Recombinant Human Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2D (KMT2D), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP014628HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP014628HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP014628HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP014628HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP014628HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:AAD10; ALL1 related gene; ALL1-related protein; ALR; CAGL114; Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase MLL2; KABUK1; Kabuki make up syndrome; Kabuki mental retardation syndrome; KMS; KMT2B; KMT2D; Lysine N methyltransferase 2D; Lysine N-methyltransferase 2B; MLL2; MLL2_HUMAN; MLL4; Myeloid/lymphoid or mixed lineage leukemia 2; Myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia protein 2; TNRC21; Trinucleotide repeat containing 21
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:partial
-
表达区域:Name:KMT2D Synonyms:ALR, MLL2, MLL4
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Histone methyltransferase that catalyzes methyl group transfer from S-adenosyl-L-methionine to the epsilon-amino group of 'Lys-4' of histone H3 (H3K4). Part of chromatin remodeling machinery predominantly forms H3K4me1 methylation marks at active chromatin sites where transcription and DNA repair take place. Acts as a coactivator for estrogen receptor by being recruited by ESR1, thereby activating transcription.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Clinical and neurobehavioral features of three novel Kabuki Syndrome unrelated patients with mosaic KMT2D mutations have been described. PMID: 29283410
- Results indicate that overexpression of MLL2 predicts poor clinical outcomes and facilitates ESCC tumor progression, and it may exert oncogenic role via activation of EMT. PMID: 29532228
- results reveal a critical role for KMT2D in the control of epithelial enhancers and p63 target gene expression, including the requirement of KMT2D for the maintenance of epithelial progenitor gene expression and the coordination of proper terminal differentiation. PMID: 29440247
- a congenital heart defects (CHD)is detected in 70% of patients with KMT2D (MLL2) pathogenic variants, most commonly left-sided obstructive lesions, including multiple left-sided obstructions similar to those observed in the spectrum of the Shone complex, and septal defects. PMID: 28884922
- analysis of highly recurrent genetic lesions in components of the NF-kappaB pathway, of NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 as well as KMT2D that may have a role in ocular adnexal MALT-type marginal zone lymphomas PMID: 27566587
- Results highlight the emerging role of mutations in epigenetic regulators, particularly MLL2, in cervical carcinogenesis, which suggests a potential disruption of histone modifications. PMID: 28390392
- Mutations of ARID1A, GPRC5A and MLL2 grant bladder cancer non-stem cells the capability of self-renewal. PMID: 27387124
- Study reports mutation screening in patients with Kabuki Syndrome Subtype 2 (KS2), in which 12 novel KDM6A mutations are identified. These results confirm that female patients with KS2 may have a rather mild manifestation of KS and may even develop normally with regard to cognitive function. PMID: 27302555
- The uniqueness of our case is the sporadic co-occurrence of two genetic disorders, that is, a de novo frameshift variant in the KMT2D gene and a de novo 3.2 Mbp 10q22.3q23.1 deletion. PMID: 28590022
- KMT2D mutation is associated with small Cell Lung Cancer. PMID: 28007623
- Two patients' presentation of Kabuki syndrome has been described caused by different KMT2D mutations, both including an interrupted/bipartite clavicle. PMID: 28256057
- data support akey role forKMT2D in modulating the chromatin competence necessary for the assembly of the ER-FOXA1-PBX1 transcriptional regulatory network in breast cancer. PMID: 28336670
- A possible correlation between the position of the KMT2D premature termination codon caused by the mutation and height SDS was assessed, but a significant difference could not be observed for the Kabuki syndrome patients PMID: 27530205
- KMT2D p.Gln3575His segregated with disease status in the family, and is associated with a unique and conserved phenotype in the affected family members, with features overlapping with Kabuki and CHARGE syndromes. Our findings further support the potential etiological link between these two classically distinct conditions. PMID: 27991736
- Three of four cases of histiocytic sarcoma had alterations in the KMT2D gene. PMID: 28805986
- Study shows the contribution of MLL2's methyltransferase and CXXC domain in the trimethylation of H3K4 in embryonic stem cells and find that while it trimethylates H3K4 at both bivalent gene promoters and non-TSS elements, it regulates transcription at a limited number of genes including those required for primordial germ cell specification. PMID: 28157506
- KMT2D Mutation is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PMID: 27749841
- MLL1 and MLL2 collaborate to regulate gene expression and leukemia maintenance not through redundancy, but through distinct pathways. PMID: 28609655
- Our findings provide evidence that CHARGE and Kabuki syndromes result from dysregulatrion of CHD7 and KMT2D genes involved embryonal development that are expressed in a tissue-specific manner. PMID: 28475860
- we demonstrate that low KMT2C and KMT2D expression in biopsies defines better outcome groups in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma PMID: 27280393
- We identify three mosaic missense and likely-gene disrupting mutations in genes previously implicated in ASD (KMT2C, NCKAP1, and MYH10) in probands but none in siblings. We find a strong ascertainment bias for mosaic mutations in probands relative to their unaffected siblings PMID: 27632392
- The enzymatic activity of H3K4 methyltransferase MLL4 is required for its protein stability. PMID: 28013028
- We have reported a female Kabuki syndrome patient with typical dysmorphic features and developmental delay and a novel KMT2D mutation. PMID: 25944076
- Pygo2 functions as a prognostic factor for glioma due to its up-regulation of H3K4me3 and promotion of MLL1/MLL2 complex recruitment. PMID: 26902498
- Mutation in the MLL2 gene is associated with Kabuki Syndrome. PMID: 26757828
- Data suggest that lysine methyltransferase 2D (KMT2D) mutations are rare in abdominal paraganglioma (PGLs). PMID: 26303934
- high proportion of recurrent somatic DICER1 and KMT2D mutations in this series of sporadic IO-MEPL points to their likely important roles in the molecular pathogenesis of these rare embryonal tumors PMID: 26841698
- Whereas Set1 targets are largely associated with the maintenance of the stem cell population, MLL1/2 targets are specifically enriched for genes involved in ciliogenesis. PMID: 26711341
- Although enhancer priming by MLL4/KMT2D is dispensable for cell-identity maintenance in mouse, it controls cell fate transition by orchestrating p300-mediated enhancer activation PMID: 27698142
- Our data suggest that MLL2 protein is overexpressed in primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B cell lymphoma and appears as a prognostic factor PMID: 26722499
- The results do not support our hypothesis that common germline genetic variants in the MLL2 genes is associated with the risk of developing medulloblastoma. PMID: 26290144
- Mutations in KMT2D gene is associated with cutaneous T cell lymphoma and Sezary syndrome. PMID: 26551667
- In patients with Kabuki Syndrome, autosomal dominant KMT2D mutations are associated with dysregulation of terminal B-cell differentiation, leading to humoral immune deficiency and, in some cases, autoimmunity. PMID: 26194542
- KMT2D represents a recurrently mutated gene with potential implication for pheochromocytoma development. PMID: 26032282
- Identify MLL4 as a major mammalian H3K4 mono- and di-methyltransferase essential for enhancer activation during cell differentiation. PMID: 24368734
- Like KMT2D, CHD7 interacts with members of the WAR complex, namely WDR5, ASH2L and RbBP5. We therefore propose that CHD7 and KMT2D function in the same chromatin modification machinery. PMID: 24705355
- KMT2D mutations may promote malignant outgrowth by perturbing the expression of tumor suppressor genes that control B cell-activating pathways PMID: 26366710
- findings suggest that KMT2D acts as a tumor suppressor gene whose early loss facilitates lymphomagenesis by remodeling the epigenetic landscape of the cancer precursor cells PMID: 26366712
- Reduced or lost expression of MLL2 was commonly observed in tumor tissues as compared with paired adjacent non-tumor tissues regardless of mutation status. PMID: 25112956
- Mutations in MLL2 are present in approximately 27% of urothelial carcinoma cases . PMID: 26138514
- Results from targeted sequencing in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia identified KMT2D and KIF1B as novel putative driver genes and a putative regulatory non-coding variant that coincided with overexpression of the growth factor MDK. PMID: 25355294
- 10 out of the 11 mutations found in patients with Kabuki syndrome were novel. KMT2D mutations included four small deletions or insertions and four nonsense and two missense mutations. PMID: 24739679
- Data identified mutations in epigenetic modifiers such as KMT2D as potential early driving events in lymphomagenesis and immune escape alterations as relapse-associated events in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. PMID: 25123191
- MLL2 mutation positive patients have a more severe and typical Kabuki phenotype than the MLL2 mutation negative group. PMID: 23320472
- Study supports that KMT2D has distinct roles in neoplastic cells, as opposed to normal cells. PMID: 24240169
- MLL3 and MLL4 function in the regulation of enhancer activity. PMID: 24081332
- The identification of novel MLL2 mutations in patients with Kabuki syndrome. PMID: 23913813
- these results indicate that the suppression of MLL genes, especially MLL2 and MLL5, take part in modulating breast carcinogenesis. PMID: 23754336
- Data indicate that seven genes showed statistical enrichment for mutation: TP53, RB1, PTEN, NFE2L2, KEAP1, MLL2, and PIK3CA. PMID: 24323028
- MLL4 (KMT2D) is a major H3K4 mono- and di-methyltransferase with partial functional redundancy with MLL3 (KMT2C) in mouse and human cells. MLL4 is enriched on enhancers and is required for enhancer activation, cell-type-specific gene expression and cell differentiation. PMID: 24368734
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Kabuki syndrome 1 (KABUK1)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Class V-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily, Histone-lysine methyltransferase family, TRX/MLL subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed in most adult tissues, including a variety of hematoipoietic cells, with the exception of the liver.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 7133
OMIM: 147920
KEGG: hsa:8085
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000301067
UniGene: Hs.731384
Most popular with customers
-
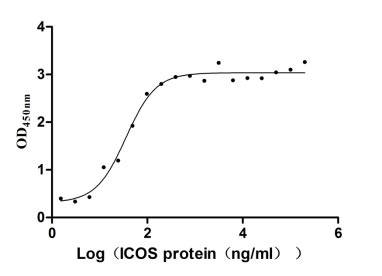
Recombinant Human ICOS ligand (ICOSLG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
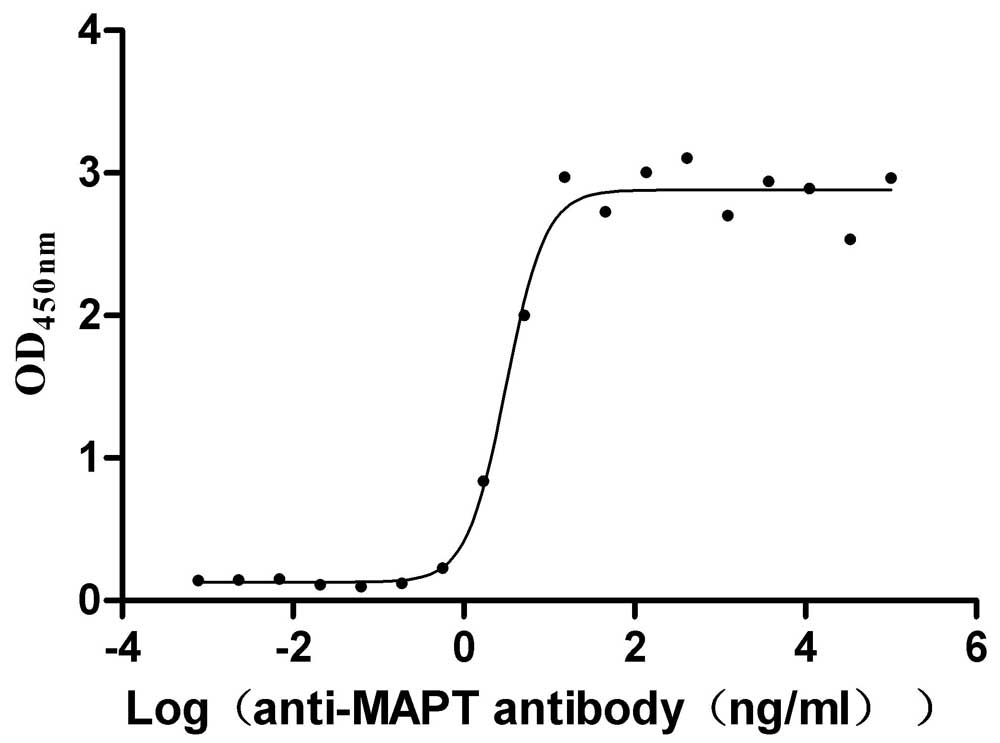
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
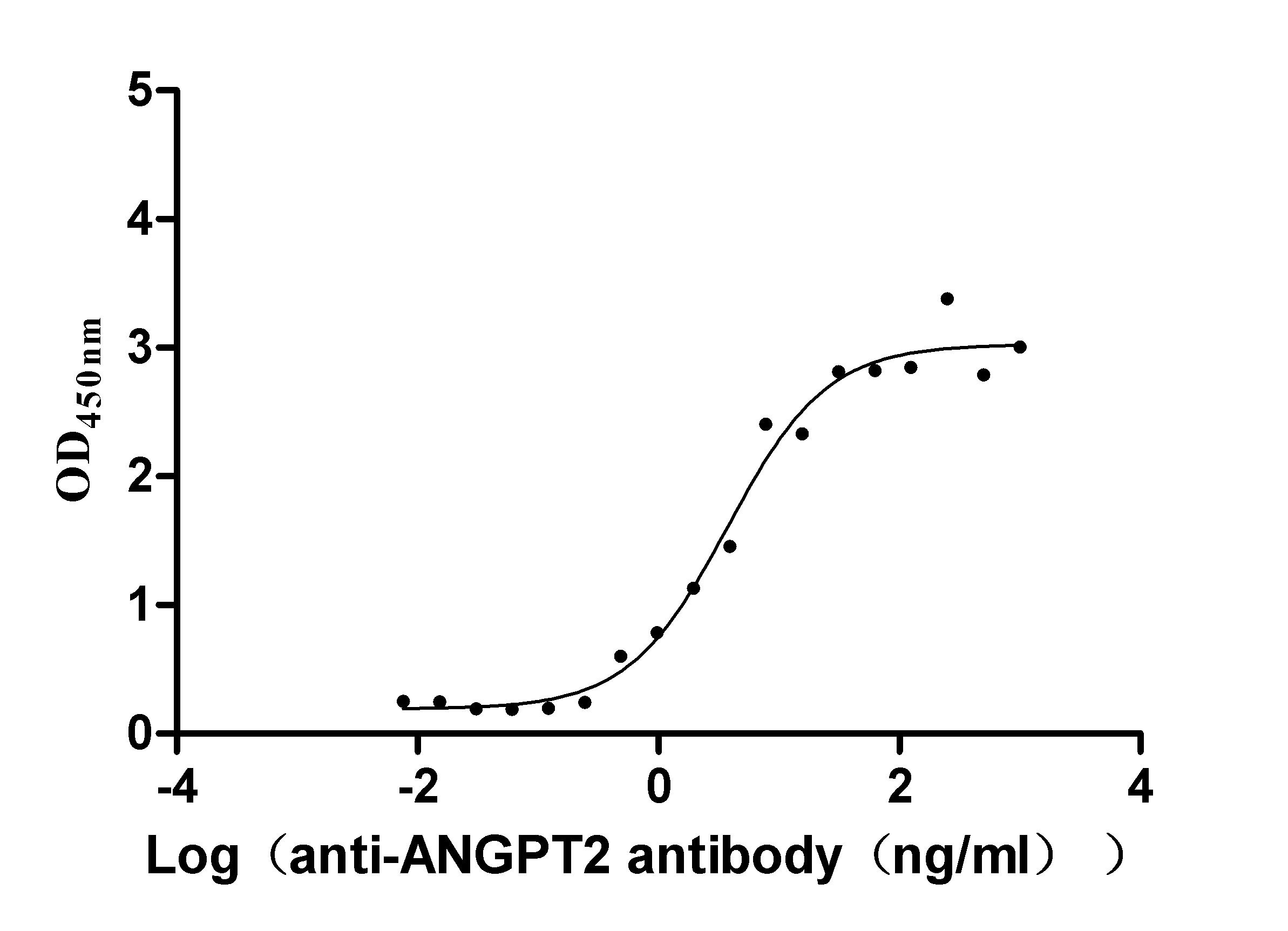
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
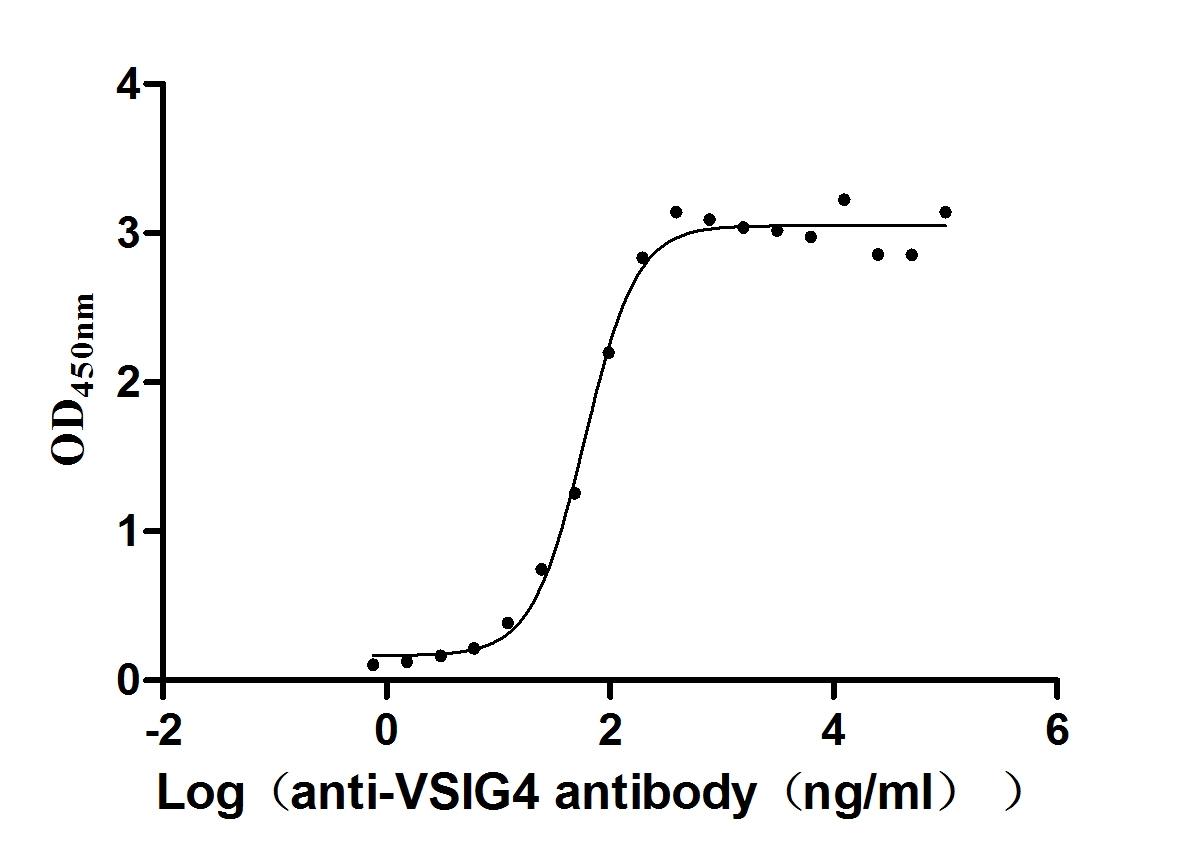
Recombinant Human V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4 (VSIG4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
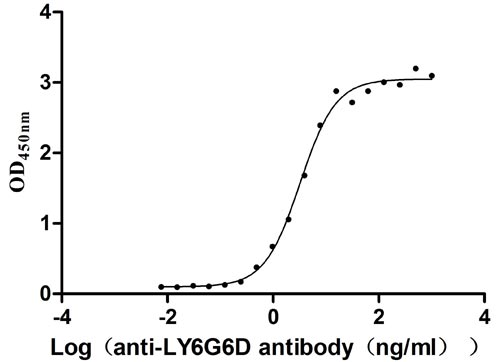
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
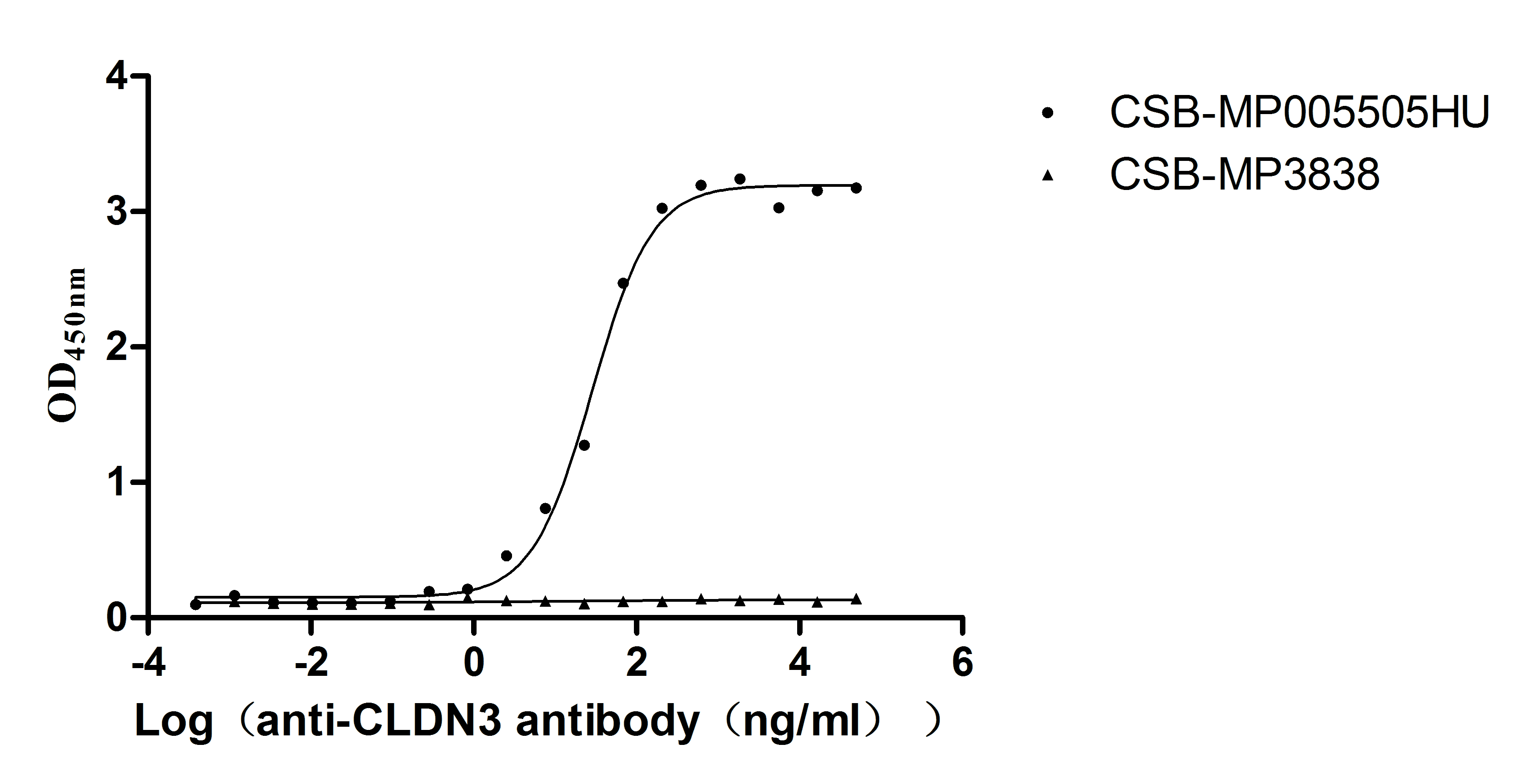
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)










