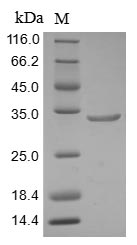
Recombinant Human AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1A (ARID1A), partial
In Stock-
货号:CSB-BP002058HU1
-
规格:¥3168
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily F member 1; ARI1A_HUMAN; ARID domain containing protein 1A; ARID domain-containing protein 1A; ARID1A; AT rich interactive domain 1A (SWI like); AT rich interactive domain 1A; AT rich interactive domain containing protein 1A; AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1A; B120; BAF250; BAF250A; BM029; brain protein 120 ; BRG1 associated factor 250; BRG1 associated factor 250a; BRG1-associated factor 250; BRG1-associated factor 250a; C1ORF4; chromatin remodeling factor p250 ; chromosome 1 open reading frame 4; ELD; hELD; hOSA1; matrix-associated; MRD14; Osa homolog 1; OSA1; OSA1 nuclear protein ; P270; SMARCF1; SWI like protein; SWI SNF complex protein p270; SWI-like protein; SWI/SNF complex protein p270; SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily f, member 1; SWI/SNF-related
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
分子量:32.4 kDa
-
表达区域:1976-2231aa
-
氨基酸序列SLAKRCVCVSNTIRSLSFVPGNDFEMSKHPGLLLILGKLILLHHKHPERKQAPLTYEKEEEQDQGVSCNKVEWWWDCLEMLRENTLVTLANISGQLDLSPYPESICLPVLDGLLHWAVCPSAEAQDPFSTLGPNAVLSPQRLVLETLSKLSIQDNNVDLILATPPFSRLEKLYSTMVRFLSDRKNPVCREMAVVLLANLAQGDSLAARAIAVQKGSIGNLLGFLEDSLAATQFQQSQASLLHMQNPPFEPTSVDMM
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Involved in transcriptional activation and repression of select genes by chromatin remodeling (alteration of DNA-nucleosome topology). Component of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes that carry out key enzymatic activities, changing chromatin structure by altering DNA-histone contacts within a nucleosome in an ATP-dependent manner. Binds DNA non-specifically. Belongs to the neural progenitors-specific chromatin remodeling complex (npBAF complex) and the neuron-specific chromatin remodeling complex (nBAF complex). During neural development a switch from a stem/progenitor to a postmitotic chromatin remodeling mechanism occurs as neurons exit the cell cycle and become committed to their adult state. The transition from proliferating neural stem/progenitor cells to postmitotic neurons requires a switch in subunit composition of the npBAF and nBAF complexes. As neural progenitors exit mitosis and differentiate into neurons, npBAF complexes which contain ACTL6A/BAF53A and PHF10/BAF45A, are exchanged for homologous alternative ACTL6B/BAF53B and DPF1/BAF45B or DPF3/BAF45C subunits in neuron-specific complexes (nBAF). The npBAF complex is essential for the self-renewal/proliferative capacity of the multipotent neural stem cells. The nBAF complex along with CREST plays a role regulating the activity of genes essential for dendrite growth.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Cells lacking ARID1A show enhanced AURKA transcription, which leads to the persistent activation of CDC25C, a key protein for G2/M transition and mitotic entry. PMID: 30097580
- the correlation between the loss of ARID1A immunoreactivity and reduced ARID1B levels indicates that ARID1B could be an attractive target for anti-cancer therapy. PMID: 29890703
- these data suggest that the combined treatment with PI3K inhibitor BKM120 and PARP inhibitor olaparib may be a promising therapeutic regimen for the treatment of gastric cancer, and ARID1A deficiency could serve as a potential predictive therapeutic biomarker. PMID: 29767248
- Although Genome-Wide Association studies have not been carried out in the field of alcohol-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), common single nucleotide polymorphisms conferring a small increase in the risk of liver cancer risk have been identified. Specific patterns of gene mutations including CTNNB1, TERT, ARID1A and SMARCA2 exist in alcohol-related HCC. [review] PMID: 28296015
- The s find that ARID1A has a dominant role in maintaining chromatin accessibility at enhancers, while the contribution of ARID1B is evident only in the context of ARID1A mutation. PMID: 28967863
- ARID1A and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (Her-2) status were found to be independent prognostic factors of both overall survival (OS) and disease free survival (DFS). PMID: 28543794
- ARID1A expression loss was associated with poor overall survival in Asians with gastric cancer. [meta-analysis] PMID: 27354232
- the significant correlation was achieved between the negative ARID1A expression and the FIGO stage of endometrium-related gynecological cancers, but not the other characteristics. PMID: 28466574
- This metaanalysis indicated that Gastric Cancer or Colorectal Cancer with ARID1A alteration might be a marker of poor prognosis. The ARID1A alteration of Gastric Cancer may result from different epigenetic factors. PMID: 28937020
- Low ARID1A expression is associated with clear cell and endometrioid carcinoma of the ovary and the endometrium. PMID: 29451900
- Loss of PTEN and ARID1A expression is highly specific for malignancy in effusion pathology PMID: 29170871
- We propose a signaling cascade involving ARID1A, GADD45B and DUSP1 as mediators of the romidepsin effects in GCC cells. PMID: 27572311
- head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients with tumors having high level of miR-31 expression and high levels of Nanog/OCT4/Sox2/EpCAM expression, together with low level of ARID1A expression, were found to have the worst survival PMID: 27528032
- loss of ARID1A leads to accumulation of ROS; elesclomol may be used to target ARID1A-mutant gynecologic cancer cells PMID: 27486766
- genomic data and clinical features of four patients carrying a small 1p36.11 microduplication encompassing the complete ARID1A gene PMID: 27906199
- Data show that 38 samples of 82 ovarian clear cell carcinoma (CCC) specimens presented no BAF250a expression, and 50 samples exhibited the loss of at least one subunit of the SWI/SNF complex. PMID: 27340867
- Partial loss (i.e. in one tissue section some cells stained positive for BAF250a while other cells, usually an adjacent group, were negative) of BAF250a protein was identified in 36% (9/25) of rectovaginal DIE samples, 40% (2/5) of endometriosis lesions involving the PSLN, 30% (6/20) of endometriomas, and also in 25% (5/20) of endometrium from controls. PMID: 26832958
- In the very high-risk Bladder Cancer patients , several genes had a higher frequency of mutations than reported in the The Cancer Genome Atlas database, including ARID1A . Mutation associations with receipt of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, nodal involvement, metastatic disease development, and survival were analyzed. PMID: 27520487
- Tumors accumulate ARID1A mutations. PMID: 27172896
- ARID1A silencing could significantly enhance the capability of migration and invasion in lentivirus miR-144-3p cells. PMID: 29073615
- we identified concurrent ARID1A and ARID1B inactivating mutations with consequent loss of protein expression in the undifferentiated component of approximately one-quarter of dedifferentiated endometrial and ovarian carcinomas PMID: 27562491
- Our study provides a novel insight into the modulatory function and mechanism of ARID1A in PI3K/AKT signaling in gastric cancer PMID: 27323812
- Of the 34 undifferentiated endometrial carcinomas examined, 17 (50%) exhibited SWI/SNF complex inactivation, with 11 tumors showing complete loss of both ARID1A and ARID1B, 5 showing complete loss of BRG1 and 1 showing complete loss of INI1. Ten of the remaining 17 undifferentiated carcinomas showed the following alterations: 5 tumors (15%) showed loss of ARID1A only with intact ARID1B, BRG1, and INI1 expression. PMID: 28863077
- BAF250a loss in AE is consistently associated with the development of BAF250a-negative endometriosis-associated cancers and appears to be an early event in most of these cases. PMID: 27051059
- Transcriptome analysis revealed ARID1A knockdown led to miR-503 upregulation. CDKN2A was identified as a target of miR-503, which contributes to cell senescence. Thus, the data suggests that ARID1A deficiency promote KRAS(G12D)-driven pancreatic tumorigenesis through miR-503/CDKN2A-mediated senescence. PMID: 28942143
- ARID1A may be a primary driver of carcinogenesis in a subset of esophageal adenocarcinomas PMID: 28440661
- ARID1A mutation inactivates the apoptosis-promoting function of p53 by upregulating HDAC6, indicating that pharmacological inhibition of HDAC6 is a therapeutic strategy for ARID1A-mutated cancers. PMID: 28737768
- ARID1A mutation can be an early stage event in the oncogenic transformation of endometriosis cells giving rise to ovarian clear cell carcinoma. PMID: 28483516
- ARID1A expression is significantly decreased in higher stages of urothelial carcinoma and its aggressive variants. PMID: 27137986
- Our data suggests that deficiency or loss of functional mutations of ARID1A in HCC cells might contribute to the increased activity of certain cancer-promoting lncRNAs. PMID: 28716731
- ARID1A loss lacks prognostic significance in early stage colorectal adenocarcinoma. PMID: 26980037
- ARID1A may play an important role in the early events of gastric carcinogenesis. PMID: 28031120
- loss of ARID1A is more common in advanced GC and is related to EBV positivity and MMR deficiency PMID: 26067140
- ARID1A protein and mRNA expression was lower in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma tissue than in normal liver tissue. PMID: 27433094
- Most HCCs had an increased level of ARID1A mRNA. PMID: 26589513
- loss of ARID1A protein expression found in TU-OC-2 cells. PMID: 26960408
- Inactivating mutations in ARID1A may be involved in a novel pathway of carcinogenesis in biliary carcinomas PMID: 27334809
- loss of ARID1A shortened time to cancer-specific mortality, and to recurrence of cancer when adjusting for potential confounders (Meta-Analysis) PMID: 26384299
- loss of ARID1A protein expression caused by inactivating mutations reactivates TERT transcriptional activity and confers a survival advantage of tumor cells by maintaining their telomeres. PMID: 26953344
- All cases with ARID1A expression are overlapped with H2B high expression. Among 15 cases with ARID1A and H2B coexpression, 13 are invasive ductal carcinoma and 2 are mucinous carcinoma. Our results indicate that ARID1A gene may be involved in carcinogenesis of some subtypes of breast cancer. PMID: 26904685
- The action of ARID1A in carcinogenesis differs between adenofibroma-related clear cell carcinoma and endometriosis-related clear cell carcinoma. PMID: 25913291
- we focus on the relationships of ARID1A mutations with ovarian and endometrial cancers[review] PMID: 26572704
- analysis of ARID1A, CDH1, cMET and PIK3CA expression and target-related microRNA expression in gastric cancer PMID: 26334097
- The loss of ARID1A was correlated with late-stage and endometriosis-associated ovarian clear cell carcinoma. ARID1A expression may predict the risk of recurrence. PMID: 26945423
- Complete or partial loss of ARID1A expression is considered an independent poor prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer. PMID: 26826411
- ARID1A positively regulates Klf15 expression with PGR to inhibit epithelial proliferation at peri-implantation. Our results suggest that Arid1a has a critical role in modulating epithelial proliferation which is a critical requisite for fertility PMID: 26378916
- Our results indicate that the Arid1a tumour suppressor gene has a key role in regulating ovarian endometrioid carcinoma differentiation PMID: 26279473
- Arid1A role in genome-wide transcriptional regulation by SWI/SNF complexes. PMID: 26716708
- Identification of this undescribed functional NLS within ARID1A contributes vital insights to rationalize the impact of ARID1A missense mutations observed in patient tumors. PMID: 26614907
- Data showed that ARID1A interacts with ATR via its C-terminal region, which mediates its recruitment to DNA double-strand breaks. PMID: 26069190
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Coffin-Siris syndrome 2 (CSS2)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in spleen, thymus, prostate, testis, ovary, small intestine, colon, and PBL, and at a much lower level in heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, and pancreas.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 11110
OMIM: 603024
KEGG: hsa:8289
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000320485
UniGene: Hs.468972
Most popular with customers
-
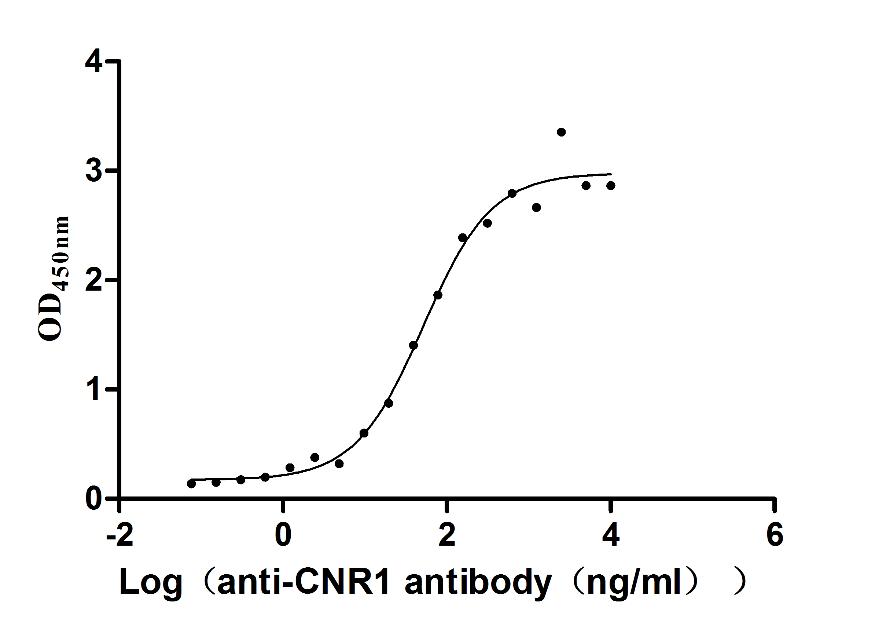
Recombinant Human Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
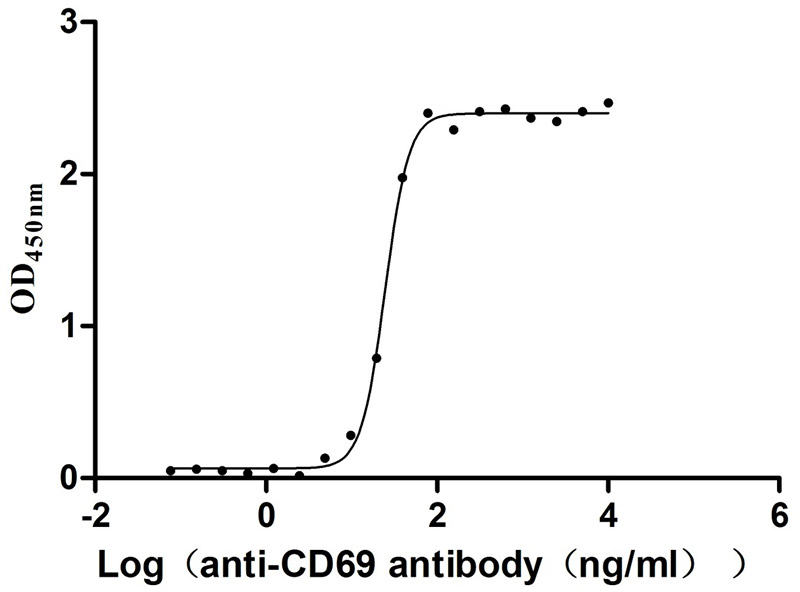
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
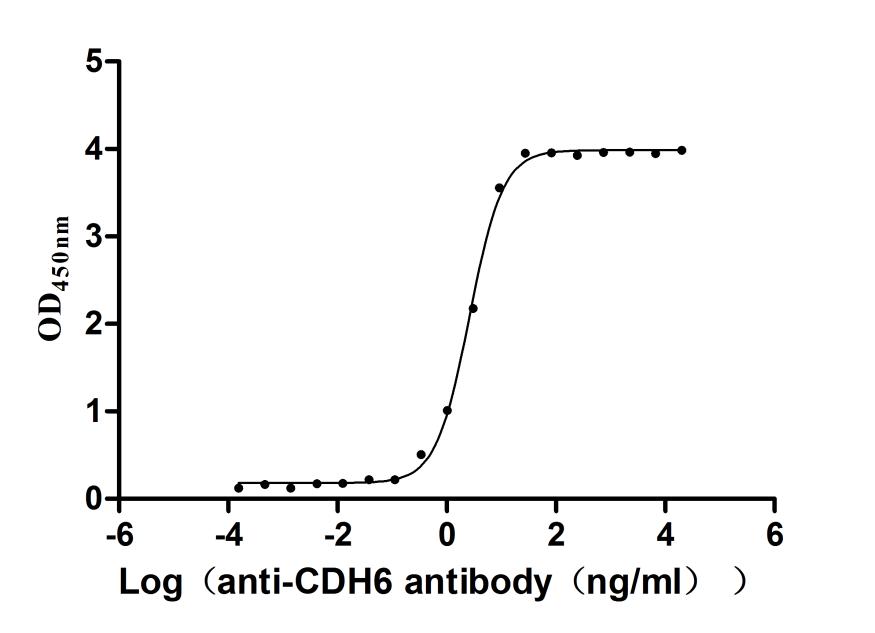
Recombinant Human Cadherin-6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
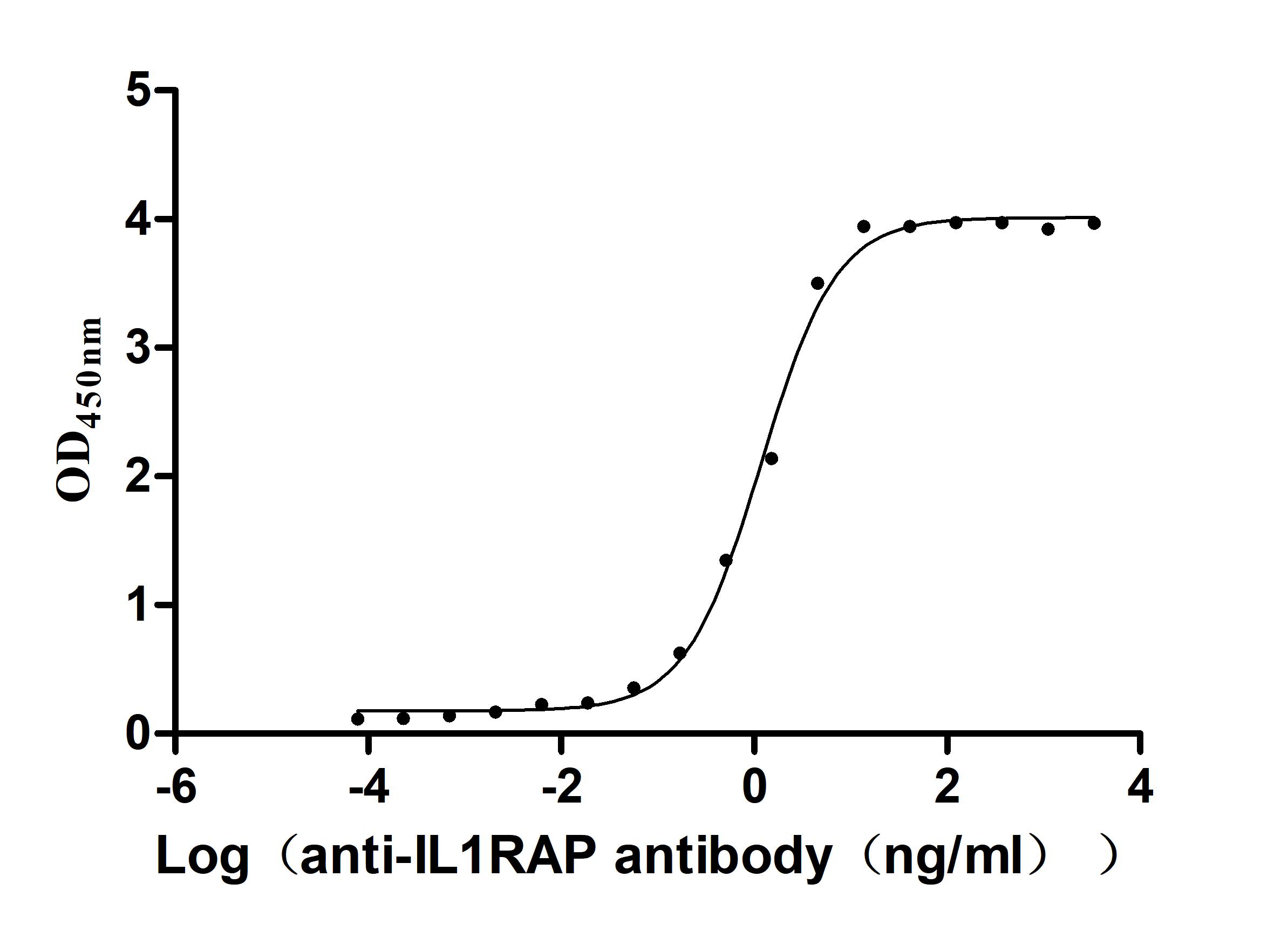
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)