-
货号:CSB-RA587302A0HU
-
规格:¥1320
-
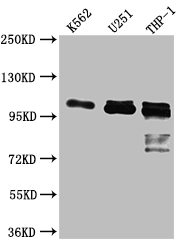
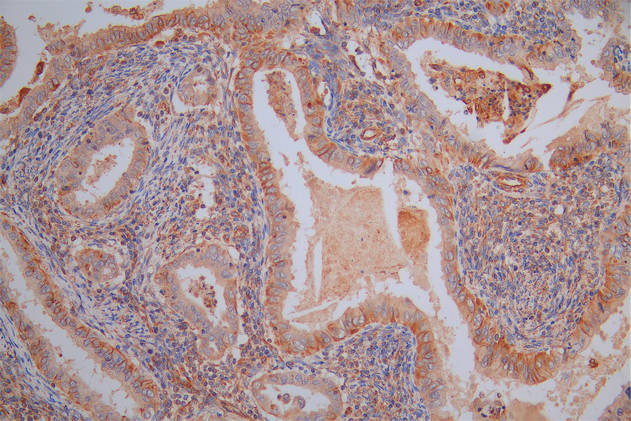
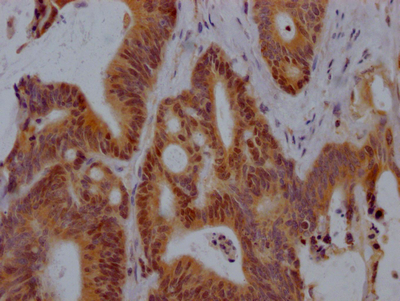
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:
ITCH is an E3 ligase with a HECT domain that is important for Th2 cell development and the degradation of ubiquitin-proteasomal proteins. The WW domain identifies the Pro-rich PPXY consensus sequence in substrate proteins, while the HECT domain attaches ubiquitin molecules to substrates, causing substrate breakdown. Due to its functionally distinct substrates, it also plays crucial roles in a variety of biological situations, including DNA damage response, T-cell differentiation, the immunological response, and cell death. ITCH deficiency has been linked to severe autoimmune illness in mice. ITCH may also be implicated in TGF β signaling and contribute to the development of marrow fibrosis.
Genes for ITCH antibody's heavy and light chains were cloned into plasma vectors, which were subsequently transfected into mammalian cells for expression. The resulting product is the recombinant ITCH antibody. This recombinant ITCH antibody was subsequently purified from the culture medium of transfected host cell lines through A synthesized peptide derived from human ITCH. It has verified to detect ITCH protein Human in the ELISA, WB. -
Uniprot No.:Q96J02
-
基因名:
-
别名:E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Itchy homolog (Itch) (EC 2.3.2.26) (Atrophin-1-interacting protein 4) (AIP4) (HECT-type E3 ubiquitin transferase Itchy homolog) (NFE2-associated polypeptide 1) (NAPP1), ITCH
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:A synthesized peptide derived from human ITCH
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆类型:Monoclonal
-
抗体亚型:Rabbit IgG
-
纯化方式:Affinity-chromatography
-
克隆号:9C3
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:5000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
引用文献
- Potential role of CXCR4 in trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer patients RM Kotb,Biochimica et biophysica acta. Molecular basis of disease,2022
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which accepts ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates. Catalyzes 'Lys-29'-, 'Lys-48'- and 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin conjugation. Involved in the control of inflammatory signaling pathways. Essential component of a ubiquitin-editing protein complex, comprising also TNFAIP3, TAX1BP1 and RNF11, that ensures the transient nature of inflammatory signaling pathways. Promotes the association of the complex after TNF stimulation. Once the complex is formed, TNFAIP3 deubiquitinates 'Lys-63' polyubiquitin chains on RIPK1 and catalyzes the formation of 'Lys-48'-polyubiquitin chains. This leads to RIPK1 proteasomal degradation and consequently termination of the TNF- or LPS-mediated activation of NFKB1. Ubiquitinates RIPK2 by 'Lys-63'-linked conjugation and influences NOD2-dependent signal transduction pathways. Regulates the transcriptional activity of several transcription factors, and probably plays an important role in the regulation of immune response. Ubiquitinates NFE2 by 'Lys-63' linkages and is implicated in the control of the development of hematopoietic lineages. Mediates JUN ubiquitination and degradation. Mediates JUNB ubiquitination and degradation. Critical regulator of type 2 helper T (Th2) cell cytokine production by inducing JUNB ubiquitination and degradation. Involved in the negative regulation of MAVS-dependent cellular antiviral responses. Ubiquitinates MAVS through 'Lys-48'-linked conjugation resulting in MAVS proteasomal degradation. Following ligand stimulation, regulates sorting of Wnt receptor FZD4 to the degradative endocytic pathway probably by modulating PI42KA activity. Ubiquitinates PI4K2A and negatively regulates its catalytic activity. Ubiquitinates chemokine receptor CXCR4 and regulates sorting of CXCR4 to the degradative endocytic pathway following ligand stimulation by ubiquitinating endosomal sorting complex required for transport ESCRT-0 components HGS and STAM. Targets DTX1 for lysosomal degradation and controls NOTCH1 degradation, in the absence of ligand, through 'Lys-29'-linked polyubiquitination. Ubiquitinates SNX9. Ubiquitinates MAP3K7 through 'Lys-48'-linked conjugation. Involved in the regulation of apoptosis and reactive oxygen species levels through the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of TXNIP. Mediates the antiapoptotic activity of epidermal growth factor through the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of p15 BID. Ubiquitinates BRAT1 and this ubiquitination is enhanced in the presence of NDFIP1. Inhibits the replication of influenza A virus (IAV) via ubiquitination of IAV matrix protein 1 (M1) through 'Lys-48'-linked conjugation resulting in M1 proteasomal degradation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The results indicated that circ-ITCH was significantly decreased in BCa and correlated with poor prognosis of BCa patients. Moreover, circ-ITCH suppressed cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro and tumorigenesis in vivo. PMID: 29386015
- Itch/beta-arrestin2 complex binds SuFu and induces its Lys63-linked polyubiquitylation without affecting its stability. PMID: 29515120
- JunB neddylation mediated by Itch promotes its ubiquitination-dependent degradation. PMID: 27245101
- Describe an autoinhibitory mechanism for ITCH ubiquitin ligase involving a linker-HECT domain interaction. This intramolecular interaction traps the HECT enzyme in its inactive state and can be relieved by linker phosphorylation. PMID: 28475870
- Data show that the E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch forms a complex with tricellulin and thereby enhances its ubiquitination. PMID: 28436082
- ASPP2 suppresses invasion, peritoneal dissemination and TGF-beta1-induced EMT by inhibiting Smad7 degradation mediated by ITCH in gastric cancer cells. PMID: 28400336
- WBP2/ITCH signaling functions to link the intricate Wnt and Hippo signaling networks in breast cancer. PMID: 27578003
- The cellular ubiquitin ligase, Itch, is required for Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus RTA induced degradation of vFLIP. PMID: 27912080
- These data demonstrate that Itch, ubiquitin, and Alix control the BFRF1-mediated modulation of the nuclear envelope and human herpesvirus 4 maturation, uncovering novel regulatory mechanisms of nuclear egress of viral nucleocapsids. PMID: 27466427
- The s demonstrate that the PPxY L domain motif of ebolavirus VP40 interacts specifically with the WW domain of the host E3 ubiquitin ligase ITCH. PMID: 27489272
- Molecular basis of interactions between SH3 domain-containing proteins and the proline-rich region of the ubiquitin ligase Itch. PMID: 28235806
- cir-ITCH may play an inhibitory role in lung cancer progression by enhancing its parental gene, ITCH, expression PMID: 27642589
- Itch monoubiquitinates SMN and monoubiquitination of SMN plays an important role in regulating its cellular localization. PMID: 26908624
- miR-106b, which itself is down regulated in metastatic pancreatic cancer, directly interacts and inhibits ITCH expression. PMID: 26621835
- LRAD3 is a component of pathways that function effectively to modulate Itch and Nedd4 auto-ubiquitination and levels. PMID: 26854353
- Cytomegalovirus UL42 induced the ubiquitination and degradation of human Itch in virus-infected fibroblasts, and was partially colocalized with p62, a ubiquitin-binding protein, and CD63, a marker of lysosome and multivesicular bodies. PMID: 26555021
- catalytic activity of Itch toward different SH3 domain-containing proteins was similar, except for beta-PIX that was not readily ubiquitylated even though it could interact with an affinity comparable to those of other substrates tested PMID: 26613292
- Upregulated microRNA-214 enhances cardiac injury by targeting ITCH during coxsackievirus infection. PMID: 25815880
- Cell proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells mediated by miR-411, is through suppression of ITCH expression. PMID: 25776495
- In the absence of Ndfip1, the Nedd4 family member Itch can bind an E2 but cannot accept ubiquitin onto its catalytic cysteine. PMID: 26245901
- These observations indicate that ITCH is involved in the cytosolic quality control pathway and may help to explain how abnormal proteins are targeted by QC ubiquitin-protein ligases. PMID: 24865853
- Results suggest that Itch is a positive regulator of the TGF-beta-mediated Smad signaling pathway via Smad7 ubiquitination and protein degradation. PMID: 25518932
- ITCH up-regulation and LATS1 down-regulation were closely associated with tumorigenesis and progression of SCC PMID: 25618271
- High ITCH expression enhances breast tumor progression by inhibiting the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway PMID: 25350971
- these observations reveal that Itch and Yap1 have antagonistic roles in the regulation of ASPP2 protein stability through competing post-translational regulatory mechanism of ASPP2. PMID: 25436413
- The C-terminal domain of PTCH1 interacts with and is ubiquitylated on K1413 by the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Itchy homolog Itch. PMID: 25092867
- ITCH as a novel component of the ATM-dependent signaling pathway. PMID: 23435430
- Data indicate that Itch interacted with viral M1 protein and ubiquitinated M1 protein. PMID: 24101521
- identify Itch as a regulator of Oct4 stability and transcriptional activity, establishing a functional link between an E3 ligase and the regulation of pluripotency PMID: 23255053
- ITCH interacts with mutant GCase variants and mediates their lysine 48 polyubiquitination and degradation. PMID: 23255161
- Amot130 repurposes AIP4 from its previously described role in degrading large tumor suppressor 1 to the inhibition of YAP and cell growth. PMID: 23564455
- FOXP3 mRNA expression correlated with CBLB and ITCH in MS patients. PMID: 23039885
- The interaction of Itch-WW2 domain with p63, was investigated. PMID: 22935697
- Overexpression of ITCH inhibited wild-type DVL2 -induced, but not DVL2-Y568F mutant-induced, Wnt reporter activity. PMID: 22826439
- JNK1-dependent increase in labile iron pool is mediated by Itch ubiquitin ligase. PMID: 21863240
- Knockdown of Nedd4, Nedd4-2 and Itch causes an accumulation of steady-state level of AMOT/p130. PMID: 22385262
- Itch/AIP4-independent proteasomal degradation of cFLIP induced by the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA sensitizes breast tumour cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. PMID: 21107885
- Overexpression of an AIP4 catalytically inactive mutant and a mutant that shows poor binding to STAM-1 fails to enhance CXCR4-induced ERK-1/2 signaling. PMID: 22275353
- LAPTM5 is a substrate of the ITCH-mediated degradation and its protein level is negatively regulated by ITCH PMID: 22009753
- Only silencing of ITCH, but not of WWP1, WWP2, and Nedd4, resulted in a reduction of HTLV-1 budding from 293T cells PMID: 21724848
- Itch protein re-localization is dependent upon the interaction with the PPXY sequences of LITAF, since disruption of these binding motifs completely abrogates Itch re-localization. PMID: 21326863
- study identifies E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch as a unique negative regulator of LATS1 and presents a possibility of targeting LATS1/Itch interaction as a therapeutic strategy in cancer. PMID: 21383157
- Findings support a role for the AKT-dependent regulation of AIP4/Itch activity in mediating the differential cyclin D1 and c-MYC transcriptional responses to rapamycin. PMID: 21135252
- ubiquitin E3 ligase ITCH physically and functionally associates with LATS1 PMID: 21212414
- Numb activates the catalytic activity of Itch, releasing it from an inhibitory intramolecular interaction between its homologous to E6-AP C-terminus and WW domains. PMID: 20818436
- MDM2 promotes Itch-mediated degradation of p73 through the interaction with Itch in HeLa cells. PMID: 21093410
- UL56 interacted with Itch, independent of additional viral proteins, and mediated more striking degradation of Itch, compared to Nedd4. PMID: 20682038
- Results indicate that cystatin B regulates Itch-mediated degradation of FLIP(L) and thereby TRAIL-induced apoptosis in melanoma cells. PMID: 20300110
- Itch ubiquitylates SNX9 and regulates intracellular SNX9 levels. Interaction with the proline-rich domain of Itch is essential for SNX9 ubiquitylation and degradation. PMID: 20491914
- Inducible regulatory T cells (iTregs) from recent onset type 1 diabetes (RO T1D) subjects had increased expression of Foxp3, E3 ubiquitin ligase (ITCH) and TGF-beta-inducible early gene 1 (TIEG1) compared with control and long-standing T1D subjects. PMID: 20143240
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Autoimmune disease, multisystem, with facial dysmorphism (ADMFD)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Early endosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Endosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side.
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 13890
OMIM: 606409
KEGG: hsa:83737
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000363998
UniGene: Hs.632272
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-