RNF168 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA814236LA01HU
-
规格:¥440
-
促销:
-
图片:
-
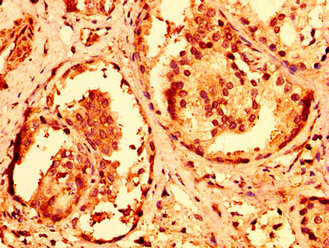
IHC image of CSB-PA814236LA01HU diluted at 1:600 and staining in paraffin-embedded human prostate cancer performed on a Leica BondTM system. After dewaxing and hydration, antigen retrieval was mediated by high pressure in a citrate buffer (pH 6.0). Section was blocked with 10% normal goat serum 30min at RT. Then primary antibody (1% BSA) was incubated at 4°C overnight. The primary is detected by a biotinylated secondary antibody and visualized using an HRP conjugated SP system.
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) RNF168 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q8IYW5
-
基因名:RNF168
-
别名:E3 ubiquitin protein ligase RNF168 antibody; E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF168 antibody; FLJ35794 antibody; FLJ39749 antibody; hRNF168 antibody; RING finger protein 168 antibody; RN168_HUMAN antibody; RNF 168 antibody; Rnf168 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF168 protein (194-296AA)
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
本页面中的产品,RNF168 Antibody (CSB-PA814236LA01HU),的标记方式是Non-conjugated。对于RNF168 Antibody,我们还提供其他标记。见下表:
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC 1:500-1:1000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase required for accumulation of repair proteins to sites of DNA damage. Acts with UBE2N/UBC13 to amplify the RNF8-dependent histone ubiquitination. Recruited to sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs) by binding to ubiquitinated histone H2A and H2AX and amplifies the RNF8-dependent H2A ubiquitination, promoting the formation of 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin conjugates. This leads to concentrate ubiquitinated histones H2A and H2AX at DNA lesions to the threshold required for recruitment of TP53BP1 and BRCA1. Also recruited at DNA interstrand cross-links (ICLs) sites and promotes accumulation of 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination of histones H2A and H2AX, leading to recruitment of FAAP20/C1orf86 and Fanconi anemia (FA) complex, followed by interstrand cross-link repair. H2A ubiquitination also mediates the ATM-dependent transcriptional silencing at regions flanking DSBs in cis, a mechanism to avoid collision between transcription and repair intermediates. Also involved in class switch recombination in immune system, via its role in regulation of DSBs repair. Following DNA damage, promotes the ubiquitination and degradation of JMJD2A/KDM4A in collaboration with RNF8, leading to unmask H4K20me2 mark and promote the recruitment of TP53BP1 at DNA damage sites. Not able to initiate 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination in vitro; possibly due to partial occlusion of the UBE2N/UBC13-binding region. Catalyzes monoubiquitination of 'Lys-13' and 'Lys-15' of nucleosomal histone H2A (H2AK13Ub and H2AK15Ub, respectively).
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Results suggest that RNF168 acts as a counterpart of PARP1 in DDR and regulates the HR/NHEJ repair processes through the ubiquitination of PARP1. PMID: 30037213
- RNF168 interacts with TOP2alpha to mediate its polyubiquitylation and RNF168 deficiency confers resistance to ICRF-193, a TOP2 catalytic inhibitor, and cytotoxic anti-cancer drug etoposide in cultured human cancers cells. PMID: 27558965
- Ub-interacting residues in UDM2 prevent the accumulation of RNF168 to double-strand breaks sites in U2OS cells, whereas those in UDM1 have little effect. PMID: 29330428
- We identified 85 overlapping deletions, of which six included the RPL35A gene and all should be had Diamond-Blackfan anemia (DBA).we sequenced the remaining RNF168 gene and examined her fibroblast culture for a DNA double strand break repair deficiency. These results were normal, indicating that the immunodeficiency is unlikely to result from a RNF168 deficiency. PMID: 28432740
- deregulated RNF168/53BP1 pathway could promote tumorigenesis by selecting for a more robust, better stress-adapted cancer cell phenotype, through altered DNA repair, fueling genomic instability and tumor heterogeneity PMID: 27841863
- The association of RNF168 with PML NBs resulted in increased ubiquitylation. PMID: 26675234
- Results reveal an important role of USP7 in regulating ubiquitin-dependent signaling via stabilization of RNF168. PMID: 25894431
- CK2/WIP1-mediated modulation of LSD1 phosphorylation facilitates RNF168-dependent ubiquitination and recruitment of 53BP1 to the DNA damage sites. PMID: 25999347
- The ubiquitin ligase RNF168 is strictly dependent on the activity that UbK27 is required to promote chromatin ubiquitination following DNA damage. PMID: 25578731
- Finding that RNF8 is less abundant than RNF168 identifies RNF8 as a rate-limiting determinant of focal repair complex assembly PMID: 25304081
- Depletion of RNF8 or RNF168 blocks the degradation of diffusely localized nuclear 53BP1. PMID: 25337968
- The E3 ligase RNF168 promotes both H2A ubiquitylation and neddylation. RNF168 is itself a substrate for NEDD8, and neddylation of RNF168 is necessary for its E3 ubiquitin activity. PMID: 24634510
- The acidic patch functions within the nucleosome as nucleosomes containing a mutated acidic patch exhibit defective H2A/H2AXub by RNF168 and RING1B/BMI1 in vitro PMID: 24603765
- Taken together, the results suggested that USP3 is a negative regulator of ubiquitination signaling, counteracting RNF168- and RNF8-mediated ubiquitination PMID: 24196443
- Before their localization to DNA double strand breaks, RNF168 interacts with 53BP1 and modifies it through the addition of a chain of ubiquitin-polypeptides. PMID: 24324146
- RNF168 physically interacts with LSD1 and we find this interaction to be important for LSD1 recruitment to DNA damage sites. PMID: 24217620
- study unveils a functional link between DNA damage-induced poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation, SMARCA5-mediated chromatin remodeling and RNF168-dependent signaling and repair of DSBs. PMID: 23264744
- RNF168, in complex with RAD6A or RAD6B, is activated in the DNA-damage-induced protein ubiquitination cascade. PMID: 23525009
- Unlike RNF8, RNF168 RING domain did not stably associate with UBC13 at double-stranded DNA breaks in vitro or in vivo. PMID: 23255131
- RNF168 is important for defects in homologous recombination caused by loss of the BRCA1 in breast cancer cells. PMID: 23055523
- Ubiquitin-dependent signaling during the DNA damage response (DDR) to double-strand breaks is initiated by two E3 ligases, RNF8 and RNF168, targeting histone H2A and H2AX. Study shows that ubiquitin chains per se are insufficient for signaling, but RNF168 target ubiquitination is required for DDR. PMID: 22980979
- Inactivation of K13 and K15 reduces RNF168- dependent ubiquitination of histones H2As, while inactivation of both N- and C-terminal sites completely abolishes histone ubiquitination. PMID: 22713238
- RNF168, its paralog RNF169, RAD18, and the BRCA1-interacting RAP80 protein accumulate at DNA double strand break sites through the use of bipartite modules composed of ubiquitin binding domains. PMID: 22742833
- Data show RING finger (RNF) E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF8 dimerizes and binds to E2 ubiquitin-conjugating complex Ubc13/Mms2 with formation of Lys-63 ubiquitin chains, whereas the RNF168 RING domain is a monomer and does not catalyze Lys-6 ubiquitylation. PMID: 22589545
- Data show that depletion of RNF8, as well as of the E3 ligase RNF168, reduces telomere-induced genome instability. PMID: 21857671
- Studies indicate that Non-proteolytic ubiquitylation of chromatin surrounding DSBs, mediated by the RNF8/RNF168 ubiquitin ligase cascade, has emerged as a key mechanism for restoration of genome integrity. PMID: 21664912
- The viral protein ICP0 targets RNF8 and RNF168 for degradation, thereby preventing the deposition of repressive ubiquitin marks and counteracting this repair protein recruitment. PMID: 21698222
- this study reveals that human NIPBL is a novel protein recruited to DSB sites, and the recruitment is controlled by MDC1, RNF168 and HP1gamma. PMID: 21784059
- The E3 Ubiquitin ligases, RNF8 and RNF168, are recruited to DNA damage foci in late mitosis, presumably to prime sites for the DNA damage response, 53BP1, recruitment in early G1. PMID: 21412056
- identification of a novel ubiquitin binding domain present in RNF168, and characterized the interaction surface with ubiquitin, centered on two Leu residues PMID: 21041483
- Data identify RNF8 and RNF168, cellular histone ubiquitin ligases responsible for anchoring repair factors at sites of damage, as new targets for ICP0-mediated degradation. PMID: 20075863
- Ubiquitin ligase does not protect cells from Nutlin-3-mediated apoptosis, indicating that RNF168 does not regulate 53BP1 protein. PMID: 20080757
- Data show that the ATM signalling mediator proteins MDC1, RNF8, RNF168 and 53BP1 are also required for heterochromatic DSB repair. PMID: 20081839
- RNF168 defines a new pathway involving sequential ubiquitylations on damaged chromosomes and uncovers a functional cooperation between E3 ligases in genome maintenance. PMID: 19203579
- RNF168 is a ubiquitin ligase that functions as chromatin modifier, through histone ubiquitination; upon DNA lesions, RNF168 is recruited to DNA damage response foci where it contributes to increase the amount of ubiquitinated proteins. PMID: 19500350
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Riddle syndrome (RIDDLES)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:RNF168 family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 26661
OMIM: 611943
KEGG: hsa:165918
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000320898
UniGene: Hs.250648
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-