REL (Ab-503) Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA194896
-
规格:¥2024
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) REL Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q04864
-
基因名:
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around aa.501~505 (T-S-S-D-S) derived from Human Rel.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic peptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific peptide.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
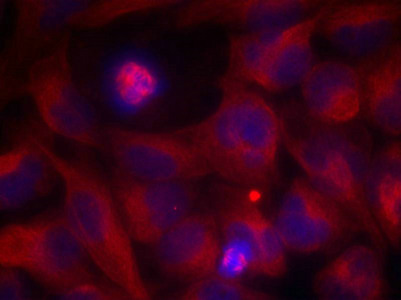
应用范围:ELISA,IF
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution IF 1:100-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Proto-oncogene that may play a role in differentiation and lymphopoiesis. NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. The NF-kappa-B heterodimer RELA/p65-c-Rel is a transcriptional activator.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The results of this study suggest a possible association of cow's milk proteins allergy with cRel G+7883T polymorphism PMID: 29336650
- TAB1 was identified as a functional target of miR-134, and the expression of TAB1 was increased by the transcription factors of NF-kappaB1, c-Rel, and ELK1 via miR-134. PMID: 28206956
- NOD2 up-regulates TLR2-mediated IL-23p19 expression via increasing c-Rel activation in Paneth cell-like cells PMID: 27563808
- this study show that inhibition of c-Rel expression by siRNA reduced cord blood-derived B-, T-, and NK cell differentiation and expansion PMID: 28090796
- Findings emphasize the importance of c-REL-signaling in a cellular model of cervical cancer particularly in terms of proliferation and resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. PMID: 28767691
- genetic association studies in population in India: Data suggest that common polymorphisms (SNPs) in CHGA promoter are associated with cardiometabolic disorders; c-Rel has a role in activating CHGA promoter haplotype 2 (variant T alleles at -1018 and -57 bp) under basal and pathophysiological conditions. (CHGA = chromogranin A; c-Rel = c-Rel proto-oncogene protein) PMID: 28667172
- findings suggest that c-Rel might play a role in promoting the invasion of choriocarcinoma cells through PI3K/AKT signaling PMID: 28259870
- miR-574 and REL interfere with apoptosis in prostate cancer stem cells. PMID: 27779701
- observations indicate that induced expression of miR-15b is modulated by c-Rel and CREB in response to JEV infection PMID: 26931521
- Gene expression levels of Rel were deregulated in 49 B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, 8 B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, 3 acute myeloid leukemia, 3 chronic myeloid leukemia, 2 hairy cell leukemia, 2 myelodysplastic syndrome, and 2 T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia patients in the post-Chernobyl period. PMID: 25912249
- The REL rs842647 polymorphism may be a susceptibility factor for Behcet's Disease pathogenesis and skin lesions. PMID: 26784953
- analysis of c-Rel nuclear expression and REL amplification and crosstalk between c-Rel and the p53 pathway reveals prognostic roles diffuse large B-cell lymphoma PMID: 26324762
- Over-expression of nuclear NF-kappaB1 and c-Rel are strong risk factors associated with chemoresistance and the prognosis of serous epithelial ovarian cancer PMID: 26683819
- Thus, our studies support a role for c-Rel in processes crucial for keratinocyte integrity and malignant transformation such as adhesion and migration. PMID: 25842167
- c-Rel is a critical mediator of NF-kappaB-dependent TRAIL resistance of pancreatic cancer cells. PMID: 25299780
- c-Rel regulates Ezh2 expression in lymphocytes and malignant lymphoid cells in a novel transcriptional network PMID: 25266721
- The REL SNP rs9309331 homozygous minor allele was associated with higher LDL levels in rheumatoid arthritis. PMID: 24489016
- Data indicate that the NF-kappaB subunit c-Rel is modified and activated by O-GlcNAcylation. PMID: 23982206
- Our studies indicate that c-Rel is a key regulator of cell fate decisions in keratinocytes such as cell growth and death and may have a role in epidermal carcinogenesis. PMID: 23892589
- The findings confirm the association of early-onset psoriasis with REL (rs13031237). PMID: 23106574
- a genetic increase in the activity of the NF-kappaB subunit c-Rel results in protection against cell death in human islets--nuclear factor-kappaB subunit c-Rel. PMID: 19706790
- Activation of NF-kappaB p65 and c-Rel may be considered an important regulator of hypersplenism and liver cirrhosis. PMID: 23195252
- REL polymorphisms lack association with rheumatoid arthritis in the Tunisian population. PMID: 22459418
- UCP4 is a target effector gene of the NF-kappaB c-Rel prosurvival pathway to mitigate the effects of oxidative stress. PMID: 22580300
- Kidney allografts from clinical operational tolerance patients show significant cellular infiltrates but a distinct expression of proteins involved in the NFkappaB1/c-rel pathway. PMID: 22955189
- c-Rel, as a member of the Rel/NF-kappaB family, is associated with psoriatic arthritis. PMID: 22170493
- IRF-4 was shown to enhance the c-Rel-dependent binding and activation of the interleukin-4 (IL-4) promoter region. IL-2 production was also enhanced by exogenously-expressed IRF-4 and c-Rel. PMID: 21890374
- Nuclear factor kappaB subunits RelB and cRel negatively regulate Toll-like receptor 3-mediated beta-interferon production via induction of transcriptional repressor protein YY1. PMID: 22065573
- Levels of c-Rel directly modulated expression of caspase-4 as well as other endoplasmic reticulum stress genes. PMID: 21984918
- By a novel, reversible dynamic mechanism TNF-alpha-induced c-REL/DeltaNp63alpha interactions inactivate tumor suppressor TAp73 function, promoting TNF-alpha resistance & cell survival in cancers with mtTP53. PMID: 21933882
- TAK1-c-Rel and IRF4 pathways play distinct roles in the maintenance of IL-9-producing Th17 phenotype of HTLV-1-transformed cells PMID: 21498517
- Three ulcerative colitis susceptibility loci are associated with primary sclerosing cholangitis and indicate a role for IL2, REL, and CARD9. PMID: 21425313
- Data show that Foxp3 directly or as part of a multimeric complex engages with the NF-kappaB component c-Rel. PMID: 21490927
- IL-23 induction by beta-glucans is due to activation of c-Rel associated with Ser-10-histone H3 phosphorylation in the il23a promoter mediated by MAPK and SAPK or PKA, and inhibition of il12a transcription PMID: 21402701
- Thus, dectin-1 and dectin-2 control adaptive T(H)-17 immunity to fungi via Malt1-dependent activation of c-Rel. PMID: 21283787
- the described effect of REL rs13031237 on the predisposition for rheumatoid arthritis was re-evaluated in a large case-control data set of 23 711 individuals and showed a modest increase in rheumatoid arthritis risk. PMID: 20876593
- Three new susceptibility loci at 2p16.1 (rs1432295, REL, 8q24.21 (rs2019960, PVT1 and 10p14 (rs501764, GATA3). PMID: 21037568
- CXCR2 signaling is critical in transgenic mice with C-rel-deficient/NFkappaB1-deficient/heterozygous Rela+/- neutrophilia causing spontaneous inflammation. PMID: 20519647
- The REL locus is associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in the UK population PMID: 19945995
- characterize the prevalence of REL, BCL11A, and MYCN gains in a consecutive CLL series at the time of diagnosis; (ii) define the prognostic relevance of REL, BCL11A, and MYCN gains in CLL. PMID: 20575024
- c-Rel, but not nuclear factor-kappa B1 (NFKB1), is required for development of transgenic regulatory T cell progenitors. PMID: 20228198
- The kinetics of NFkappaB subunit activation are partly responsible for the observed pattern of acute inflammation in the adenoviral-infected cornea. PMID: 20038977
- REL rather than BCL11A may be the target of the 2p13 alterations in classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. PMID: 11830502
- REL has an important pathologic role in Hodgkin's lymphoma PMID: 12478664
- The correlation of structural aberrations of the REL locus & nuclear c-Rel accumulation in Reed-Sternberg cells qualifies REL as a target gene of the frequent gains in 2p in cHL. REL aberrations contribute to constitutive NF-kappa B/Rel activation in cHL. PMID: 12511414
- calmodulin binds c-Rel and RelA after their release from I kappa B and can inhibit nuclear import of c-Rel while letting RelA translocate to the nucleus and act on its target genes PMID: 12556500
- v-REL has a role in NF-kappaB-regulated cell death PMID: 12588973
- Deletion of either C-terminal transactivation subdomains enhances the in viitro transforming activity of REL in chicken spleen cells. PMID: 14534540
- REL amplification may not be causative in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma PMID: 14615382
- Rel/NF-kappaB factors could take part in the occurrence of senescence by generating an oxidative stress. PMID: 14744759
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 9954
OMIM: 164910
KEGG: hsa:5966
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000295025
UniGene: Hs.631886
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-