Recombinant Mouse Glucagon receptor (Gcgr), partial
In Stock-
货号:CSB-EP009316MO
-
规格:¥1836
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
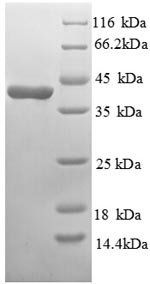
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:GcgrGlucagon receptor; GL-R
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Extracellular Domain
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:40.8kDa
-
表达区域:27-143aa
-
氨基酸序列AQVMDFLFEKWKLYSDQCHHNLSLLPPPTELVCNRTFDKYSCWPDTPPNTTANISCPWYLPWYHKVQHRLVFKRCGPDGQWVRGPRGQPWRNASQCQLDDEEIEVQKGVAKMYSSQQ
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal GST-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:G-protein coupled receptor for glucagon that plays a central role in the regulation of blood glucose levels and glucose homeostasis. Regulates the rate of hepatic glucose production by promoting glycogen hydrolysis and gluconeogenesis. Plays an important role in mediating the responses to fasting. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Promotes activation of adenylate cyclase. Besides, plays a role in signaling via a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data, including data from studies using knockout mice, suggest that control of whole-body energy expenditure by Gcgr agonism requires intact Fxr signaling and Fgf21 secretion in liver. (Gcgr = glucagon receptor glucagon; Fxr = farnesoid X receptor; Fgf21 = fibroblast growth factor-21) PMID: 29925501
- we show that glucagon receptor (GCGR) inhibition with a monoclonal antibody normalized blood glucose and beta-hydroxybutyrate levels. Insulin receptor antagonism increased pancreatic beta-cell mass threefold. Normalization of blood glucose levels with GCGR-blocking antibody unexpectedly doubled beta-cell mass relative to that observed with S961 alone and 5.8-fold over control PMID: 28115707
- These results show that Slc38a5 is a key component of the feedback circuit between glucagon receptor signaling in the liver and amino-acid-dependent regulation of pancreatic alpha cell mass in mice. PMID: 28591637
- GcgR knockout (Gcgr(-/-)) mice displayed lower blood glucose levels accompanied by elevated plasma ghrelin levels. Hyperglycemia was averted in streptozocin treated Gcgr(-/-) mice and the plasma ghrelin level was further increased. PMID: 28487437
- glucagon receptor antagonist improves glycemia in diet-induced obese angptl4 knockout mice without increasing glucagon levels or alpha-cell proliferation, underscoring the importance of this protein. PMID: 26621734
- Data indicate that the exocrine pancreas in the glucagon receptor Gcgr-/- mice exhibited larger nuclear size than in WT or heterozygous controls, most obviously at old ages. PMID: 24326371
- Simultaneous and sufficient activation of GLP1R is required to reduce GCCR mediated blood glucose elevation following administration of a GLP1R/GCGR co-agonist. PMID: 23203689
- Knockdown of liver glucagon receptor in mice reduces blood glucose and increases blood LDL levels. PMID: 23828778
- Gcgr(-/-) mice became lethargic & cachexic & died early. Autopsy revealed numerous PNETs up to 15 mm in diameter in most well-preserved Gcgr(-/-) pancreata. PMID: 22951296
- Data suggest that GcgR activation raises hepatic expression of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) and increases circulating levels of FGF21; GcgR activation induces body weight loss and stimulates lipid metabolism. PMID: 23305646
- These results suggest that a circulating factor generated after disruption of hepatic Gcgr signaling can increase alpha-cell proliferation independent of direct pancreatic input. PMID: 23160527
- GRA1 is a potent glucagon receptor antagonist with strong antihyperglycemic efficacy in preclinical models and prominent effects on hepatic gene-expression related to amino acid metabolism PMID: 23185367
- Data suggest that both Gcgr activity and glucagon-like peptide 1/Glp1r signal transduction in central nervous system are involved in control of interscapular brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. PMID: 22933116
- A novel transgenic mouse was generated which had muscle specific expression of glucagon receptor. The transgenic mice maintained an appropriate ratio of glucagon to insulin, which appears important in maintaining glucose homeostasis. PMID: 22318544
- in addition to activation of the classic cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) pathway, activation of GCGR also induced beta-catenin stabilization and activated beta-catenin-mediated transcription PMID: 22438981
- Data from glucagon receptor knockout mice suggest that glucagon receptor action and glucagon/glucagon receptor signaling contribute to normal female reproductive function (i.e., normal ovulation, placentation, and fetal development). PMID: 22167521
- ChREBP directly regulates rat Gcgr expression in INS-1E cells. PMID: 22198437
- Defective glucagon signaling causes pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in the Gcgr(-/-) mice. PMID: 21853126
- complete ablation of hepatic glucagon receptor function results in major metabolic alterations in the liver PMID: 21631939
- functional plasticity in the enteroinsular axis involves GLP1R and GcgR and induction of compensatory mechanisms that control nutrient-dependent regulation of insulin secretion PMID: 21540554
- Blocking glucagon action by knocking out glucagon receptors prevents type 1 diabetes mellitus in mice. PMID: 21270251
- glucagon receptor has a role in maintenance of normal glycemia and postnatal regulation of islet and alpha and delta cell numbers PMID: 12552113
- glucagon were unaffected by the GLP-1 receptor antagonist exendin-(9-39) but abolished by des-His1-[Glu9]-glucagon-amide, a specific blocker of the glucagon receptor PMID: 15459251
- Glucagon signaling is required for normal beta-cell function and that insulin action is improved when disrupting the signal by glucagon receptor knockout. PMID: 17130493
- Blocking glucagon signalling by targeted Gcgr gene deletion leads to an improvement in metabolic control in this mouse model of streptozotocin-mediated beta cell loss and hyperglycaemia. PMID: 17131145
- Nestin expression is regulated by glucagon signaling. PMID: 17366624
- Glucagon receptor has a role in islet function in mice with insulin resistance PMID: 17479245
- Restoration of hepatic Gcgr expression in Gcgr-/- mice attenuated the development of hepatocellular injury. PMID: 18809404
- Gcgr receptor is required for control of lipid metabolism during the adaptive metabolic response to fasting. PMID: 19046568
- Oxyntomodulin, a glucagon receptor agonist, reverses obesity in diet-induced obese mice, and may be a novel therapeutic approach to the treatment of obesity. PMID: 19602537
- Increased pancreatic beta-cell expression of the Gcgr increased insulin secretion, pancreatic insulin content, beta-cell mass, and, when mice were fed a HFD, partially protected against hyperglycemia and IGT. PMID: 19602585
- These results suggest that GLP-1 may affect the maturation of postnatal but not prenatal beta cells. PMID: 19647035
- hepatic energy state is sensitive to glucagon receptor activation and requires PEPCK-C, thus providing new insights into liver metabolism. PMID: 19662685
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 2 family
-
组织特异性:Expressed predominantly in liver, kidney, adrenal, lung and stomach, while lower levels of expression are detected in brown and white adipose tissue, cerebellum, duodenum and heart.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:14527
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000026119
UniGene: Mm.22329
Most popular with customers
-
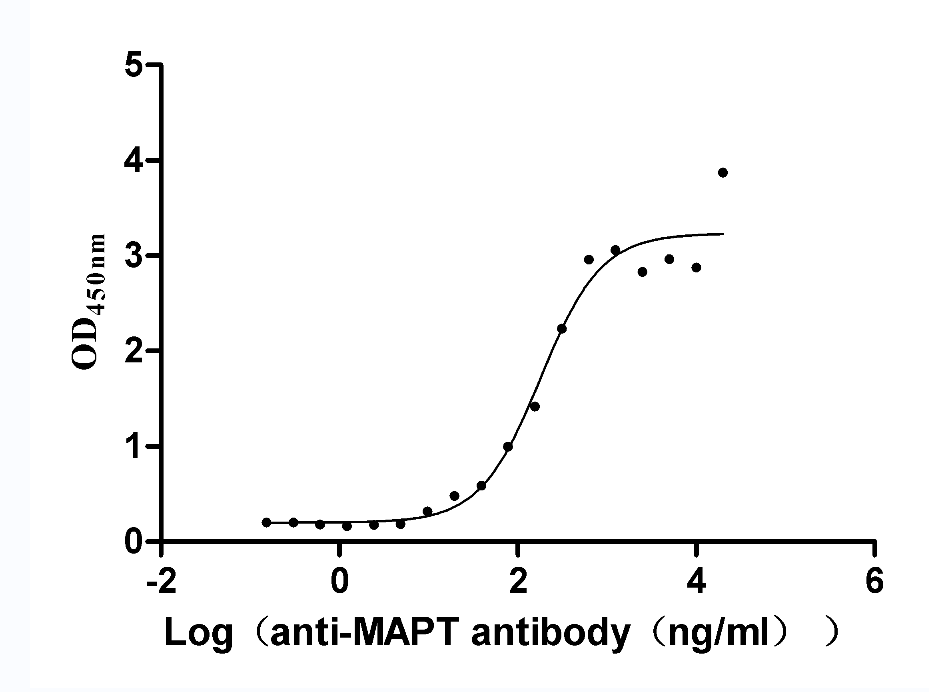
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Recombinant Human Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
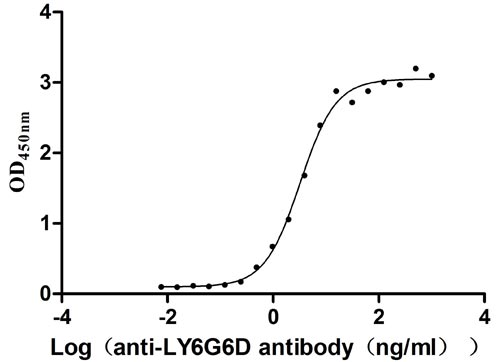
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
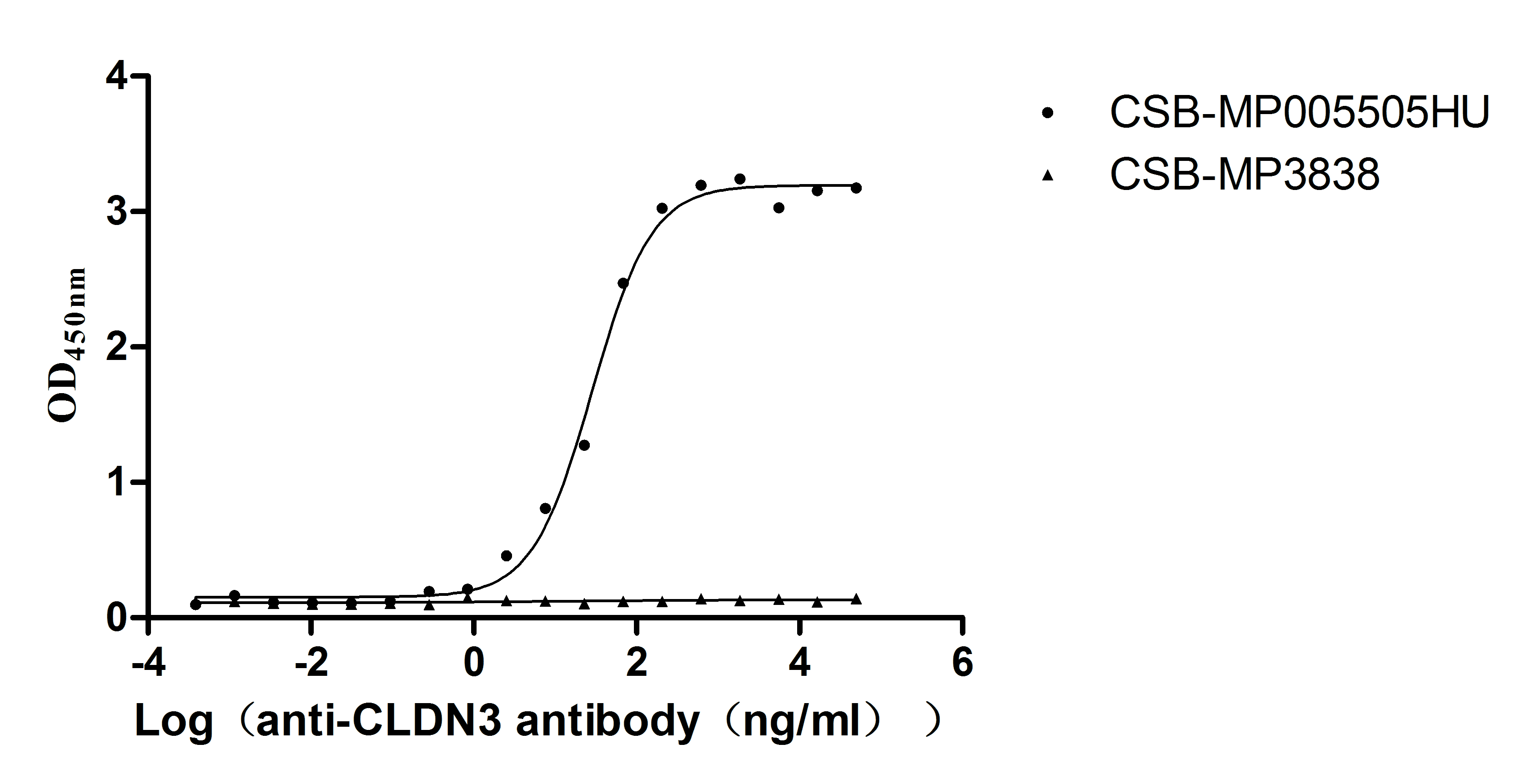
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cell adhesion molecule 1 (Cadm1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
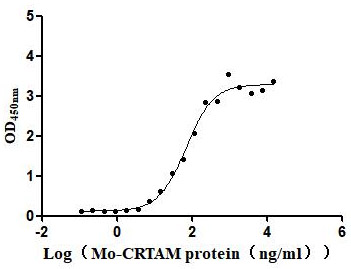
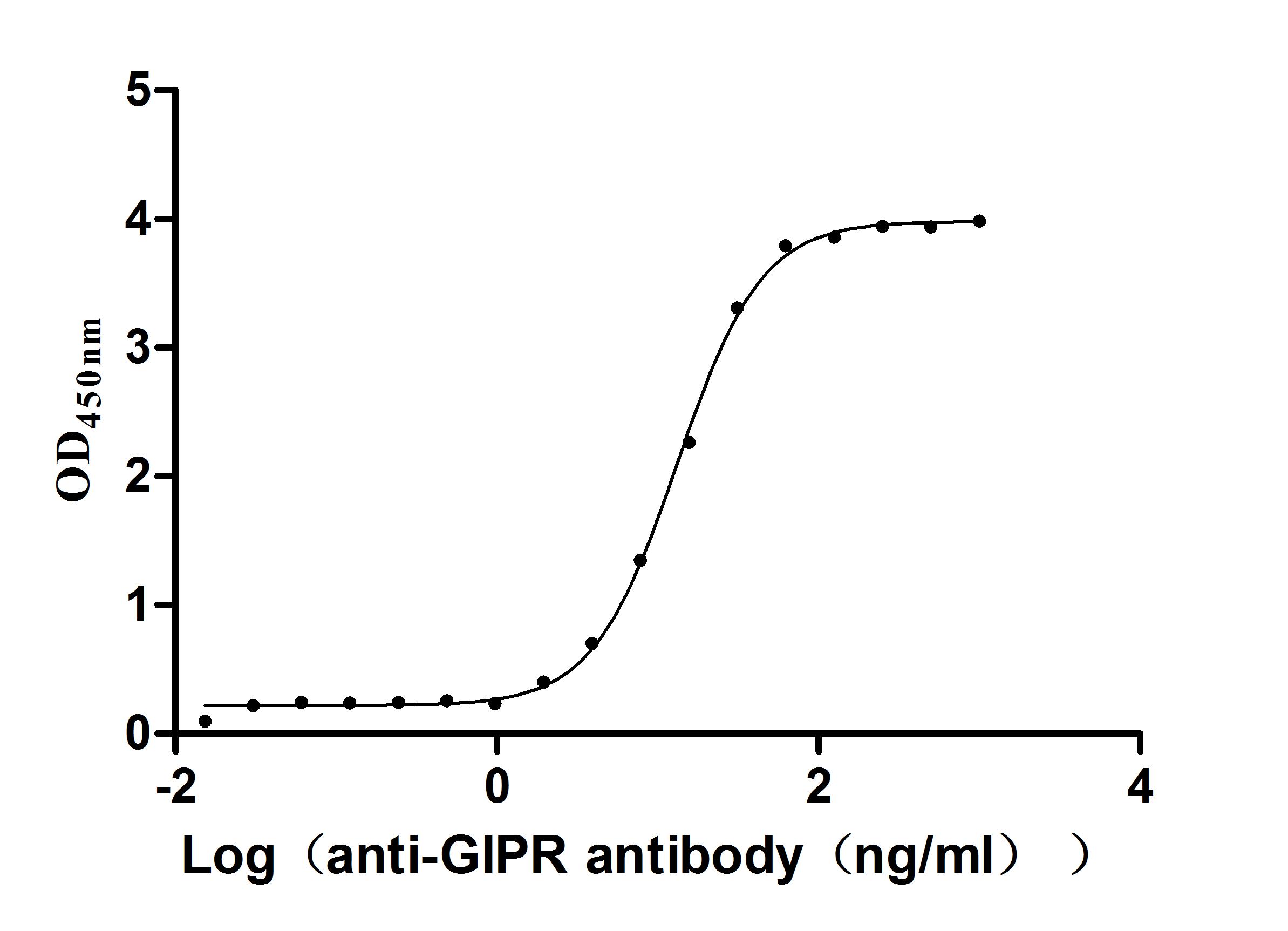
Recombinant Macaca Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR), partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
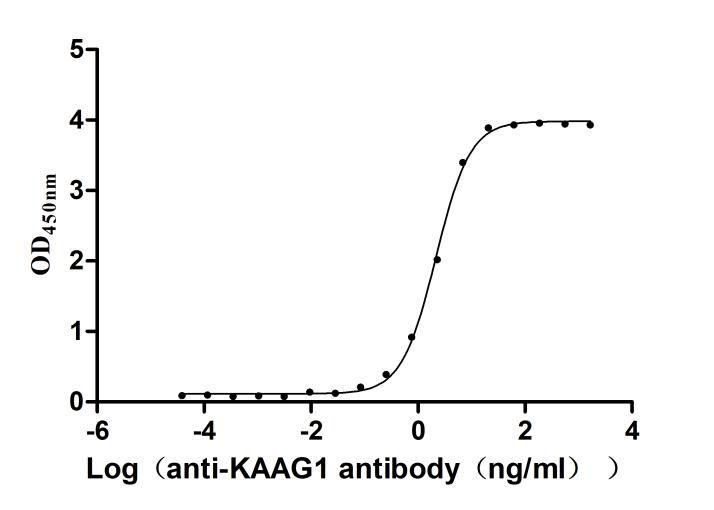
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
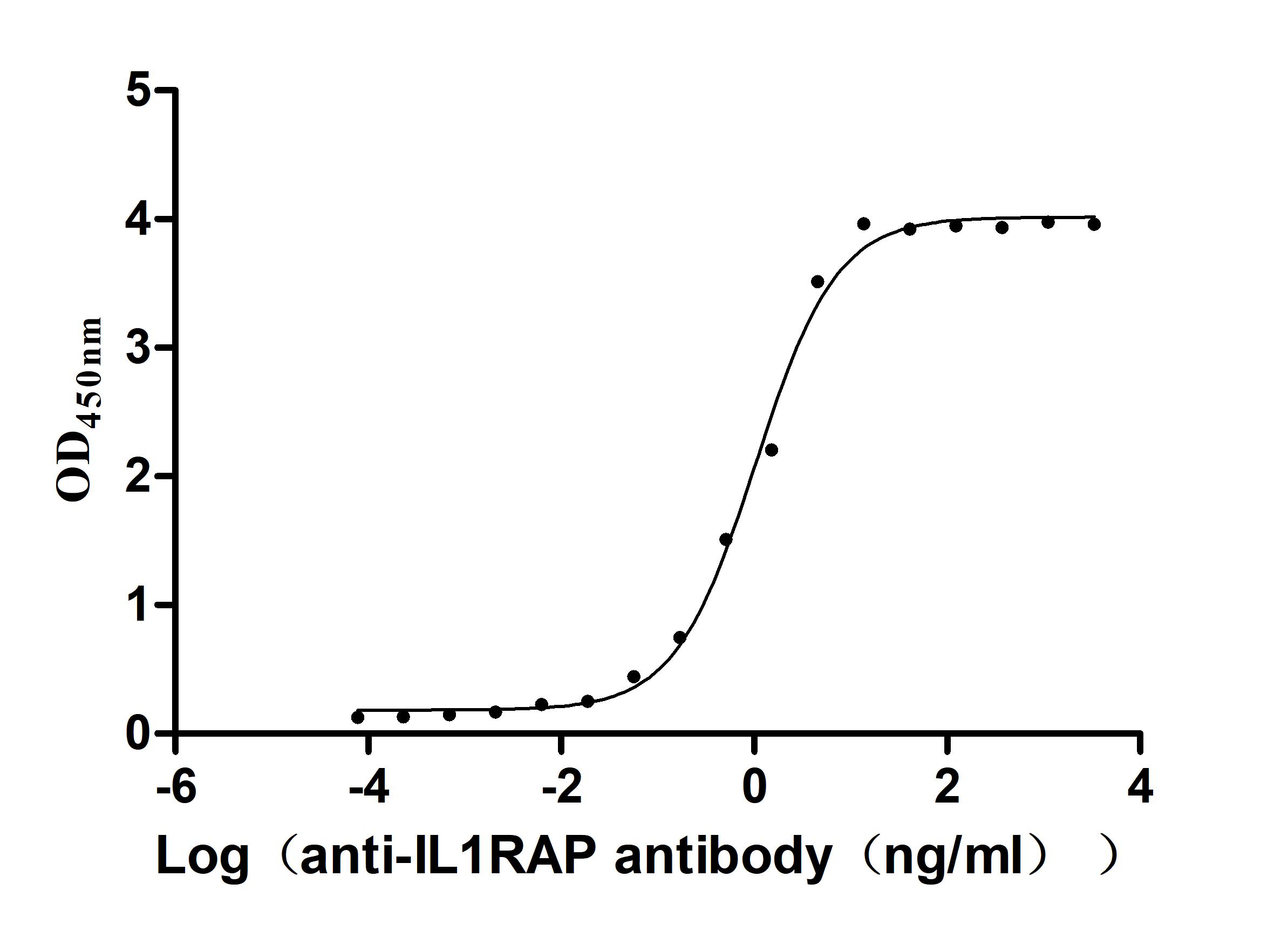
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein(IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)