TRAIL. PMID: 22116828
- TRAIL regulates the magnitude of the influenza A virus (IAV)-specific CD8 T cell response during a clinically significant IAV infection to decrease the chance for infection-induced immunopathology. PMID: 21940678
- TRAIL-deficient mice had an enhanced inflammatory response with increased neutrophil numbers and reduced neutrophil apoptosis PMID: 21562052
- Data suggest that deficiency of TRADD sensitizes cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, and that enhanced cell death in TRADD(-/-) MEFs is associated with defective NF-kappaB activation. PMID: 21627969
- study concludes that TRAIL attenuates plaque size at early stages of atherosclerosis PMID: 21324463
- TRAIL and osteoprotegerin are expressed in atherosclerotic plaques in a calcification-prone mouse model PMID: 21426505
- Data show that the number of tumors observed in TRAIL transgenic animals was significantly lower than in the control animals, and the lesions observed were mostly benign. PMID: 21463519
- is not required for the development of peripheral lymphopenia or granuloma necrosis during infection with Mycobacterium avium PMID: 21470210
- resveratrol can enhance the apoptosis-inducing potential of TRAIL by activating FKHRL1 and its target genes PMID: 21209944
- CD8-positive regulatory T cells generated after anterior chamber injection of antigen via the retro-orbital plexus enforce systemic tolerance in a TRAIL-dependent manner to inhibit inflammation in the eye. PMID: 21169546
- TRAIL suppresses autoimmunity by two mechanisms: the inhibition of Th1 cells and the promotion of Tregs PMID: 20921531
- extrinsic and intrinsic pathways, via Trail/Dr5 and Puma respectively, could be engaged in distinct subpopulations of spermatogonia PMID: 20711434
- sTRAIL is inversely associated with the mortality risk in chronic kidney disease patients. PMID: 20190248
- Data show that in Abelson cells, the inhibition of both NF-kappaB and FoxO3a activity is required for suppression of TRAIL transcription and maintenance of the transformed state. PMID: 20213318
- TRAIL- and GITRL-activated pathways synergise in the development of SCI-related inflammatory damage. PMID: 20107429
- apoptotic cells generated during sepsis induced a CD8+ regulatory T cell that suppressed delayed-type hypersensitivity by TRAIL production PMID: 20483771
- results indicate that cells that survive TRAIL treatment may do so by activation of a TAK1-NF-kappaB pathway that drives expression of cFlipL, and suggest that TAK1 may be a good target for overcoming TRAIL resistance PMID: 20062539
- mice defective in both tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and Fas ligand reveal new roles for TRAIL in lymphocyte homeostasis and autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndromes PMID: 20185587
- TRAIL induction involves FGF-2, Sp1-phosphorylation and NFkappaB and that TRAIL promotes VSMC proliferation and neointima formation after arterial injury. PMID: 20150555
- Data show that alpha-GalCer/AdmIL-2 treatment expanded the absolute numbers of lung and liver NK, NKT and T-cells as well as the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) expression of these cells. PMID: 19901518
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Tumor necrosis factor family
-
组织特异性:Widespread.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:22035
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000040271
UniGene: Mm.1062
Most popular with customers
-
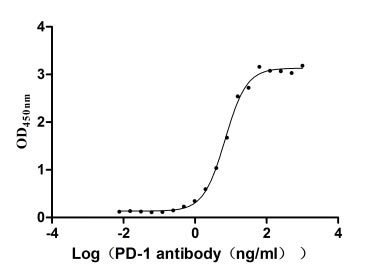
Recombinant Human Programmed cell death protein 1 (PDCD1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
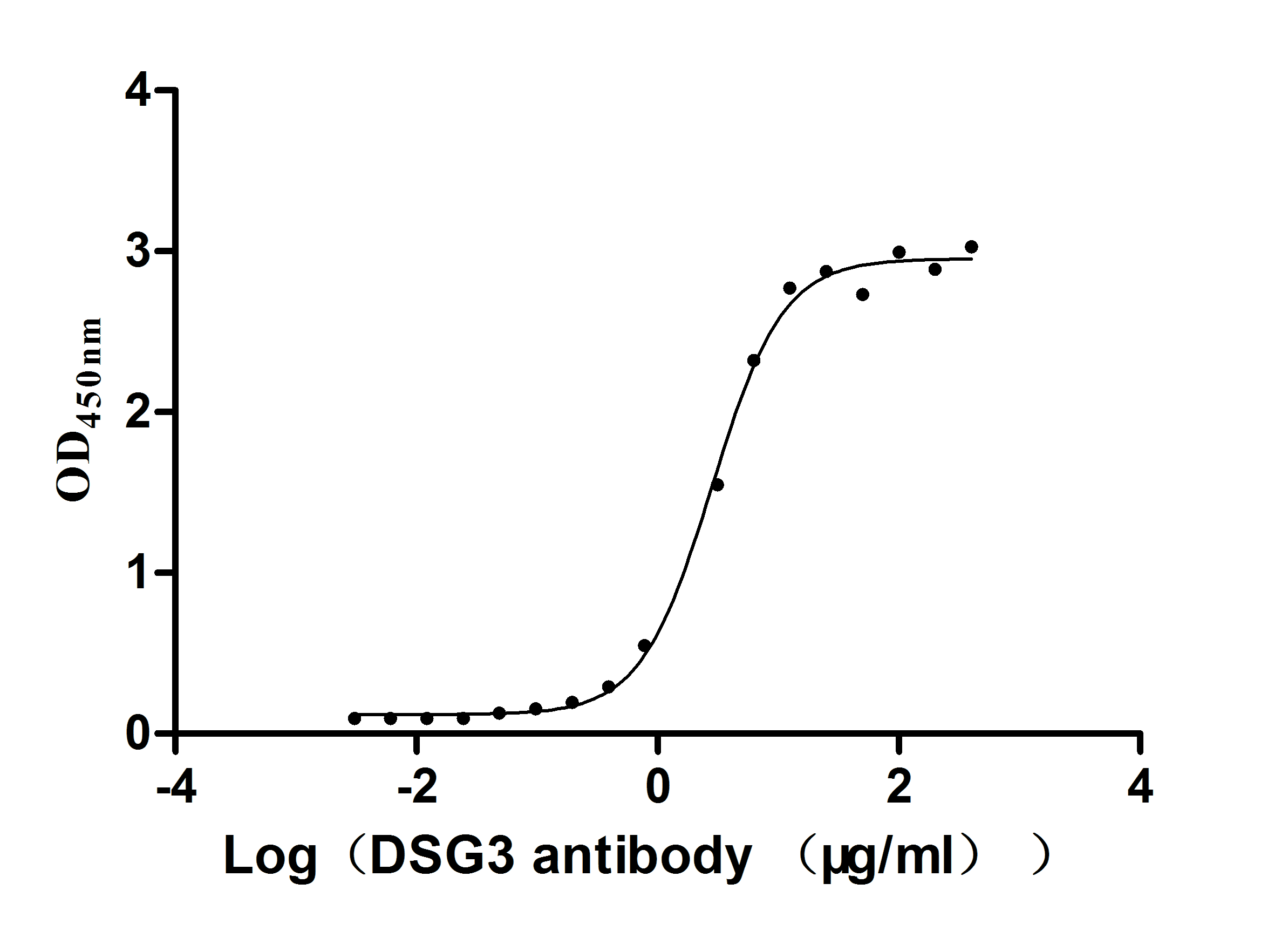
Recombinant Mouse Desmoglein-3 (Dsg3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
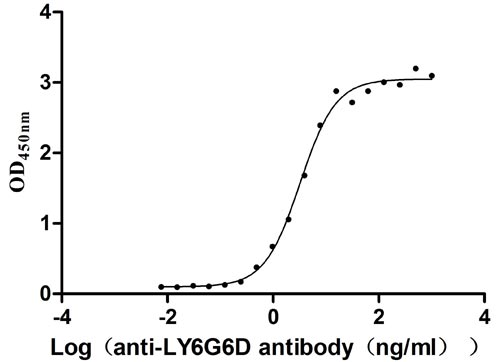
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
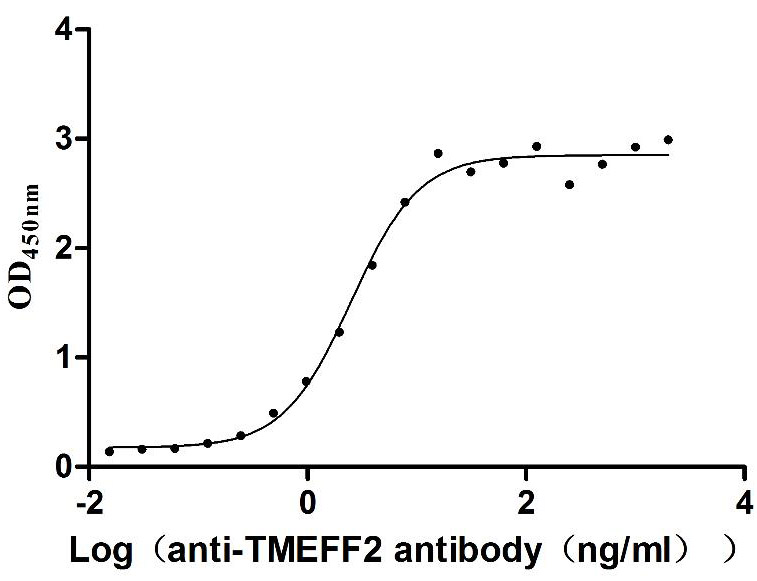
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
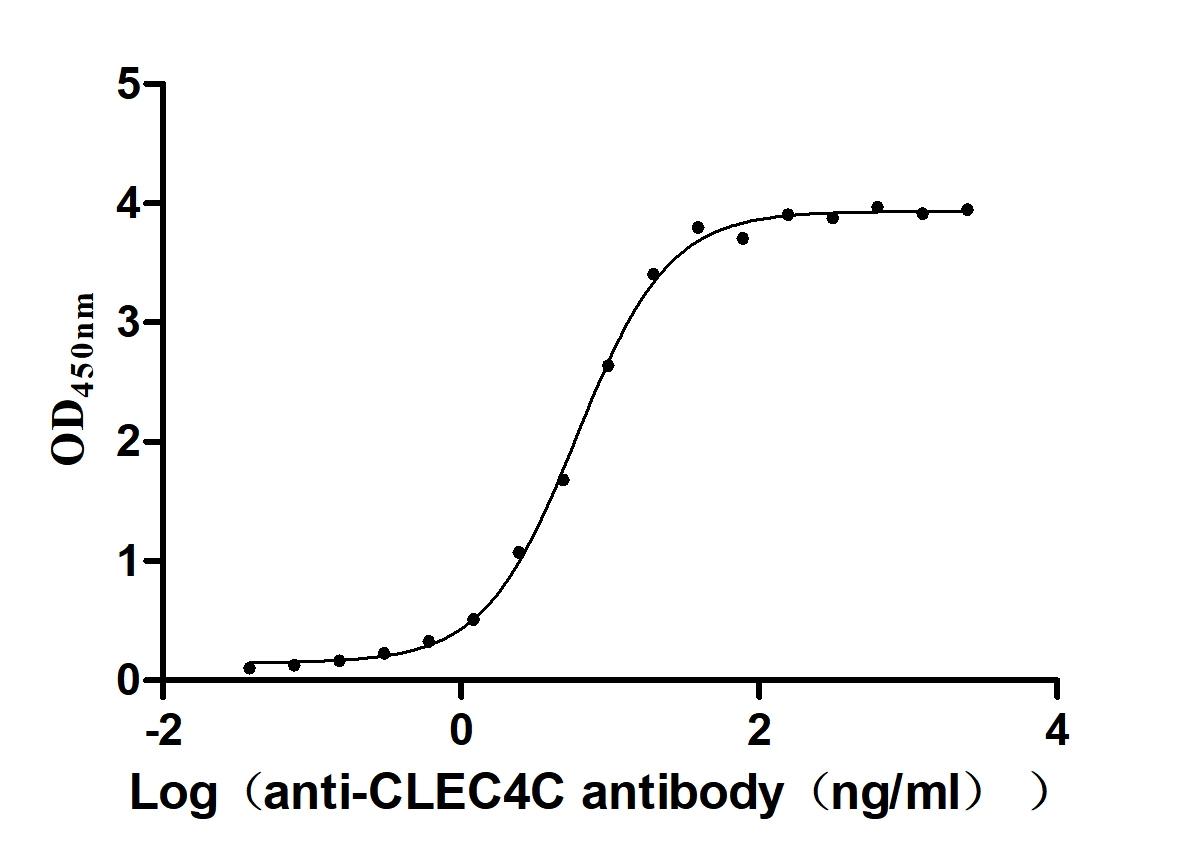
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis C-type lectin domain family 4 member C(CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
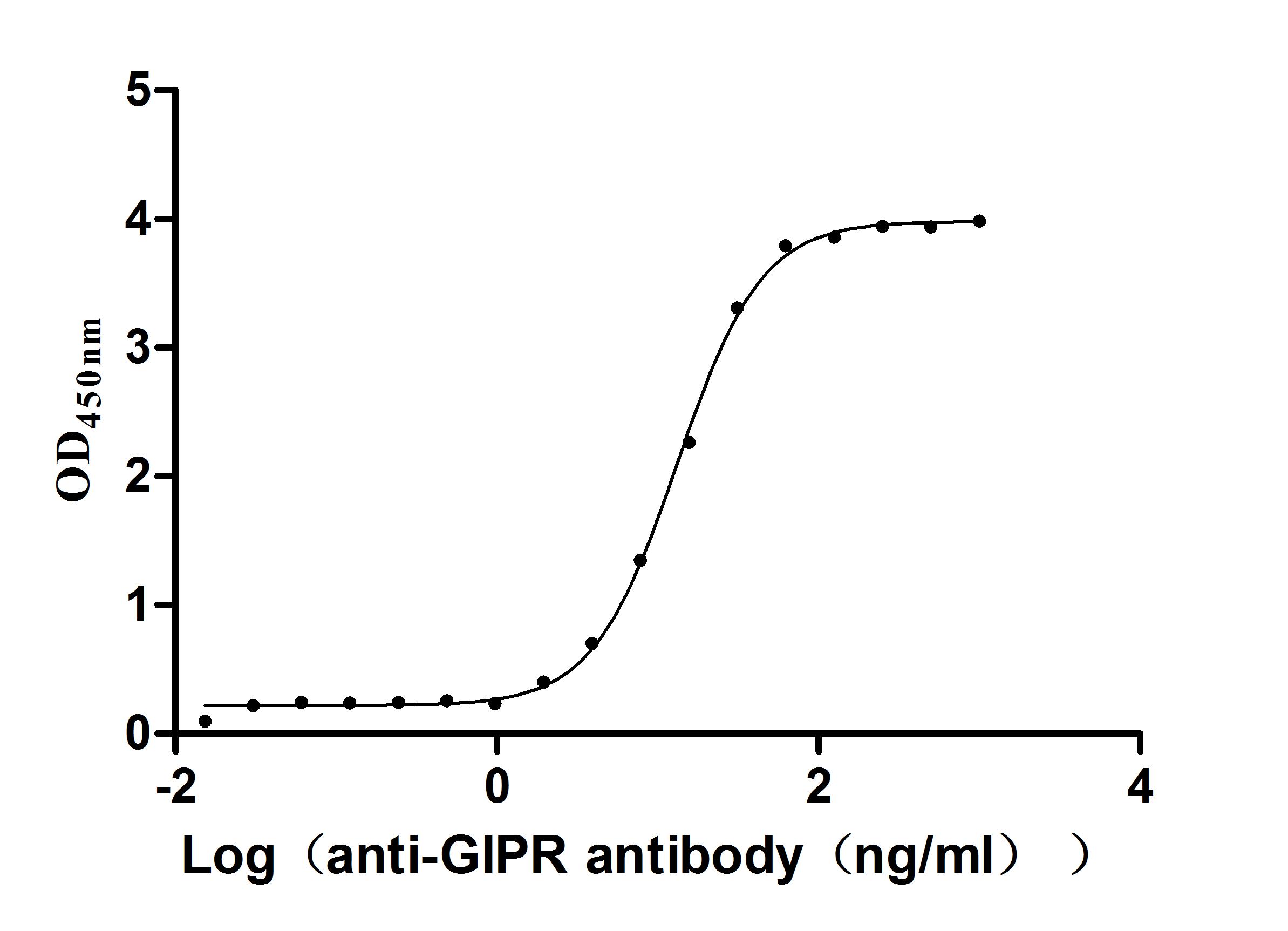
Recombinant Macaca Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR), partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)


-AC1.jpg)