RHCE Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA093489
-
规格:¥1100
-
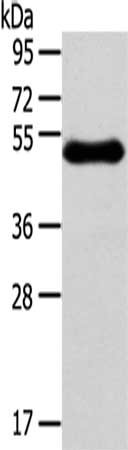
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P18577
-
基因名:RHCE
-
别名:RHCE antibody; RHC antibody; RHE antibody; Blood group Rh(CE) polypeptide antibody; Rh polypeptide 1 antibody; RhPI antibody; Rh30A antibody; RhIXB antibody; Rhesus C/E antigens antibody; CD antigen CD240CE antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Synthetic peptide of Human RHCE
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen affinity purification
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:-20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution ELISA 1:2000-1:5000 WB 1:500-1:2000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:May be part of an oligomeric complex which is likely to have a transport or channel function in the erythrocyte membrane.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Among the weak D phenotypes in Tunisia, no novel RHD allele was found and almost 90% were caused by alleles of the weak D Type 4 cluster, of which 88% represented the weak D Type 4.0 allele. Based on established RH haplotypes for variant RHD and RHCE alleles and the lack of adverse clinical reports, we recommend D+ transfusions for patients with weak D Type 4.0 in Tunisia. PMID: 29193104
- study 94.9% of the partial D samples revealed altered RHCE variant alleles and 5.7% of the samples with altered RHD allele predicted partial c, partial e and the lack of the high prevalence hr(B) and hr(S) antigens. PMID: 27111588
- sequence comparisons revealed high sequence similarity between Patr_RHbeta and Hosa_RHCE, while the chimpanzee Rh gene closest to Hosa_RHD was not Patr_RHalpha but rather Patr_RHgamma PMID: 26872772
- The purpose of this study was to determine the diversity and frequency of RHD-CE genotypes, predicting partial antigens in patients with sickle cell disease and in African Brazilian donors in order to find, through the use of RH genotyping, more closely matched donors for sickle cell disease patients who are alloimmunised to Rh antigens. PMID: 27177398
- The RHCE gene intron 4 of Han Chinese, Tibetans, and Mongols differs from the RHD gene intron 4 in the presence of a 652-bp fragment. PMID: 26579938
- Six new RHCE alleles were identified, namely, RHCE*cE84A, RHCE*ce202G, RHCE*ce307T, RHCE*Ce377G, RHCE*ce697G,712G,733G,744C, and RHCE*Ce733G in individuals of diverse racial origin. PMID: 26435076
- RHCE*cE94G encodes variable expression of c (RH4). PMID: 26286238
- Rh antibodies in SCD patients with RH variants can be clinically significant and, therefore, matching patients based on RH variants should be considered. PMID: 24960646
- Through molecular genotyping we also identified polymorphisms in RhCE, Kell, Duffy, Colton, Lutheran and Scianna loci in donors and patients. PMID: 25582271
- An uneven distribution of RH variant alleles between Dogon and Fulani, in Mali. A high incidence of predicted partial-C phenotype encoded by RHCE*Ce-D(4)-ce was found in Fulani. PMID: 25857637
- These data showed the presence of the (C)ce(s) haplotype at a low frequency (0.625%) compared to that among Africans in whom it is common. Nevertheless, the presence of RHD-CE-D(s) in Tunisians, even at a lower frequency PMID: 24333089
- One allele was found to be the known allele RHCE*Ol.20.01(RHCE*ce733G) and the second was novel: RHCE*Ol.06.02(RHCE*ce254G,733G). PMID: 25695437
- RHD*weak partial 4.0 is associated with an altered RHCE*ce(48C, 105T, 733G, 744C, 1025T) allele in the Tunisian population. PMID: 23742316
- RHCE*ceMO was present in one in 50 African-American persons with an allele frequency of 0.01, is often linked to RHD*DAU0, and is potentially of clinical significance for transfusion. PMID: 23772606
- In addition to hybrid alleles and nucleotide deletion, intronic mutations may be associated with the nonexpression of RhCE antigens. PMID: 23252593
- A QMPSF-based method is reliable to individually quantify the exons of both RH genes, including hybrid D-CE genes in compound heterozygous samples. PMID: 23550903
- Frequencies of aberrant RHD and RHCE alleles were similar, irrespective of location and ethnicity. PMID: 24033223
- A novel RHCE*cE allele, RHCE*cE734C, was found in two probands whose red blood cells had weakened c expression and typed E- with conventional anti-E reagents. PMID: 22958092
- RHD*DIVa and RHCE*ceTI almost always, but not invariably, travel together. This haplotype is found in people of African ancestry and the red blood cells can demonstrate aberrant reactivity with anti-C. RHCE*ceTI encodes partial c and e antigens. PMID: 22804620
- Low-prevalence Rh antigen STEM (RH49) is encoded by two different RHCE*ce818T alleles that are often in cis to RHD*DOL. PMID: 22738288
- The rare RHCE*ceBI allele appears to be in cis either with RHD*DOL1 or with RHD*DOL2 in people of African descent. PMID: 22690701
- Two novel RHCE*ce 48C,733G,1006T alleles have been identified: RHD*186T and RHD*DIIIa150C. PMID: 23286557
- A novel allele of RHCE, RHCE*cE 907delC, silences c and E and in the homozygous state resulting in a D- - phenotype and production of anti-Rh17. PMID: 21517889
- Allele-specific oligonucleotide polymerase chain reaction for the determination of Rh C/c and Rh E/e antigens in thalassaemic patients. PMID: 21251469
- Study identifies a novel allele, RHCE*ce 48C, 733G, 941C, 1006T which is predicted to encode 16Cys, 245Val, 314Ala, and 336CyS and was shown to encode c, V/VS, and an altered expression of e and hrB antigens. PMID: 20576012
- RHCE*ceAR encodes a partial c (RH4) antigen. PMID: 20932075
- The low prevalence Rh antigen, Be(a), is associated with a single nucleotide change in exon 5 of RHCE*ce; that of 662C>G. and This changes proline-221 of Rhce to arginine, which may impose a steric and/or charge-related effect on the protein. PMID: 19951310
- JAL and JAHK antigens are expressed by Ce and ce and varients of RhCE protein PMID: 20233350
- RHCE represents the ancestral RH position, while RHD is the duplicated gene PMID: 11902138
- Molecular analysis of Hor+, Mol+ variants revealed a hybrid gene structure RHCe-D(5)-Ce, in which exon 5 of RHCE (RHCe allele) was replaced by exon 5 of RHD (the so-called RHCeVA allele). PMID: 12084172
- strong selection might be working to maintain the RHCE/RHD antigen variation in the two-locus system PMID: 12857961
- disruption of f (Rh6) by Arg229 deletion suggests that external loop 4 is a major structural element contributing to the expression of RHCE cis interacting antigenic products. PMID: 14996197
- The single-point mutation T500A in exon 4 of the RHCE gene is a molecular basis of the rare Rhesus antigen Ew. PMID: 14996199
- A high incidence of Trp16Cys in RHCE ce was seen in sickle cell disease. Many of these patients were heterozygous for VS antigen. cDNA analysis showed that the 2 mutations were on different alleles, weakening expression of the e antigen on RBCs. PMID: 15023184
- Review. The genetic, structural, and immunologic features of RHCE are reviewed. PMID: 15373666
- RhCE may not function directly in ammonia transport and may be evolving a new function in the RBC membrane. PMID: 16563829
- Review. 3-D models of the subunit and oligomeric architecture are proposed, using hydrophobic cluster analysis. PMID: 16584906
- Although the F223V substitution is regarded as the initial event in the evolution of the weak D Type 4 cluster, the current DFV allele probably evolved independently, as evident from different RHCE haplotypes PMID: 17900276
- It is possible to examine fetal c allele of RHCE gene in the plasma of pregnant women with anti-c by means of a noninvasive method. PMID: 18382999
- The nucleotide 340C>T change in RHCE exon 3 (predicted to encode 114Trp) of the RHCE*ce(S)(340) allele is associated with a JAL+ phenotype and the altered expression of the c, V and VS antigens. PMID: 19076333
- Homology modeling of the JAL+ RhCE protein suggests that the Arg-->Trp change eliminates a critical loop-stabilizing H-bond between the side chain of Arg114 and the e-specific amino acid Ala226. PMID: 19170983
- the previously described RhCeMA and ce(s)(340) alleles encode the JAL antigen. PMID: 19207167
- RHcE(M167K) known as E variant I was the most frequent allele, found in 70 of 122 analyzed blood donors in the northwest of Germany. Among 13 referred samples, C typing problems predominated. PMID: 19453979
- Single-amino-acid substitutions were the molecular basis for variant RhCE antigen expression in most samples of German blood donors and patients . PMID: 19453980
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Ammonium transporter (TC 2.A.49) family, Rh subfamily
-
组织特异性:Restricted to tissues or cell lines expressing erythroid characters. Isoform 4g and isoform RhPI-Alpha are expressed in immature erythroblasts but not in mature erythroblasts.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 10008
OMIM: 111690
KEGG: hsa:6006
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000294413
UniGene: Hs.449968
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-