Phospho-LCK (Tyr394) Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA096222
-
规格:¥2454
-
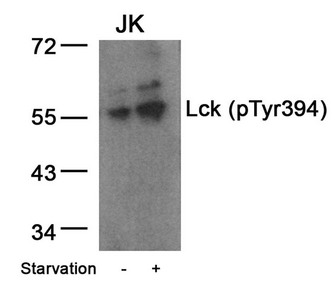
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) LCK Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:P06239
-
基因名:
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of tyrosine 394 (N-E-Y(p)-T-A) derived from Human Lck.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic phosphopeptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific phosphopeptide. Non-phospho specific antibodies were removed by chromatogramphy usi
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:1000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase that plays an essential role in the selection and maturation of developing T-cells in the thymus and in the function of mature T-cells. Plays a key role in T-cell antigen receptor (TCR)-linked signal transduction pathways. Constitutively associated with the cytoplasmic portions of the CD4 and CD8 surface receptors. Association of the TCR with a peptide antigen-bound MHC complex facilitates the interaction of CD4 and CD8 with MHC class II and class I molecules, respectively, thereby recruiting the associated LCK protein to the vicinity of the TCR/CD3 complex. LCK then phosphorylates tyrosine residues within the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAM) of the cytoplasmic tails of the TCR-gamma chains and CD3 subunits, initiating the TCR/CD3 signaling pathway. Once stimulated, the TCR recruits the tyrosine kinase ZAP70, that becomes phosphorylated and activated by LCK. Following this, a large number of signaling molecules are recruited, ultimately leading to lymphokine production. LCK also contributes to signaling by other receptor molecules. Associates directly with the cytoplasmic tail of CD2, which leads to hyperphosphorylation and activation of LCK. Also plays a role in the IL2 receptor-linked signaling pathway that controls the T-cell proliferative response. Binding of IL2 to its receptor results in increased activity of LCK. Is expressed at all stages of thymocyte development and is required for the regulation of maturation events that are governed by both pre-TCR and mature alpha beta TCR. Phosphorylates other substrates including RUNX3, PTK2B/PYK2, the microtubule-associated protein MAPT, RHOH or TYROBP. Interacts with FYB2.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The ionic CD3-epsilon -Lck interaction controls the phosphorylation level of the T-cell receptor. PMID: 28659468
- a previously unappreciated role for PLC-gamma1 in the positive regulation of Zap-70 and T-cell receptor tyrosine phosphorylation. Conversely, PLC-gamma1 negatively regulated the phosphorylation of SLP-76-associated proteins, including previously established Lck substrate phosphorylation sites within this complex. PMID: 28644030
- autophosphorylation of the LCK active-site loop is indispensable for its catalytic activity and LCK can stimulate its own activation by adopting a more open conformation, which can be modulated by point mutations, and CD4 and CD8, T-cell coreceptors, can enhance LCK activity PMID: 29083415
- the central biological role of the novel IL-2-R/Lck/PLCgamma/PKCtheta;/alphaPIX/Rac1/PYGM signalling pathway is directly related to the control of fundamental cellular processes such as T cell migration and proliferation. PMID: 27519475
- Possible models of regulation of Lck by Aurora-A during T cell activation are described in the review. PMID: 27910998
- Mutation of the basic clusters in the CD28 cytoplasmic domain reduced the recruitment to the CD28-Lck complex of protein kinase Ctheta; (PKCtheta;), which serves as a key effector kinase in the CD28 signaling pathway. PMID: 27460989
- Data suggest that T cell activation through the TCR complex is accompanied by the de novo activation of T-lymphocyte specific protein tyrosine kinase p56lck (Lck) and that phosphorylation of Tyr(394) plays a role in Lck function that goes beyond inducing an open conformation of the kinase. PMID: 28096507
- WASH has a pivotal role for regulation of NK cell cytotoxicity through Lck-mediated Y141 tyrosine phosphorylation. PMID: 27441653
- A phosphosite within the SH2 Domain of Lck regulates its activation by CD45. A negative feedback loop that responds to signaling events tunes active Lck amounts and TCR sensitivity. PMID: 28735895
- The results have revealed a novel splicing homozygous mutation of LCK that may be responsible for the clinical phenotype of HPV infection from latency to invasive carcinoma. PMID: 27087313
- this study show that Lck as a major signaling hub of CD147 in T cells PMID: 28148733
- data indicate that HSP65 suppresses cholesterol efflux and increases cellular cholesterol content through an Lck-mediated pathway in T cells PMID: 27742830
- LSKlow cells, which are derived from LSK cells in p18(-/-) mice, possess lymphoid differentiation ability and short-term repopulation capability. PMID: 27287689
- These results suggest that PM lipids, including phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate, modulate interaction of Lck with its binding partners in the TCR signaling complex and its TCR signaling activities in a spatiotemporally specific manner via its SH2 domain. PMID: 27334919
- this study shows that p56(lck), which is essential for activation of T cells through the T-cell receptor, is also critical for signal transduction through Toll-like receptors in T cells PMID: 26888964
- Aurora A inhibition causes delocalized clustering of Lck at the immunological synapses and decreases its phosphorylation levels thus indicating Aurora A is required for maintaining Lck active during T-cell activation. PMID: 27091106
- Results demonstrate that Lck represses oxidative phosphorylation through competitive binding with mitochondrial CRIF1 in a kinase-independent manner. PMID: 26210498
- introducing bulky side-chains into this patch (GGxxG to GVxxL) impairs the Lck-independent role of CD4 in T cell activation upon TCR engagement of agonist and weak agonist stimulation. PMID: 26147390
- our results support a novel function of nuclear Lck in promoting human leukemic T cell survival through interaction with a tumor suppressor, CRIF1 PMID: 25997448
- TSAD binds to and co-localizes with Nck. Expression of TSAD increases both Nck-Lck and Nck-SLP-76 interaction in T cells. PMID: 26163016
- These findings demonstrate highly dynamic Lck palmitoylation kinetics that are essential for signaling downstream of the Fas receptor. PMID: 26351666
- Cells from PAX5 translocated patients show LCK up-regulation and over-activation, as well as STAT5 hyper-phosphorylation, compared to PAX5 wt and PAX5 deleted cases. PMID: 25595912
- T cell receptor (TCR)-CD3 complex and the Lck kinase were required for Ca(2+) mobilization but not for apoptosis induction in Jurkat cells. PMID: 25947381
- In T-cells, cholesterol-dependent domains function in the regulation of the Src family kinase Lck (p56lck) by sequestering Lck from its activator CD45. (Review) PMID: 25658353
- Phosphatase CD45 both positively and negatively regulates T cell receptor phosphorylation in reconstituted membrane protein clusters, depending on LCK activity. PMID: 25128530
- Lck is retained in the cytosol of CD222-deficient cells, which obstructs the recruitment of Lck to CD45 at the cell surface, resulting in an abundant inhibitory phosphorylation signature on Lck at the steady state. PMID: 25127865
- Lck mediates signal transmission from CD59 to the TCR/CD3 pathway in Jurkat T cells. PMID: 24454946
- NUP214-ABL1-mediated cell proliferation in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia is dependent on the LCK kinase and various interacting proteins. PMID: 23872305
- LCK phosphorylated Tyr-342 of FOXP3 by immunoprecipitation and in vitro kinase assay, and the replacement of Tyr-342 with phenylalanine (Y342F) abolished the ability to suppress MMP9 expression. PMID: 24155921
- our data reveal how SAP nucleates a previously unknown signaling complex involving NTB-A and LCK to potentiate restimulation-induced cell death of activated human T cells. PMID: 24688028
- Data show a major role for LCK in proximal and distal BCR-mediated signaling in CLL cells and suggest that LCK expression is important in the pathogenesis of CLL. PMID: 23505068
- Nef thus interferes with a specialized membrane microdomain-associated pathway for plasma membrane delivery of newly synthesized Lck whose specificity is determined by the affinity of cargo for these sorting platforms. PMID: 23601552
- In the absence of FAK, the inhibitory phosphorylation of Lck is impaired. PMID: 24227778
- spatial regulation of Lck by CD45 and GM1 ganglioside determines the outcome of apoptotic response to Gal-1 and this local regulation may occur only upon intimate effector (Gal-1 expressing) cell-T-cell attachment. PMID: 24231767
- VP11/12 SFK-binding motifs recruit Lck and the activated Src family kinase then leads (directly or indirectly) to phosphorylation of additional motifs involved in recruiting p85, Grb2, and Shc. PMID: 23946459
- LCK (lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase) plays a crucial role in T-cell response by transducing early activation signals triggered by TCR (T-cell receptor) engagement. [REVIEW] PMID: 23931554
- conformational states regulate clustering in early T cell signaling PMID: 23202272
- T-cell receptor-induced stimulation of T cells led to simultaneous phosphorylation of p56(lck) residues. PMID: 22674786
- LCK-positive tumour infiltrate is associated with a significantly longer overall survival and time to relapse in patients with radically resected stage I NSCLC. PMID: 22457183
- Data show that cytoskeletal modulation of lipid interactions regulates Lck kinase activity. PMID: 22613726
- increases in Ca(2+) lead to CaMKII activation and subsequent Lck-dependent p66Shc phosphorylation on Serine 36. This event causes both mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired Ca(2+) homeostasis, which synergize in promoting Jurkat T-cell apoptosis. PMID: 21983898
- The Kv1.3/Dlg1/Lck complex is part of the membrane pathway utilized by cyclic AMP to regulate T-cell function. PMID: 22378744
- DHHC2 localizes primarily to the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus suggesting that it is involved in S-acylation of newly-synthesized or recycling Lck involved in T cell signalling. PMID: 22034844
- the segment comprising residues 112-126 of human LAT is required for its interaction with Lck. PMID: 22034845
- Feedback circuits monitor and adjust basal Lck-dependent events in T cell receptor signaling. PMID: 21917715
- These results showed that MG132-induced apoptosis was caused by ER stress and subsequent activation of mitochondria-dependent caspase cascade; the presence of p56(lck) enhances MG132-induced apoptosis by augmenting ER stress-mediated apoptotic events. PMID: 21819973
- Data show that MAL regulates membrane order and the distribution of microtubule and transport vesicle docking machinery at the IS and, by doing so, ensures correct protein sorting of Lck and LAT to the cSMAC. PMID: 21508261
- Deregulations of Lck-ZAP-70-Cbl-b cross-talk and miR181a in T cells were found to be associated with cholesterol-dependent-dismantling of HLA-DR rafts in macrophages in leprosy progression. PMID: 21453975
- Preactivated Lck is both necessary and sufficient for T cell activation but remains uncoupled from the T cell receptor in the absence of antigen. PMID: 21266711
- Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 interacts with oncogenic lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase. PMID: 21234523
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Immunodeficiency 22 (IMD22)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor; Cytoplasmic side. Cytoplasm, cytosol.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, SRC subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed specifically in lymphoid cells.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6524
OMIM: 153390
KEGG: hsa:3932
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000337825
UniGene: Hs.470627
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-