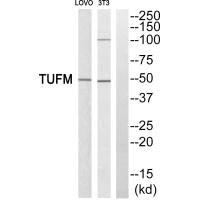
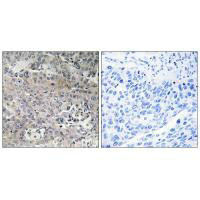
TUFM Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA559509
-
规格:¥2024
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) TUFM Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:P49411
-
基因名:TUFM
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from internal of Human TUFM.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB,IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:3000 IHC 1:50-1:100 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Promotes the GTP-dependent binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to the A-site of ribosomes during protein biosynthesis. Plays also a role in the regulation of autophagy and innate immunity. Recruits ATG5-ATG12 and NLRX1 at mitochondria and serves as a checkpoint of the RIG-I/DDX58-MAVS pathway. In turn, inhibits RLR-mediated type I interferon while promoting autophagy.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Novel mutation in mitochondrial Elongation Factor EF-Tu associated to dysplastic leukoencephalopathy and defective mitochondrial DNA translation. PMID: 28132884
- study revealed a novel role for TUFM as a host restriction factor that exerts an inhibitory effect on avian-signature PB2627E influenza virus propagation in human cells; found that increased TUFM-dependent autophagy correlates with the inhibitory effect on avian-signature influenza virus replication and may serve as a key intrinsic mechanism to restrict avian influenza virus infection in humans PMID: 28611246
- High expression of TUFM is associated with colorectal cancer. PMID: 28449687
- we identify a novel signaling hub centering on the NLRX1 TUFM protein complex, promoting autophagic flux. Defects in the expression of either NLRX1 or TUFM result in compromised autophagy when treated with EGFR inhibitors.These findings expand our understanding of the components involved in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma autophagy machinery that responds to EGFR inhibitors. PMID: 26876213
- TUFM is a novel regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT); there may be a molecular link between mitochondrial dysfunction and EMT induction PMID: 26781467
- NLRX1 and TUFM work in concert to reduce cytokine response and augment autophagy. PMID: 23321557
- Increased expression of TUFM is a promising new prognostic indicator for colorectal carcinoma. PMID: 22772342
- By recruiting Atg5-Atg12 and NLRX1, TUFM serves as a nodal checkpoint of the RIG-I-MAVS axis. It acts similarly to NLRX1 by inhibiting RigI-like-receptor-induced IFN-I but promoting autophagy. PMID: 22749352
- Genetic investigation of patients with defective mitochondrial translation led to the discovery of novel mutations in the mitochondrial elongation factor G1 (EFG1) in one affected baby and in the mitochondrial elongation factor Tu (EFTu) in another one PMID: 17160893
- Myoblasts isolated from the MELAS patients show A3243G mutation in tRNALeu(UUR) produces a severe respiratory chain deficiency and this phenotype can be partially suppressed by overexpression of EFTu and EFG2. PMID: 18753147
- Results suggest that the R336Q mutant mt-EFTu variant fails to bind to aminoacylated mitochondrial tRNAs, thus explaining the observed impairment of mitochondrial translation. PMID: 19524667
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 4 (COXPD4)
-
亚细胞定位:Mitochondrion.
-
蛋白家族:TRAFAC class translation factor GTPase superfamily, Classic translation factor GTPase family, EF-Tu/EF-1A subfamily
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 12420
OMIM: 602389
KEGG: hsa:7284
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000322439
UniGene: Hs.12084
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
-
-
-
-
-