SACS Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA873707LA01HU
-
规格:¥440
-
促销:
-
图片:
-
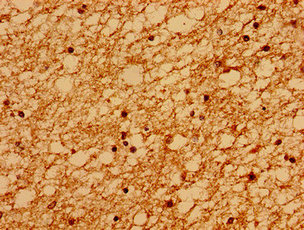
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue using CSB-PA873707LA01HU at dilution of 1:100
-
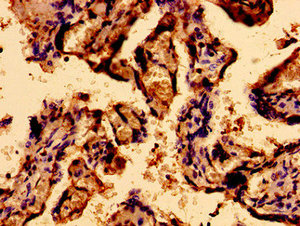
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human placenta tissue using CSB-PA873707LA01HU at dilution of 1:100
-
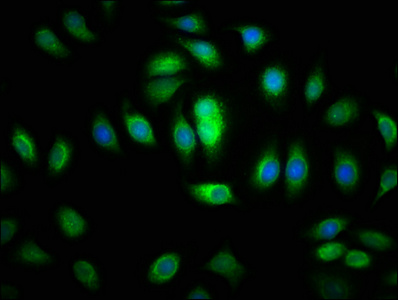
Immunofluorescence staining of A549 cells with CSB-PA873707LA01HU at 1:200, counter-stained with DAPI. The cells were fixed in 4% formaldehyde, permeabilized using 0.2% Triton X-100 and blocked in 10% normal Goat Serum. The cells were then incubated with the antibody overnight at 4°C. The secondary antibody was Alexa Fluor 488-congugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L).
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) SACS Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q9NZJ4
-
基因名:SACS
-
别名:DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 29 antibody; DNAJC29 antibody; SACS antibody; SACS_HUMAN antibody; Sacsin antibody; Spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Sacsin protein (983-1150AA)
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
本页面中的产品,SACS Antibody (CSB-PA873707LA01HU),的标记方式是Non-conjugated。对于SACS Antibody,我们还提供其他标记。见下表:
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, IHC, IF
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC 1:20-1:200 IF 1:200-1:500 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Co-chaperone which acts as a regulator of the Hsp70 chaperone machinery and may be involved in the processing of other ataxia-linked proteins.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Our findings confirm the broad clinical spectrum associated with SACS mutations, including pure polyneuropathy without characteristic clinical and brain imaging manifestations of autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay. PMID: 30460542
- we present the first Polish family with a comprehensive clinical and neuropsychological assessment, harboring two novel mutations in the SACS gene PMID: 28843771
- the twins described by Fitzsimmons had heterozygous mutations in the SACS gene, the gene responsible for autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix Saguenay as well as a heterozygous mutation in the TRPS1, the gene responsible in Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1A TBL1XR1 mutation was identified in the patient described in 2009 as contributing to his cognitive impairment and autistic features.. PMID: 27133561
- This study provides a potential genetic diagnosis for the patient and expands the spectrum of SACS mutations. PMID: 28658676
- We established a genetic diagnosis in six families with autosomal recessive HSP (SPG11 in three families and TFG/SPG57, SACS and ALS2 in one family each). A heterozygous mutation in a gene involved in an autosomal dominant HSP (ATL1/SPG3A) was also identified in one additional family PMID: 27601211
- The results are consistent with the HEPN domain contributing to the functional activity of sacsin by binding to nucleotides or other multiply charged anionic compounds in neurons. PMID: 26366743
- Various SACS mutations have functional consequences on the mitochondrial compartment in ARSACS patients. PMID: 26288984
- study reports an Italian family affected by an autosomal recessive form of hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) and peripheral neuropathy caused by a novel mutation in the SACS PMID: 23800155
- To clarify the segregation pattern of the mutations found in this family, having excluded somatic mosaicism for the specific mutations, we fully reanalyzed the SACS gene PMID: 24164681
- Whole-exome sequencing identified a hemizygous novel spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay (SACS) stop-codon mutation in 2 brothers PMID: 24180463
- Abnormal retinal thickening is a common feature in patients with SACS mutation phenotype. PMID: 24457356
- Widespread tissue damage may be associated with extensive loss of sacsin protein in the brain and may explain a wide range of progressive neurologic abnormalities in patients with spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay. PMID: 23598833
- A novel missense mutation in sacsin, p.Arg272His, was identified in a patient with sacsin-related spastic ataxia. PMID: 23338241
- the relative position of mutations in subrepeats will variably influence sacsin dysfunction PMID: 23280630
- We identified a new mutation in the SACS gene in Autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia PMID: 23043354
- This study demonistrated that 16 novel SACS gene mutations in recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay showed Supratentorial and pontine abnormalitie. PMID: 22816526
- Compares the GHKL-type-ATPase domain of this human protein to that of related plant, protozoan, yeast and bacterial proteins. PMID: 19880797
- Novel compound heterozygous frameshift mutations were detected in the SACS gene in two siblings with a sensorimotor neuropathy, ataxia, and spasticity PMID: 22751902
- As more SACS mutations are identified worldwide, the clinical spectrum of 'sacsinopathies' will expand PMID: 17853117
- we describe two unrelated Autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix Saguenay patients from central Italy carrying two novel mutations in SACS PMID: 22805644
- This study demonistrated that Autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay with compound heterozygotes for nonsense mutations of the SACS gene. PMID: 21745802
- novel insights into the oligomerization state of sacsin and functions that are lost in mutations that cause ARSACS. PMID: 21507954
- Data show that uniparental isodisomy of the paternal chromosome 13 carrying the mutated SACS gene played an etiologic role in a case of the disease. PMID: 20852969
- This study, enlargeg the ARSACS phenotype and the underlying genetic spectrum of SACS mutations. Patients with ARSACS are more common than previously known and risk underdiagnosis due to late onset age and unusual presentation. PMID: 20876471
- These data indicate that sacsin repeating regions necessitate nucleotide hydrolysis for their function, provided by the common Hsp90 ATPase domain, which may give rise to a novel activity related to protein quality control. PMID: 20488193
- Our results expand the genotype phenotype correlation of mutations in the sacsin gene in ataxia patients PMID: 19892370
- Report of a reliable and inexpensive method to detect more than 95% of the ARSACS disease alleles. PMID: 11788093
- The s report a new mutation (1859insC), leading to a frameshift with a premature termination of the gene product sacsin, in two sisters from consanguineous parents. The phenotype is similar to previously described patients with ARSACS PMID: 14718706
- The s identified three new SACS mutations in two Italian patients whose phenotype closely matches that of Quebec cases, but without retinal striation. PMID: 14718707
- A homozygous missense mutation (T7492C) in the SACS gene, which resulted in the substitution of arginine for tryptophan at amino acid residue 2498 (W2498R) was identified in two sibling Japanese early onset spastic ataxia patients PMID: 14718708
- analysis of SACS mutations in autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay families PMID: 15156359
- The s describe two Japanese siblings with autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay without spasticity, usually a core feature of this disorder. They had a novel homozygous missense mutation (T987C) of the SACS gene. PMID: 15985586
- The s report here identical twin sisters with novel compound heterozygous mutations (c.[2951_2952delAG]+[3922delT]) in the SACS gene. PMID: 16198375
- Japanese autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay (ARSACS) patient with a compound heterozygous mutation in a new exon of the SACS gene. PMID: 16606928
- report of Japanese siblings with a new missense mutation (C922T, L308F) in exon 7 of SACS PMID: 17290461
- We describe four patients in a Belgian family with autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay (ARSACS). A novel homozygous missense mutation of the SACS gene was identified in the present family. PMID: 17716690
- Both point mutation and deletion associated with autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay. PMID: 18398442
- In a Dutch cohort of 43 index patients with ataxia onset before age 25, we identified 16 index patients (total 23 patients) with mutations in the SACS gene. Nine of them had homozygous mutations, and seven of them had compound heterozygous mutations. PMID: 18465152
- The s report a clinical and genetic analysis of a Japanese family with ARSACS with novel compound heterozygous mutations in the SACS gene (N161fsX175, L802P). The phenotype is similar to that of previously reported ARSACS patients. PMID: 18484239
- Results report the identification of an unconventional SACS mutation, a large-scale deletion sized approximately 1.5 Mb encompassing the whole gene, in two unrelated patients. PMID: 19031088
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Spastic ataxia Charlevoix-Saguenay type (SACS)
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Note=Predominantly cytoplasmic, a small portion is present in the nucleus and also shows a partial mitochondrial overlap with the mitochondrial marker Hsp60.
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in the central nervous system. Also found in skeletal muscle and at low levels in pancreas.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 10519
OMIM: 270550
KEGG: hsa:26278
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000371729
UniGene: Hs.159492
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-