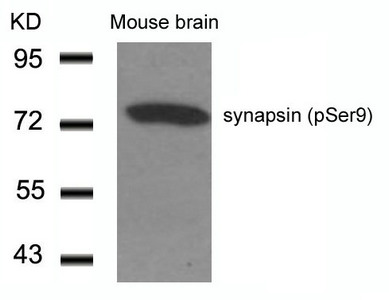
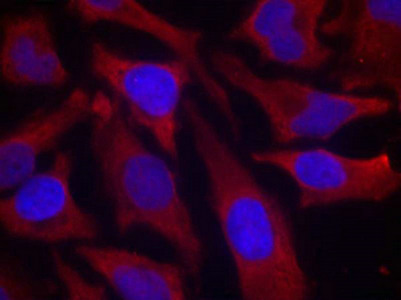
Phospho-SYN1 (Ser9) Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA580795
-
规格:¥2454
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) SYN1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:P17600
-
基因名:
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 9 (R-L-S(p)-D-S) derived from Human SYN1/synapsin.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic phosphopeptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific phosphopeptide. Non-phospho specific antibodies were removed by chromatogramphy usi
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB,IF
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:1000 IF 1:100-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Neuronal phosphoprotein that coats synaptic vesicles, binds to the cytoskeleton, and is believed to function in the regulation of neurotransmitter release. The complex formed with NOS1 and CAPON proteins is necessary for specific nitric-oxid functions at a presynaptic level.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- s identified the c.236 C > G/p.S79W mutation in SYN1 as causative for the non-syndromic ID of the MRX50 family. Accordingly, the in vitro characterization of S79W SynI clearly indicates that the mutation does not interfere with neurodevelopmental aspects, but perturbs spontaneous SV exocytosis, SV clustering and SV lateral mobility along axons. PMID: 28973667
- These findings contribute to previous work showing dysregulation of Synapsins, particularly SYN2, in mood disorders and improve our understanding of the regulatory mechanisms that precipitate these changes likely leading to the BD or MDD phenotype. PMID: 27515700
- Cerebral malaria causes pre-synaptic excitation and eventually activation of synapsin I, leading to increased neurotransmitter release. PMID: 26823711
- Patterns of the immunoreactivity with antibodies to SNAP-25, synapsin-I and synaptophysin are completely appropriate to those of adult's OB on the 38-40 weeks of the prenatal development. PMID: 26204769
- The implementation of the AlphaScreen pSYN1 assay and future development of additional primary neuronal HTS assays provides an attractive approach for discovery of novel classes of therapeutic candidates for a variety of CNS disorders. PMID: 24088370
- these findings suggest PRICKLE1 mutations contribute to ASD by disrupting the interaction with SYN1 and regulation of synaptic vesicles. PMID: 24312498
- Data indicate that in patients carrying the W356x mutation the function of synapsin I is markedly impaired, and support the value of Syn1(-/-) mice as an experimental model mimicking the human pathology. PMID: 23818987
- Epileptogenic Q555X SYN1 mutant triggers imbalances in release dynamics and short-term plasticity. PMID: 23406870
- The histone modification marks were significantly increased in major depression and this effect was correlated with significant increases in SYN1b gene expression. PMID: 22571925
- The allelic frequencies of SYN1 are associated with Korean female schizophrenia. PMID: 22807112
- SYN1 loss-of-function mutations in autism and partial epilepsy cause impaired synaptic function. PMID: 21441247
- the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of dysbindin-1 regulates synapsin I expression and thus may be involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. PMID: 20921223
- The s propose claudin-2 and SYN1 work in concert to enhance microbial translocation across the intestinal epithelial barrier to contribute to chronic immune activation and CD4 T-cell depletion in HIV-1-infected patients. PMID: 20700059
- The results showed that synapsin I was significantly decreased in the stratum radiatum of CA1 subfield and the molecular layer of DG in AD patients. PMID: 14673601
- SYN1 nonsense mutation is the likely cause of epileptic and other phenotypes PMID: 14985377
- Synapsins and S100A1 interact in nerve terminals where coexpresssed; S100A1 cannot bind SV-associated synapsin I and may function as a cytoplasmic store of monomeric synapsin I; synapsin dimerization and interaction with S100A1 are mutually exclusive PMID: 15147519
- This study concluded that the human synapsin I gene is positively regulated by nuclear respiratory factor 1 and mediates the function of nuclear respiratory factor 1 in neurite outgrowth. PMID: 19301426
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Epilepsy X-linked, with variable learning disabilities and behavior disorders (XELBD)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell junction, synapse. Golgi apparatus.
-
蛋白家族:Synapsin family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 11494
OMIM: 300491
KEGG: hsa:6853
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000295987
UniGene: Hs.225936
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-