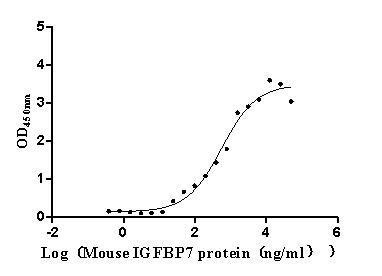
Recombinant Mouse Junctional adhesion molecule A (F11r), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP007917MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP007917MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP007917MO1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP007917MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP007917MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:F11r; Jam1; Jcam; Jcam1; Junctional adhesion molecule A; JAM-A; Junctional adhesion molecule 1; JAM-1; CD antigen CD321
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Seems to play a role in epithelial tight junction formation. Appears early in primordial forms of cell junctions and recruits PARD3. The association of the PARD6-PARD3 complex may prevent the interaction of PARD3 with JAM1, thereby preventing tight junction assembly. Plays a role in regulating monocyte transmigration involved in integrity of epithelial barrier. Ligand for integrin alpha-L/beta-2 involved in memory T-cell and neutrophil transmigration. Involved in platelet activation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Deletion JAM-A from platelets increases early-stage neointima formation after carotid artery wire injury in hyperlipidemic mice. PMID: 28211187
- JAM-A is present in the prostate and seminal vesicles and in all three regions of the epididymis where it is secreted in epididymosomes in the luminal fluid and can be delivered to sperm. PMID: 28062807
- Soluble JAM-A secreted from cardiac progenitor cells reduces infiltration of neutrophils after myocardial infarction and ameliorates tissue damage through prevention of excess inflammation. PMID: 25468657
- JAM-A up-regulation can increase the proliferation, cytokine secretion and wound-homing ability of MSCs, thus accelerating the repair rate of full-thickness skin defects PMID: 25994236
- Endothelial JAM-A but not hematopoietic JAM-A facilitates reovirus T1L bloodstream entry and egress. PMID: 25149763
- Deletion of JAM-A causes a gain-of-function in platelets, with lower activation thresholds and increased inflammatory activities. This leads to an increase of plaque formation, particularly in early stages of the disease. PMID: 25472975
- The F11r gene is directly regulated by retinoic acid in the embryonic mesoderm. PMID: 25251699
- Redistribution of JAM-A in endothelial cells after stimulation with pro-atherogenic oxidized lipoproteins results in increased transmigration of mononuclear cells. PMID: 24704627
- JAM-A has a prominent role in regulating leukocyte infiltration after brain I/R injury and could be a new target in limiting post-ischemic inflammation. PMID: 24657919
- JAM-A regulates epithelial permeability via association with ZO-2, afadin, and PDZ-GEF1 to activate Rap2c and control contraction of the apical cytoskeleton. PMID: 23885123
- Cancer stem cells selectively express JAM-A, which regulates self-renewal. PMID: 24373972
- These studies establish F11R as a novel monocyte prognostic marker for GBM critical for defining a subpopulation of stromal cells for future potential therapeutic intervention. PMID: 24147027
- Our data identify endothelial JAM-A as an important effector molecule integrating atherogenic conditions to direct inflammatory cell entry at predilection sites of atherosclerosis. PMID: 24065611
- The JAM-A and ZO-1 genes were highly expressed in all the tested tissues. PMID: 23568966
- Junctional adhesion molecule-A regulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 signaling-dependent mouse corneal wound healing. PMID: 23667656
- The crucial role of JAM-A in the transmigration of neutrophils from the vasculature into inflamed tissues. PMID: 22904169
- The chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) induced JAM-A redistribution from the interendothelial cell area to the apical surface of brain endothelial cells. PMID: 22733993
- CASK negatively regulates PMCA4b by directly binding to it and JAM-A positively regulates it indirectly through CASK PMID: 22020416
- JAM-A normally limits platelet accumulation by inhibiting integrin outside-in signaling thus preventing premature platelet activation. PMID: 22271446
- Data suggest that aPKC phosphorylates JAM-A at S285 to regulate cell-cell contact maturation, TJ formation, and single lumen specification. PMID: 22371556
- downregulation of JAM-A reduces tumor aggressive behavior by increasing cell susceptibility to apoptosis PMID: 21695058
- Data demenstrate that JAM-A restricts intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) proliferation in a dimerization-dependent manner, by inhibiting Akt-dependent beta-catenin activation. PMID: 21372850
- Our data show that JAM-A is a novel surface marker for NG2-glia cells of the adult brain. PMID: 20184779
- In the Rip1Tag2 tumor model, abrogation of JAM-A reduces cancer development by increasing antitumor immune response. PMID: 20160037
- JAM-1 did not contribute to global embryo compaction and adhesion but rather regulated the timing of blastocoel cavity formation dependent upon establishment of the trophectoderm tight junction paracellular seal. PMID: 15494378
- By regulating cytoskeletal and adhesive structures, JAM-A expression prevents cell motility, probably in a PSD95-Dlg-ZO1-dependent manner. PMID: 15657074
- JAM-A is up-regulated in hepatic venules and serves as an endothelial receptor of neutrophil transmigration, but it does not mediate leukocyte rolling, adhesion, or platelet-endothelial cell interactions. PMID: 15827135
- JAM-A is required for the correct infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes into an inflamed peritoneum or in the heart upon ischemia-reperfusion injury. PMID: 16027360
- crucial role of JAM-A in accelerated lesion formation and monocyte infiltration in atherosclerosis-prone mice PMID: 16306427
- Taken together, these data indicate that JAM-A regulates cell motility by cooperating with microtubule-stabilizing pathways. PMID: 16783819
- Essential role for JAM-A in FGF-2-induced angiogenesis. PMID: 16809549
- JAM-A is expressed in the corneal epithelium where it appears to regulate cell shape. PMID: 17118692
- Junctional adhesion molecule-A is critical for the formation of pseudocanaliculi and modulates E-cadherin expression in hepatic cells PMID: 17623668
- JAM-A is expressed on hematopoietic precursors in various hematopoietic tissues PMID: 17986666
- The findings show that JAM-A is involved in sperm tail formation and is essential for normal motility, which may occur via its signal transduction and protein phosphorylation properties. PMID: 18022613
- JAM-A plays a role in intestinal homeostasis by regulating epithelial permeability, inflammation, and proliferation PMID: 18039951
- A short bond lifetime imparts a highly dynamic nature to homophilic JAM-A interactions for regulating tight junction permeability while stable interactions between sigma1 and JAM-A likely anchor the virus to the cell surface and facilitate viral entry. PMID: 18446885
- nonredundant and novel role of JAM-A in controlling mucosal homeostasis by regulating the integrity and permeability of epithelial barrier function PMID: 18514073
- Nectin plays a novel role in the co-localization of JAM and claudin at the same cell-cell adhesion membrane domains. PMID: 18547333
- These data indicate that JAM-A is required for the correct internalization and recycling of integrins during cell migration. PMID: 19118219
- The s inoculated wild-type (WT) and isogenic JAM-A(-/-) mice perorally with reovirus and found that JAM-A is dispensable for viral replication in the intestine but required for systemic dissemination. PMID: 19154988
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell junction, tight junction. Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Note=Localized at tight junctions of both epithelial and endothelial cells.
-
蛋白家族:Immunoglobulin superfamily
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:16456
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000041907
UniGene: Mm.294882
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
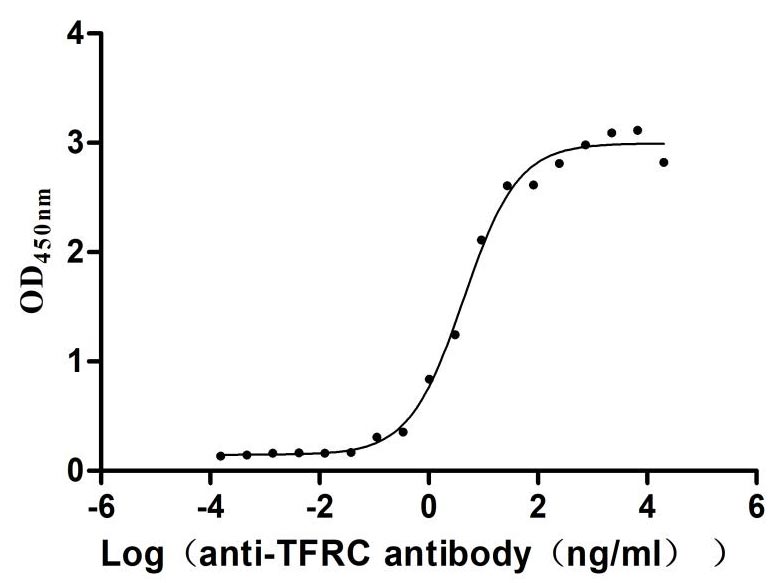
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
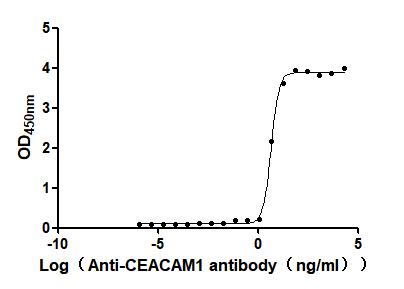
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)