Recombinant Mouse Mucin-1 (Muc1), partial
Unavailable-
货号:CSB-YP312543MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP312543MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP312543MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP312543MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP312543MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Muc1; Muc-1; Mucin-1; MUC-1; Episialin; CD antigen CD227) [Cleaved into: Mucin-1 subunit alpha; MUC1-NT; MUC1-alpha); Mucin-1 subunit beta; MUC1-beta; MUC1-CT)]
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:The alpha subunit has cell adhesive properties. Can act both as an adhesion and an anti-adhesion protein. May provide a protective layer on epithelial cells against bacterial and enzyme attack.; The beta subunit contains a C-terminal domain which is involved in cell signaling, through phosphorylations and protein-protein interactions. Modulates signaling in ERK, Src and NF-kappaB pathways. In activated T-cells, influences directly or indirectly the Ras/MAPK pathway. Regulates P53-mediated transcription and determines cell fate in the genotoxic stress response. Binds, together with KLF4, the PE21 promoter element of P53 and represses P53 activity.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The results showed that co-administration of an adjuvant plasmid and a DNA vaccine stimulated the production of higher titers of specific antibodies and a T cell response and suppressed the growth of subcutaneous tumors expressing MUC1. PMID: 30111221
- these data showed that sustained abnormal MUC1 induction accompanies failing epithelial repair, chronic inflammation and kidney fibrosis. In conclusion, MUC1 exerts opposite effects during kidney response to IR: first protective and then harmful PMID: 28366875
- MUC1 plays an important role in protection against severe pneumococcal disease, potentially mediated by facilitating macrophage phagocytosis. PMID: 28605238
- this study implicates the MUC1 as a critical and dynamic component of the innate host response that limits the severity of influenza and provides the foundation for exploration of MUC1 in resolving inflammatory disease PMID: 28327617
- Muc1 has anti-fibrotic properties in the mouse lung. PMID: 28916165
- our data suggest a novel molecular mechanism by which tMUC1 may modulate NRP1-dependent VEGFR signaling in PDA cells. PMID: 26804176
- Low expression of MUC1 is associated with lung carcinogenesis. PMID: 28472347
- Gp91phox NADPH oxidase modulates litter size by up-regulating mucin1 expression in the uterus of mice. PMID: 28301257
- In summary, we have demonstrated that MUC1 on immune cells is a novel regulator of the NLRP3 inflammasome, and propose this is mediated by an interaction with signalling components at the cytoplasmic domains of TLRs that involves inhibition of IRAK4 activation. PMID: 26079943
- MUC1 regulates IL-1beta secretion induced by the NLRP3-activating bacteria Haemophilus influenzae but not bacteria that activate other inflammasomes. PMID: 26938663
- Muc1 protection during acute kidney injury proceeds by enhancing both the HIF-1 and beta-catenin protective pathways. PMID: 26739894
- MAMs MUC1 and MUC16 contribute to the maintenance of immune homeostasis at the ocular surface by limiting TLR-mediated innate immune responses. PMID: 25563498
- the present study provides evidence that Muc1 is a direct target of let-7a and let-7b in mouse uteri during embryo implantation. PMID: 25739861
- Muc1 clearly plays a significant role in enhancing the hypoxia-inducible transcription factors protective pathway during ischemic insult and recovery in kidney epithelia PMID: 25925251
- Epithelial Muc1 is important for gastric mucosa healing by enhancing cell migration and proliferation. PMID: 25387004
- the present study provides evidence that MUC1 is a direct target of miRNA-199a during embryo implantation. PMID: 23759257
- Helicobacter pylori infection is the most definite insult leading to gastric cancer, and a protective function of mucin 1 protein has been suggested by studies on Muc1 knocked-out mice. PMID: 24810688
- These results suggest that sSiglec-9 has an antitumor benefit against MUC1-expressing tumor in the transgenic mice. PMID: 24924635
- Downregulation of hematopoietic MUC1 during experimental colitis increases tumor-promoting myeloid-derived suppressor cells. PMID: 23873692
- MUC1 overexpression in alveolar epithelial cells does not account for the anti-inflammatory effects of the NSAID, Tanshinone IIA, in the airway. PMID: 24153432
- Siglec-9 expressed on immune cells may play a role as a potential counterreceptor for MUC1 and that this signaling may be another MUC1-mediated pathway and function in parallel with a growth factor-dependent pathway. PMID: 24045940
- This is the first report demonstrating the possible involvement of Muc1 in the development of multiple sclerosis and might provide a potential target for immunotherapy PMID: 23261777
- MUC1c regulates cell survival in pancreatic cancer by preventing lysosomal permeabilization. PMID: 22912777
- diabetic NOD mice overexpressed MUC1 mucin at embryo implantation sites PMID: 22539679
- MUC1 may play a crucial role in the resolution of inflammation during chronic respiratory infections, and MUC1 dysfunction likely contributes to the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory respiratory disease PMID: 22643830
- MUC1 mucin stabilizes and activates hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha to regulate metabolism in pancreatic cancer PMID: 22869720
- Muc1, which is up-regulated by Th17 signaling, functions in a negative feedback pathway that prevents an excessive Th17 cell response in inflamed colons of mice. PMID: 22202458
- MUC1 protein expression in tumor cells regulates transcription of proinflammatory cytokines by forming a complex with nuclear factor-kappaB p65 and binding to cytokine promoters PMID: 22021035
- These data suggest that Muc1 may contribute to a physical barrier that protects against mouse adenovirus type 1 respiratory infection. PMID: 21816184
- data indicate a critical role for MUC1-CD in the development of mammary gland preneoplasia and tumorigenesis, suggesting MUC1-CD as a potential target for the diagnosis and chemoprevention of human breast cancer PMID: 21533058
- Soy protein diet, but not Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, decreases mucin-1, trefoil factor-3, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in colon of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. PMID: 21593350
- the up-regulation of Muc1 during airway P. aeruginosa infection might be crucial for suppressing excessive and prolonged inflammatory responses, and is induced mainly by TNF-alpha, the key proinflammatory mediator PMID: 20448050
- Data suggest that pancreatitis is an extraintestinal site of IBD, characterized by proinflammatory abnormal expression of MUC1. PMID: 20084048
- Muc1 binds to IKKgamma, thereby inhibiting formation of the catalytically active IKK complex and blocking the ability of Helicobacter pylori to stimulate IkappaBalpha phosphorylation. PMID: 20430889
- Our results indicate that deletion of Muc1 promotes a heightened functional response of DC in response to TLR4 and TLR5 signaling pathways, and suggests a previously under-appreciated role for Muc1 in regulating innate immune responses of DC. PMID: 20375631
- This is the first demonstration showing that MUC1 can suppress the virus-induced inflammatory responses. PMID: 20081068
- MUC1 is a substrate for gamma-secretase PMID: 19711367
- anti-MUC1 antibodies and Foxp3+ regulatory T cells are present in a mouse model for human MUC1-positive endometriosis PMID: 19841240
- The -750 and -250 regions are conserved between the human MUC1 and mouse Muc1 genes and may be associated with functionally important genetic elements. PMID: 11984004
- MUC1-specific anti-tumor responses: molecular requirements for CD4-mediated responses PMID: 12147624
- CD227 is expressed on human and murine activated dendritic cells PMID: 12377938
- MUC1 expression is increased, and it appears that alternate cytoplasmic tails may change its role in signaling in CFTR-deficient mice; MUC1 could be an important contributor to the CF intestinal phenotype PMID: 12529261
- Analysis of MMTV-Wnt-1 tumors on a wild-type Muc1 background shows a tumor-specific complex formation between Muc1 and beta-catenin that can be observed in both the membrane and the cytoplasm of transformed epithelium. PMID: 12618757
- decreased gallstone formation in mice with disrupted Muc1 gene results from reduced mucin secretion and accumulation in the gallbladder PMID: 14703511
- activation of ErbB2, which only occurs in c-Neu tumors, selectively inhibits Muc1 expression PMID: 14737104
- Our results indicate that, T cell responses necessary for protection against MUC1-expressing tumours that are induced by IM injection of MUC1 cDNA are independent of the tandem repeat domain as well as the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. PMID: 14999776
- physiological levels of the epithelial mucin produced by the Muc1 gene are necessary for normal intestinal uptake and absorption of cholesterol in mice PMID: 15075252
- Several genes are up-regulated by MUC1/sec expression, including MCP-1 (CCL-2). PMID: 15265901
- PPAR gamma controls Muc1 transcription in trophoblasts. PMID: 15572671
- The results suggest that MUC1 is not a major component in the accumulated mucus of CF mice and that MUC1 can influence the amount of other mucins in a still unknown way. PMID: 16500918
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Apical cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Mucin-1 subunit beta]: Cell membrane. Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in a variety of epithelial tissues.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:17829
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000041963
UniGene: Mm.16193
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 (DDR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
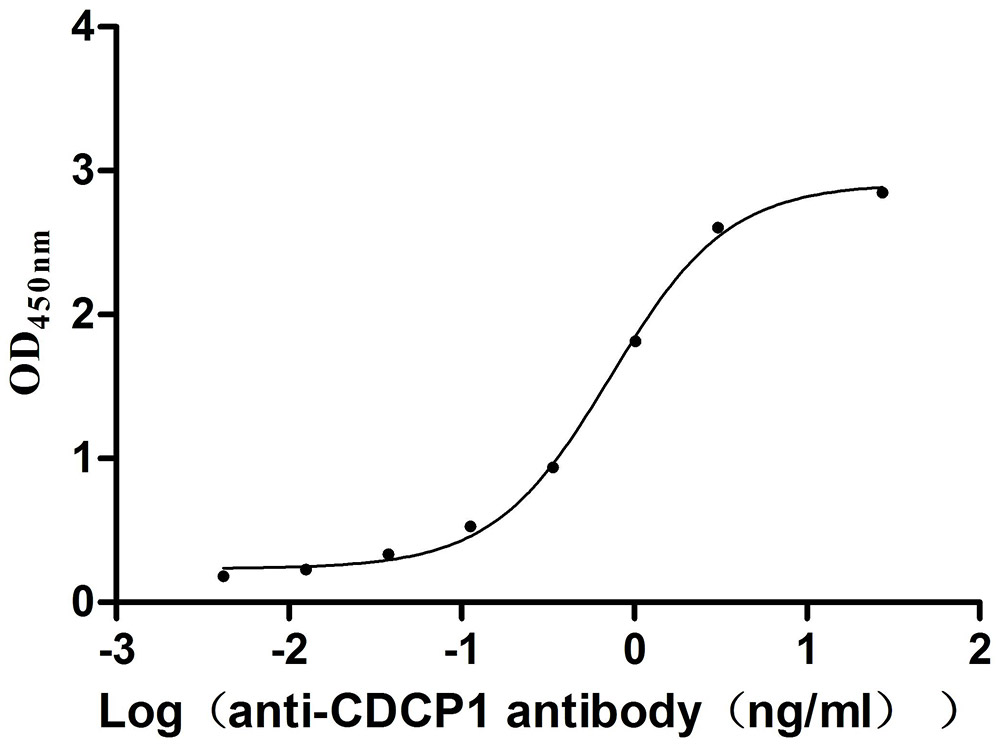
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
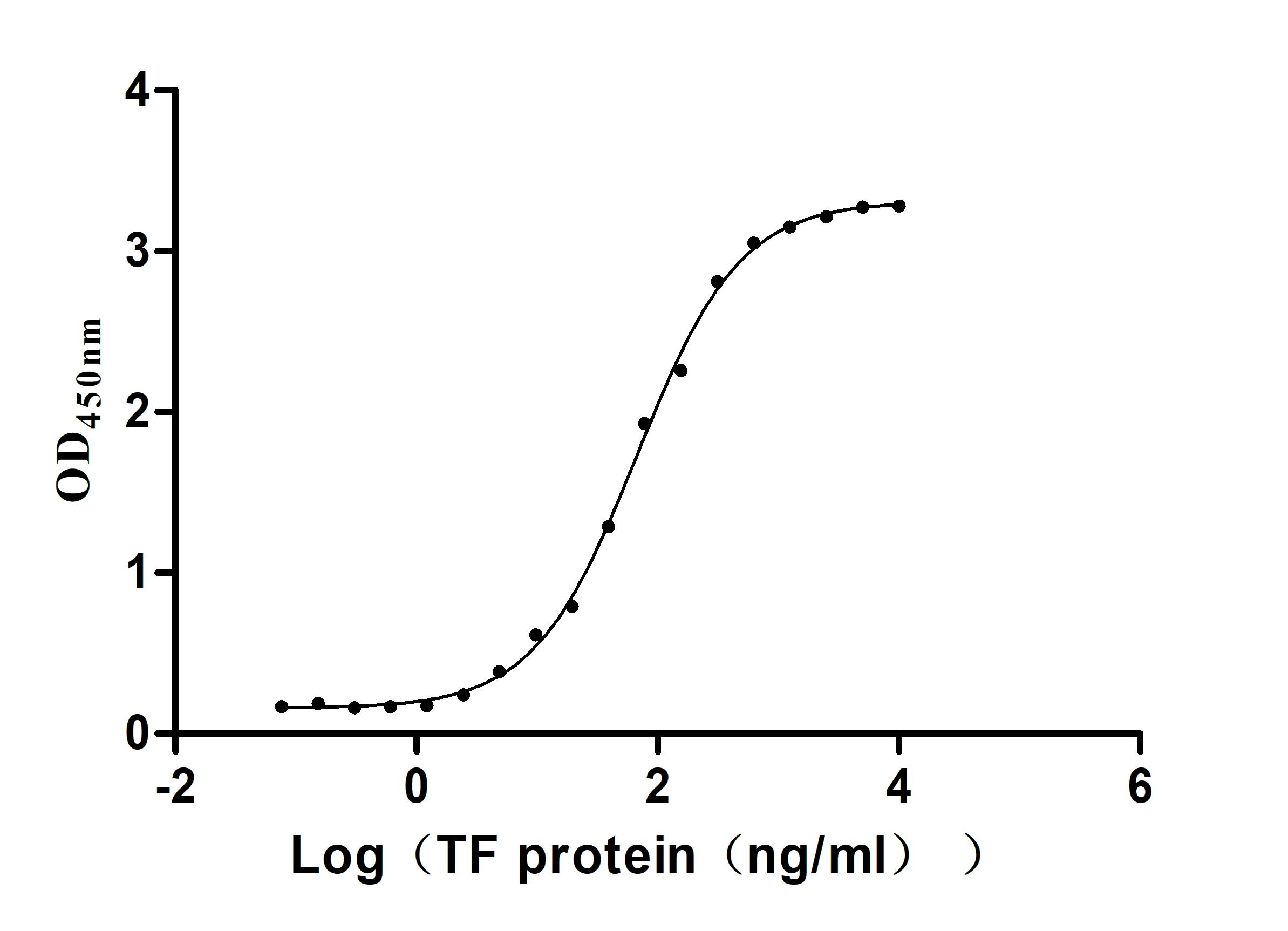
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
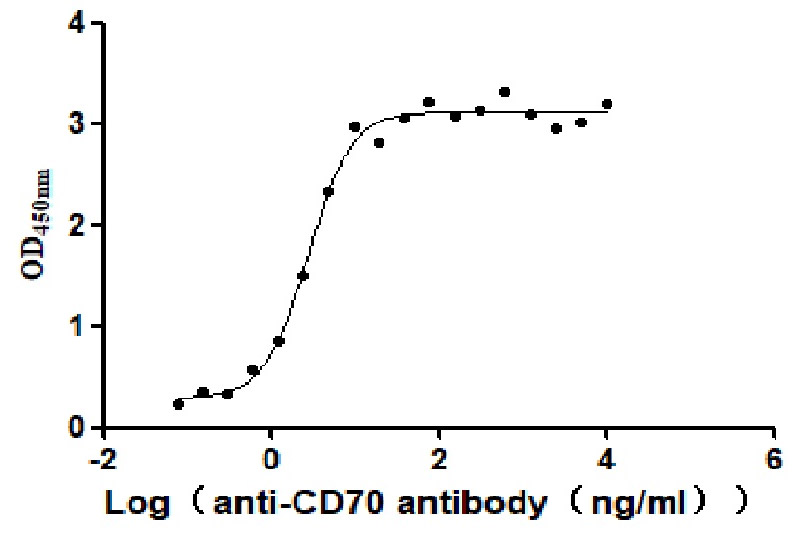
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
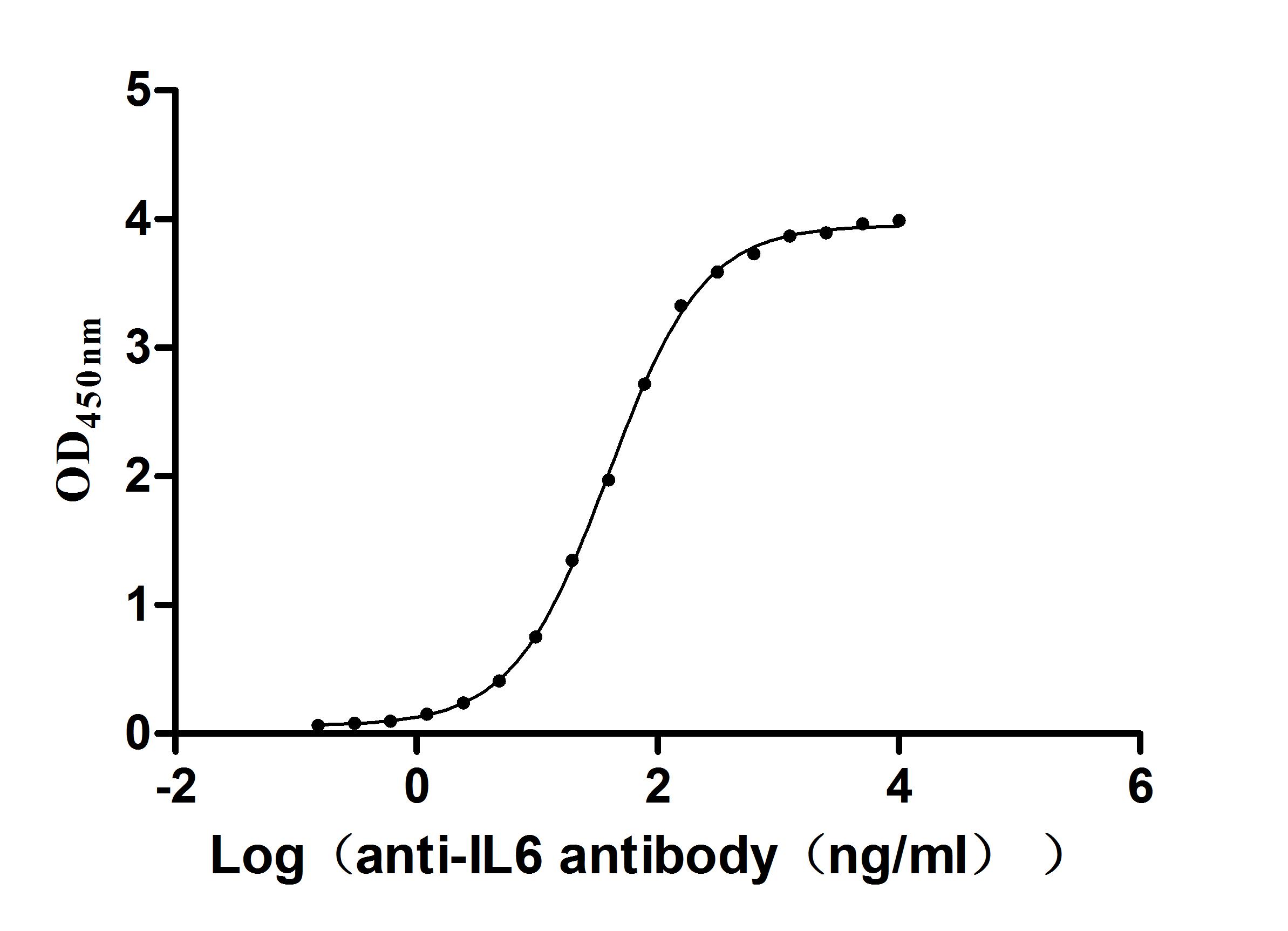
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)