Recombinant Mouse Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4 (Atf4)
-
货号:CSB-YP002272MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP002272MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP002272MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP002272MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP002272MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
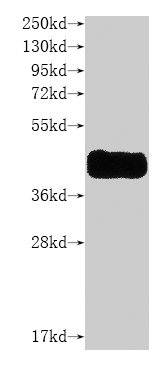
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Atf4Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4; cAMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4; Activating transcription factor 4; C/EBP-related ATF; C/ATF; Tax-responsive enhancer element-binding protein 67 homolog; TaxREB67 homolog
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-349
-
氨基酸序列MTEMSFLNSE VLAGDLMSPF DQSGLGAEES LGLLDDYLEV AKHLKPHGFS SDKAGSSEWP AMDDGLASAS DTGKEDAFSG TDWMLEKMDL KEFDFDALFR MDDLETMPDE LLTTLDDTCD LFAPLVQETN KEPPQTVNPI GHLPESLIKV DQVAPFTFLQ PFPCSPGVLS STPEHSFSLE LGSEVDISEG DRKPDSAAYI TLIPPCVKEE DTPSDNDSGI CMSPESYLGS PQHSPSTSRA PPDNLPSPGG SRGSPRPKPY DPPGVSLTAK VKTEKLDKKL KKMEQNKTAA TRYRQKKRAE QEALTGECKE LEKKNEALKE KADSLAKEIQ YLKDLIEEVR KARGKKRVP
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor that binds the cAMP response element (CRE) (consensus: 5'-GTGACGT[AC][AG]-3') and displays two biological functions, as regulator of metabolic and redox processes under normal cellular conditions, and as master transcription factor during integrated stress response (ISR). Binds to asymmetric CRE's as a heterodimer and to palindromic CRE's as a homodimer. Core effector of the ISR, which is required for adaptation to various stress such as endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, amino acid starvation, mitochondrial stress or oxidative stress. During ISR, ATF4 translation is induced via an alternative ribosome translation re-initiation mechanism in response to EIF2S1/eIF-2-alpha phosphorylation, and stress-induced ATF4 acts as a master transcription factor of stress-responsive genes in order to promote cell recovery. Promotes the transcription of genes linked to amino acid sufficiency and resistance to oxidative stress to protect cells against metabolic consequences of ER oxidation. Activates the transcription of NLRP1, possibly in concert with other factors in response to ER stress. Activates the transcription of asparagine synthetase (ASNS) in response to amino acid deprivation or ER stress. However, when associated with DDIT3/CHOP, the transcriptional activation of the ASNS gene is inhibited in response to amino acid deprivation. Together with DDIT3/CHOP, mediates programmed cell death by promoting the expression of genes involved in cellular amino acid metabolic processes, mRNA translation and the terminal unfolded protein response (terminal UPR), a cellular response that elicits programmed cell death when ER stress is prolonged and unresolved. Together with DDIT3/CHOP, activates the transcription of the IRS-regulator TRIB3 and promotes ER stress-induced neuronal cell death by regulating the expression of BBC3/PUMA in response to ER stress. May cooperate with the UPR transcriptional regulator QRICH1 to regulate ER protein homeostasis which is critical for cell viability in response to ER stress. In the absence of stress, ATF4 translation is at low levels and it is required for normal metabolic processes such as embryonic lens formation, fetal liver hematopoiesis, bone development and synaptic plasticity. Acts as a regulator of osteoblast differentiation in response to phosphorylation by RPS6KA3/RSK2: phosphorylation in osteoblasts enhances transactivation activity and promotes expression of osteoblast-specific genes and post-transcriptionally regulates the synthesis of Type I collagen, the main constituent of the bone matrix. Cooperates with FOXO1 in osteoblasts to regulate glucose homeostasis through suppression of beta-cell production and decrease in insulin production. Activates transcription of SIRT4. Regulates the circadian expression of the core clock component PER2 and the serotonin transporter SLC6A4. Binds in a circadian time-dependent manner to the cAMP response elements (CRE) in the SLC6A4 and PER2 promoters and periodically activates the transcription of these genes. Mainly acts as a transcriptional activator in cellular stress adaptation, but it can also act as a transcriptional repressor: acts as a regulator of synaptic plasticity by repressing transcription, thereby inhibiting induction and maintenance of long-term memory. Regulates synaptic functions via interaction with DISC1 in neurons, which inhibits ATF4 transcription factor activity by disrupting ATF4 dimerization and DNA-binding.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data suggest that endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced CHOP/Ddit3 inhibits expression of Bip/Grp78 and Atf4; ATF4, in turn, plays critical role in CHOP-mediated regulation of B-cell receptor-controlled murine gammaherpesvirus-68 lytic replication. (CHOP/Ddit3 = DNA-damage inducible transcript-3; Bip/Grp78 = chaperone BiP 78 kDa; Atf4 = activating transcription factor-4) PMID: 29305424
- The results suggest that ATF4 may serve a protective role in the mouse liver. PMID: 29845243
- Golgi stress response elicited by monensin stimulates CSE by acting via ATF4 with characteristics distinguishable from the endoplasmic reticulum stress response PMID: 29317536
- established Neuro2a cells with edited GADD34 and ATF4/GADD34 genes and found that ATF4 acts as a proapoptotic factor, but GADD34 depletion did not attenuate the expression of cleaved caspase-3 induced by tunicamycin treatment. PMID: 28825160
- Atg7 ablation mainly induced the PERK-ATF4-CHOP axis of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response in growth plate chondrocytes. PMID: 28304100
- under nutrient-limiting conditions that stimulate ATF4 activity, TRIB3 is implicated in the regulation of metabolic adaptation by restraining the transcription of Fgf21. PMID: 29378327
- these findings reveal a new crucial combined effect of the silencing of PERK and ATF4 in modulating ER stressmediated apoptosis during chondrocyte differentiation and proliferation. PMID: 28498443
- Sirt1 reduced endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis of brown adipocytes in vivo/in vitro by inhibiting Smad3/ATF4 signaling pathway. PMID: 28030827
- These findings indicate that the aggregation of S-opsin induced by exposure to blue -emitting diode light causes endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ATF4 activation in particular. PMID: 28331281
- We hypothesize that the essential role of methionine-charged initiator tRNA in forming ternary complex is responsible for the robust ability of methionine deficiency to induce ATF4 and the ISR even in the absence of GCN2 or eIF2alpha kinase activity. PMID: 27613409
- BTG1 has a role in regulating hepatic lipid metabolism and in preventing ATF4 and SCD1 from inducing liver steatosis PMID: 27188441
- Transcriptional profiling reveals that mouse neuroblastoma sphere-forming cells acquire a metabolic program characterized by transcriptional activation of the cholesterol and serine-glycine synthesis pathways, primarily as a result of increased expression of sterol regulatory element binding factors and Atf4, respectively PMID: 27705805
- MIF-2/D-DT is an early response cytokine in the I/R injury repair of the proximal tubule, enhancing regeneration through SLPI- and ATF4-dependent mechanisms. PMID: 28539339
- ATF4 has a role in gene expression during basal conditions, with 385 genes altered by the loss of ATF4 in the absence of apparent stress. Deletion of ATF4 alters genes that are required for the conversion of cholesterol to bile acid (CYP7A1), esterification of cholesterol (SOAT2), and transport from the hepatocyte (ABCA1); when ATF4 loss is coupled with ER stress, results in increase in free cholesterol within hepatocyte PMID: 26960794
- ATF4 pathway is activated in vivo upon mitochondrial stress. PMID: 28566324
- Data, including data from studies using cells from knockout mice, suggest that gasotransmitter H(2)S up-regulates eIF2a phosphorylation by inhibiting PPP1CA via persulfidation, which in turn leads to transient suppression of global translation and activation of Atf4 expression. (eIF2a = eukaryotic initiation factor-2alpha; PPP1CA = protein phosphatase 1 catalytic subunit alpha; Atf4 = activating transcription factor 4) PMID: 28637872
- Results identify the beneficial role of hypothalamic ATF4/ATG5 axis in the regulation of energy expenditure, obesity, and obesity-related metabolic disorders. PMID: 28213613
- SLC30A10 has a protective role in 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced toxicity via PERK-ATF4 pathway. PMID: 28688763
- ER stress-induced increase in ATF4 and CHOP expression is initiated by an increase in Atf4 and Chop mRNA, which is also dependent upon eIF2alpha phosphorylation. PMID: 28478109
- Augmented ATF4 signals during retinal degeneration plays a cytotoxic role by triggering photoreceptor cell death. PMID: 27144303
- ATF4 might inhibit the transcription of Srebp1c through TRB3, which is repressed by IBMX and DEX during early adipogenesis PMID: 27452504
- ATF4 activates a negative-feedback loop, leading to the downregulation of RET expression while upregulating expression of proapoptotic genes. PMID: 27935748
- Data demonstrate a novel function of ATF4 in agouti-related peptide neurons of the hypothalamus in energy balance and lipid metabolism. PMID: 27993927
- The role of dietary zinc in the expression of proteins involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response is reported. PMID: 27605406
- these results identify the ATF4-TRB3-AMPK axis as a novel pathway responsible for ethanol-induced liver steatosis. PMID: 27405764
- arsenic trioxide -mediated apoptosis is regulated by both endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria events that are facilitated by ATF4 and the unfolded protein response PMID: 27638049
- Findings indicate that PERK kinase-activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) pathway affected the efficiency of X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) mRNA splicing by regulating inositol-requiring enzyme 1alpha (IRE1alpha) expression. PMID: 27052593
- Interference with DOT1L activity resulted in transcriptional activation of Atf4 and Ddit3 accompanied by decreased levels of H3K79 dimethylation. PMID: 26299268
- results suggest that by inducing an atypical ISR and p53-independent apoptosis, ONC201 has clinical potential in hematological malignancies. PMID: 26884599
- TFEB-regulated signaling pathway for osteoblast differentiation is involved in ATF4/CHOP-dependent signaling pathway. PMID: 26519689
- These findings identify C/EBPgamma as a novel antioxidant regulator and an obligatory ATF4 partner that controls redox homeostasis in normal and cancerous cells. PMID: 26667036
- Gcn2 & Atf4 are involved in L-proline metabolism regulation in embryonic stem cells. PMID: 25857264
- This study outlines the mechanism of NIR laser phototoxicity and the utility of monitoring surface temperature and ATF4 expression as potential biomarkers to develop safe and effective clinical applications. PMID: 26030745
- ATF4 plays a pivotal role in functional expansion and repopulating efficiency of HSCs in developing FL PMID: 26384355
- results identify ursolic acid and tomatidine as potential agents and/or lead compounds for reducing ATF4 activity, weakness, and atrophy in aged skeletal muscle PMID: 26338703
- The CARE-LUC mouse model represents an innovative tool to investigate the eIF2alpha-ATF4 axis and to develop drugs targeting this important pathway in the remediation of related pathologies. PMID: 25921292
- exogenous overexpression of ATF4 in breast cancer cells may facilitate the recruitment of macrophages into tumor tissues and promote tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth indirectly. PMID: 25883982
- We conclude that ATF4 is a key regulator of the physiological state necessary for neuronal plasticity and memory. PMID: 25865882
- Elevation of ATF4, at least in liver, thus seems to be a shared feature of diets, drugs, genes, and developmental alterations that extend maximum lifespan in mice. PMID: 25156122
- ATF4 signaling pathway is essential for mediating the effect of ER stress on beta-klotho expression. PMID: 25727012
- The miR-214-ATF4 axis is a novel pathway for the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis. PMID: 25657009
- Target genes of ATF4 activity are not only important to osteoblast differentiation but also in maintaining bone toughness and fracture toughness. PMID: 24509412
- The minimum promoter region required for Mc3r expression has been identified, along with two binding sites for AP-1 and ATF4 and in the 5' upstream-flanking region of Mc3r that are essential for Mc3r expression. PMID: 25701401
- Fibroblasts from two long-lived mice mutants (Snell dwarf and PAPP-A knockout) were found to have higher levels of ATF4 protein expression suggesting a connection to longevity. PMID: 24691093
- FGF21 is the target gene for activating transcription factor 4. PMID: 24900988
- BMP-2 stimulates differentiation of myoblasts into osteoblasts via the PERK-eIF2alpha-ATF4 pathway but in addition stimulates Tmem119, which itself increases ATF4 PMID: 24362451
- Data (from studies in transgenic/knockout mice) suggest p21/Cdkn1a (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A) expression is up-regulated in immobilized, atrophied skeletal muscle via combined actions of Atf4 and p53 (transformation related protein 53). PMID: 24895282
- C/EBPbeta and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (but not tribbles homolog 3) are targeted for activation by activating ATF4, a member of cAMP response element-binding/activator transcription factor family. PMID: 24673832
- ATF4 expression in the liver is responsible for the protective effects against high fat diet-induced CYP2E1 expression. PMID: 24373582
- the loss of function of either DISC1 or ATF4 increases PDE4D9 transcription, and the association of DISC1 with the PDE4D9 locus requires ATF4 PMID: 23587879
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Nucleus speckle. Cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome.
-
蛋白家族:BZIP family
-
组织特异性:Ubiquitously expressed in adults.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:11911
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000105234
UniGene: Mm.641
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-17A (IL17A) (T26A) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
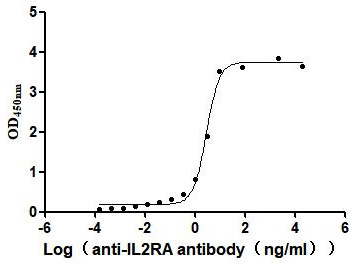
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha (IL2RA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
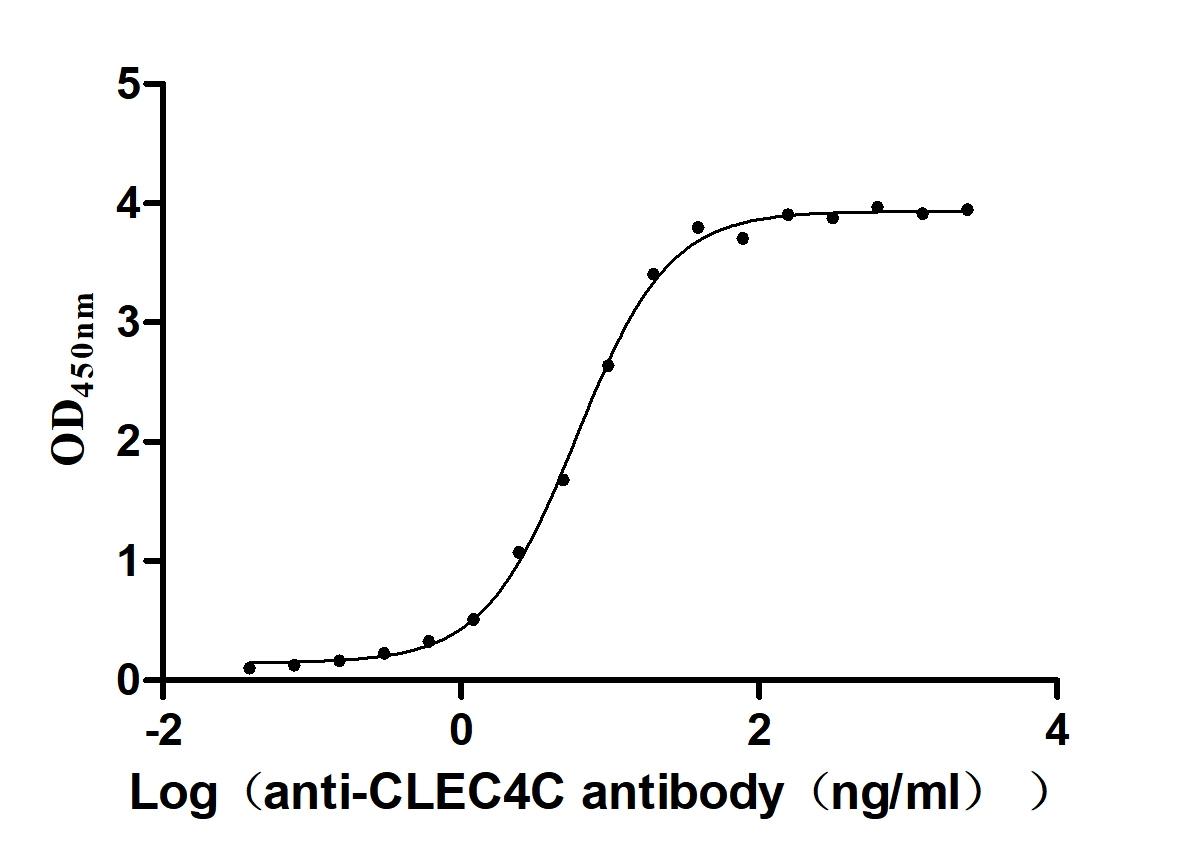
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis C-type lectin domain family 4 member C(CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1 (TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
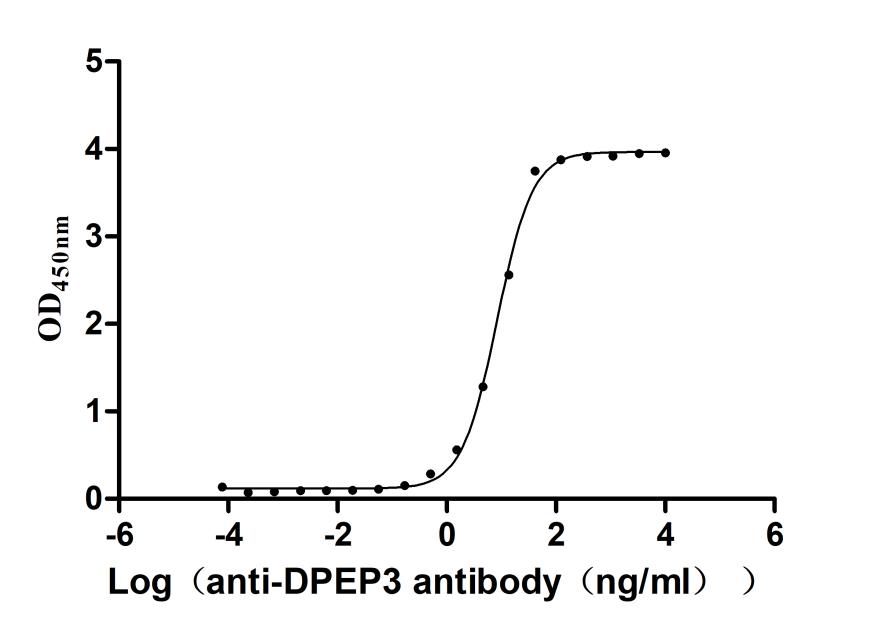
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)


-AC1.jpg)