Recombinant Human Krueppel-like factor 4 (KLF4)
-
货号:CSB-YP012394HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP012394HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP012394HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP012394HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP012394HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Endothelial Kruppel like zinc finger protein ; Epithelial zinc finger protein EZF; EZF; GKLF; gut Kruppel-like factor; Gut-enriched krueppel-like factor; KLF; KLF4; KLF4_HUMAN; Krueppel-like factor 4; Kruppel like factor 4 (Epithelial zinc finger protein EZF) (Gut enriched Krueppel like factor); Kruppel like factor 4 (gut)
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-513
-
氨基酸序列MRQPPGESDM AVSDALLPSF STFASGPAGR EKTLRQAGAP NNRWREELSH MKRLPPVLPG RPYDLAAATV ATDLESGGAG AACGGSNLAP LPRRETEEFN DLLDLDFILS NSLTHPPESV AATVSSSASA SSSSSPSSSG PASAPSTCSF TYPIRAGNDP GVAPGGTGGG LLYGRESAPP PTAPFNLADI NDVSPSGGFV AELLRPELDP VYIPPQQPQP PGGGLMGKFV LKASLSAPGS EYGSPSVISV SKGSPDGSHP VVVAPYNGGP PRTCPKIKQE AVSSCTHLGA GPPLSNGHRP AAHDFPLGRQ LPSRTTPTLG LEEVLSSRDC HPALPLPPGF HPHPGPNYPS FLPDQMQPQV PPLHYQGQSR GFVARAGEPC VCWPHFGTHG MMLTPPSSPL ELMPPGSCMP EEPKPKRGRR SWPRKRTATH TCDYAGCGKT YTKSSHLKAH LRTHTGEKPY HCDWDGCGWK FARSDELTRH YRKHTGHRPF QCQKCDRAFS RSDHLALHMK RHF
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor; can act both as activator and as repressor. Binds the 5'-CACCC-3' core sequence. Binds to the promoter region of its own gene and can activate its own transcription. Regulates the expression of key transcription factors during embryonic development. Plays an important role in maintaining embryonic stem cells, and in preventing their differentiation. Required for establishing the barrier function of the skin and for postnatal maturation and maintenance of the ocular surface. Involved in the differentiation of epithelial cells and may also function in skeletal and kidney development. Contributes to the down-regulation of p53/TP53 transcription.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- the downstream targets of KLF4-mCpG binding, guanine nucleotide exchange factors, serve as the effector of KLF4-induced mitochondrial fusion, cell cycle arrest, and cell protection. PMID: 29507094
- Human and mouse WNT10A mutant palmoplantar and tongue epithelia also display specific differentiation defects that are mimicked by loss of the transcription factor KLF4. PMID: 28589954
- The KLF4 might be a potential marker to predict prognosis in solid cancer patients. PMID: 29940144
- SOX5 overexpression increased Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) gene expression, which was decreased by SOX5 silencing. KLF4 knockdown abrogated the suppressive effect of SOX5 overexpression on osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs. PMID: 29890823
- Results showed that SIRT1 interacts with and deacetylated KLF4. The deacetylation by SIRT1 promoted nuclear accumulation of KLF4 and enhanced the binding of KLF4 to the CLDN5 promoter in the nucleus. PMID: 28888043
- miR-145 promotes hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by targeting KLF4. PMID: 28091538
- These findings identify a novel regulatory loop between miR-34a and KLF4 during keratinocytes replicative senescence. PMID: 29580988
- Knockdown of KLF4 promoted the migration and invasion of nonsmallcell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells, whereas rescue of KLF4 expression reduced cell motion ability in miR25overexpressing NSCLC cells. PMID: 29568911
- the subcellular localization of Klf4 might be related to the resistance of A549 cells to cisplatin. PMID: 29665649
- s observed that saRNAs induced overexpression of KLF4 could promote cell migration/invasion in NCM460 and HCT116 cell lines. PMID: 29274293
- This is, to our knowledge, the first report of decreased expression of TFF3, SPDEF, KLF4, and goblet cell population in the colon of patients with HSCR. Altered goblet cell function may result in intestinal barrier dysfunction contributing to the development of HAEC. PMID: 29383490
- KLF4 overcomes tamoxifen resistance by suppressing MAPK signaling pathway and predicts good prognosis in breast cancer. PMID: 28988130
- KLF4 activated the transcription activity of iNOS promoter in MH7A cells stimulated by TNF-alpha. This study indicates that KLF4 is important for regulating the expression of iNOS by TNF-alpha in human synoviocytes. PMID: 28744810
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer cells show high expression of KLF4, and KLF4 expression is necessary for maintaining the undifferentiated phenotype and drug resistance. PMID: 28920531
- KLF4 could transcriptionally inhibit Cav-1 expression by binding directly to the promoter domain of Cav-1. PMID: 29587259
- Impairment of IGF2 gene expression in prostate cancer is triggered by epigenetic dysregulation of IGF2-DMR0 and its interaction with KLF4 PMID: 29017567
- Data show that Kruppel like factor 4 (KLF4) was overexpressed in met proto-oncogene protein (c-Met)-overexpressing non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells and tissues. PMID: 29624806
- KLF4 may act as an administered indicator to assess whether adjuvant postoperative pharmaceutical therapy is needed for patients with colorectal cancer. Low KLF4 expression was significantly correlated with reductions of overall survival and recurrence rate. PMID: 28752861
- Lower expression of KLF4 and NDRG2 in colorectal cancer patients was correlated with poor overall survival. Thus, KLF4 inhibited the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells dependent on NDRG2 signaling, which provides a novel strategy for therapy and early diagnosis of colorectal cancer. PMID: 28656310
- KLF4 is downregulated in anaplastic meningioma compared with low-grade meningioma subtypes. By manipulating KLF4 expression in anaplastic meningioma stem-like cells, this study demonstrated that KLF4 acts as a tumor suppressor during malignant progression in meningioma, affecting apoptosis, proliferation, invasion, and cell cycle. PMID: 28651379
- KLF4 was a direct target of miR-212, and miR-212 repressed KLF4 expression in a post-transcriptional manner. Moreover, miR-212-mediated protection effects were abated following KLF4 expression restoration in MPP-induced SH-SY5Y cells, represented as lowered cell viability and enhanced apoptotic rate. PMID: 29611404
- Results revealed that novel crosstalk between KLF4 and ZEB1 regulated gemcitabine resistance in PDAC. PMID: 28849150
- This is the first demonstration that dysregulated KLF4 expression associates with poor differentiation of pancreatic cancer. Epigenetic activation of miR-152/DNMT1/KLF4 signaling pathway by dietary DIM causes differentiation and significant growth inhibition of pancreatic cancer cells, highlighting its translational implications for pancreatic and other cancers. PMID: 28659310
- The present study found that the KLF4 and KLF5 3'-UTR contains one conserved target site of miR-506 and miR-124, and the overexpression of miR-506 and miR-124 inhibited the H2O2-induced upregulation of KLF4 and KLF5 in HCMs. PMID: 28849090
- KLF4 enhances the sensitivity of cisplatin to ESCC cells through apoptosis induction and cell cycle arrest. PMID: 28694421
- KLF4 was identified as an important regulatory factor in the host response to fungi and as a controlling element in the IL-6 immune response with a unique expression pattern comparing fungal and lipopolysaccharide stimulation. PMID: 27346433
- level in vascular endothelium decreased with age PMID: 29030550
- Results showed the expression levels of KLF4 were increased in bladder cancer (BC) patients which strongly correlated with the expression levels of PTBP1 but inversely correlated with the expression level of miR-145. These findings suggest that KLF4 is likely to positively contribute to carcinogenesis in certain types of BC. PMID: 28380435
- Transcriptional inhibition of MSI2 expression by KLF4 occurred in multiple PDAC cell lines as well as mouse models of PDAC. Lost expression of KLF4, a transcriptional repressor of MSI2 results in overexpression of MSI2 in PDACs, which may be a biomarker for accurate prognosis. A dysregulated KLF4/MSI2 signaling pathway promotes PDAC progression and metastasis. PMID: 27449499
- the results of the present study demonstrated that by regulating KLF4, miR145 may be involved in regulating smooth muscle differentiation of ASCs induced by TGFbeta1 and BMP4. PMID: 28440409
- our findings reveal KLF4 as a key regulator of miR-182 cluster expression in hESCs and a main contributor to its aberrant expression in melanoma and potentially in other tumors PMID: 28412746
- Surprisingly, 116 genes are directly activated via mCpG-dependent KLF4 binding activity. In-depth mechanistic studies reveal that recruitment of KLF4 to the methylated cis-regulatory elements of these genes result in chromatin remodeling and transcription activation. PMID: 28553926
- KLF4 transcriptionally repressed FOXO1 expression in glioma cells, contributing to glioma cell invasion and growth. PMID: 27835585
- Data suggest that KLF4 could promote cell senescence through a complex network: miR-203, survivin, and p21, which were all regulated by overexpression of KLF4 and contributed to cell senescence. PMID: 27531889
- Our results establish KLF4alpha as a KLF4 isoform that opposes the function of KLF4(FL) and as an important factor in the complex and unresolved role of KLF4(FL) in breast carcinogenesis. PMID: 27323810
- Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) inactivation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia correlates with promoter DNA-methylation and can be reversed by inhibition of NOTCH signaling. PMID: 27081174
- Data suggest that the Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) /telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT)/MAPK pathway is a potential new therapeutic target for lung cancer. PMID: 27153563
- The expression of KLF4 was significantly increased in human osteosarcoma tissues compared with the normal tissues. Elevated KLF4 promoted human osteosarcoma cell proliferation and metastasis. Mechanistic studies revealed KLF4 specifically bound the promoter of CRYAB and upregulated CRYAB expression in human osteosarcoma cells. PMID: 27105535
- In urothelial bladder carcinoma, strong KLF4 expression was associated with higher risk of metastasis and death. KLF4 positively correlates with TWIST1 and vimentin, and inversely with E-cadherin. In vitro, it is accompanied by decreased E-cadherin and beta-catenin, increased vimentin and fibronectin, and enhanced migration/invasion. KLF4 knockdown suppressed TWIST1 expression and EMT, migration and invasion. PMID: 27519276
- TGF-beta1 down-regulated KLF4 by activating miR-135a-5p, promoting proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma PMID: 27302923
- our data suggest that KLF4 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition -enhanced hepatocellular carcinoma growth and invasion PMID: 27102441
- CSF and plasma expression of KLF4 mRNA was significantly decreased around 1-3 days after subarachnoid hemorrhage and remained lower than in controls. PMID: 28893694
- PARP1 recruits KLF4 to activate telomerase expression and stem cell pluripotency, indicating a positive regulatory role of the PARP1-KLF4 complex in telomerase expression in cancer and stem cells. PMID: 28985359
- KLF2 and KLF4 serve as important regulators that promote hemoglobin alpha expression in the endothelium. PMID: 28825355
- Loss of KLF4 expression is associated with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PMID: 27872496
- IRF4 protects arteries against neointima formation by promoting the expression of KLF4 by directly binding to its promoter. PMID: 28851732
- High KLF4 expression is associated with breast cancer tumorigenesis. PMID: 28068319
- High KLF4 expression is associated with melanoma. PMID: 28068326
- KLF4 transactivates Ch25h and LXR, thereby promoting the synergistic effects between ECs and macrophages to protect against atherosclerosis susceptibility. PMID: 28794002
- findings evidence a positive correlation between SIRT1 and BCL6 expression increase in follicular lymphomas (FL) . SIRT1 methylation decreases in FL and diffuse large-B cell lymphomas (DLBCL)and this parallels the increase of KLF4, DAPK1 and SPG20 methylation PMID: 28324774
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Krueppel C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6348
OMIM: 602253
KEGG: hsa:9314
UniGene: Hs.376206
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 (TNFRSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Poliovirus receptor (PVR) (I340M), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
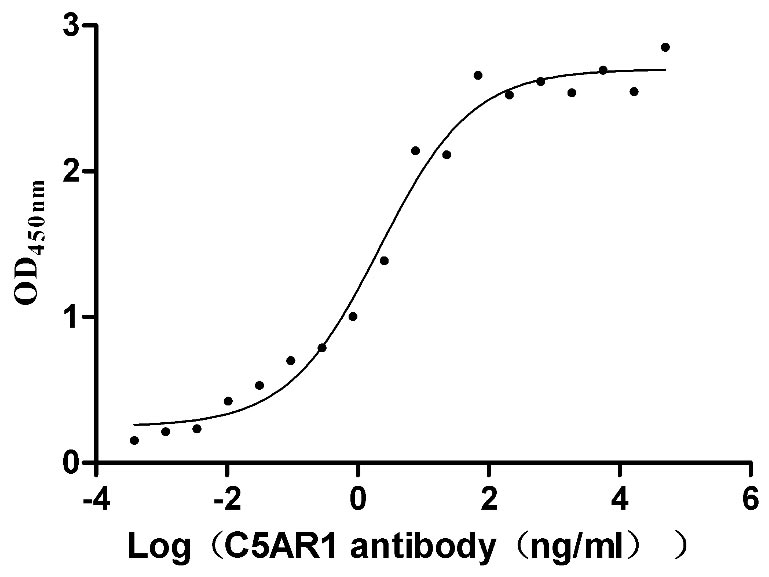
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
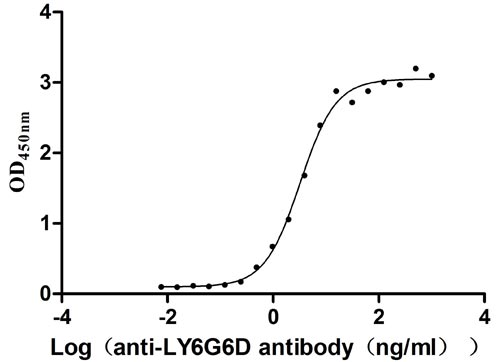
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
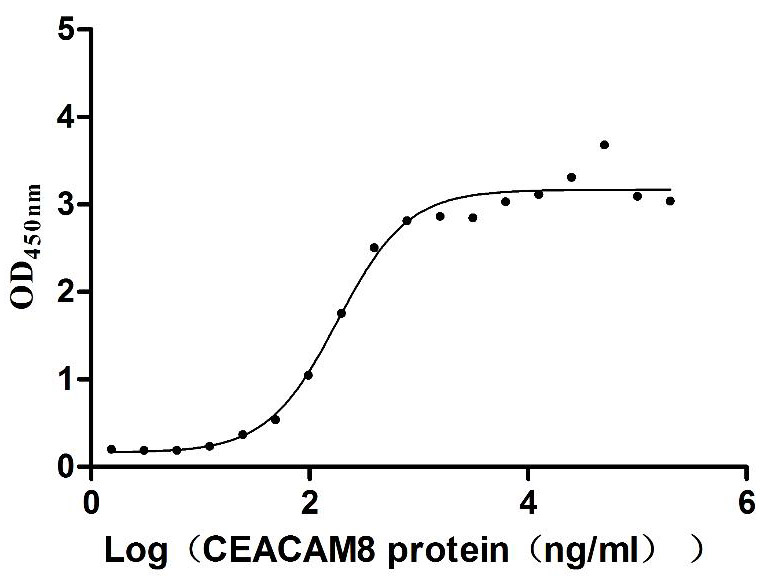
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
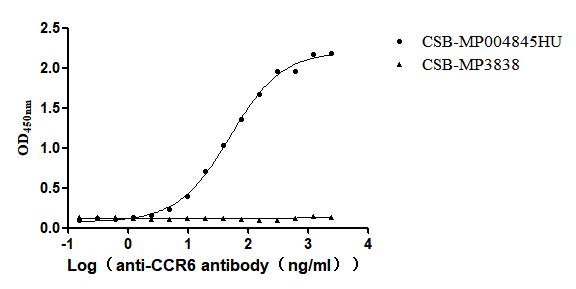
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)