MTNR1B Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA003225
-
规格:¥880
-
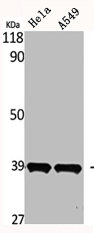
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P49286
-
基因名:
-
别名:MTNR1B; Melatonin receptor type 1B; Mel-1B-R; Mel1b receptor
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from the C-terminal region of Human MEL-1B-R.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:WB, ELISA
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 ELISA 1:5000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:High affinity receptor for melatonin. Likely to mediate the reproductive and circadian actions of melatonin. The activity of this receptor is mediated by pertussis toxin sensitive G proteins that inhibit adenylate cyclase activity.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Genome-wide significant (P < 5 x 10(-8) ) interaction with MTNR1B and joint effects were detected for CMIP intronic rs17197883. PMID: 29691896
- The reduced titer of melatonin, along with altered fasting blood glucose due to MTNR1B genetic variant, acts as a risk factor towards type 2 diabetes in the Gujarat population of India. PMID: 29674279
- that MTNR1B and IRS2 gene variants impacted epicardial fat thickness, lipid profile and glucose homeostasis PMID: 28708046
- melatonin stimulates PINK1 expression via an MT2 /Akt/NF-kappaB pathway, and such stimulation is important for the prevention of neuronal cell apoptosis under high glucose conditions. PMID: 28580603
- MTNR1B rs10830963 polymorphism is associated with gestational diabetes susceptibility, and women with a higher number of G alleles have an increased risk of gestational diabetes development. PMID: 28084098
- In women with psychosis, troponin T levels were associated with genetic variants in MTNR1B. PMID: 28167435
- The present data suggested that MTNR1B polymorphisms could influence the clinical features in lupus patients, and especially the susceptibility to leucopenia PMID: 27115109
- MTNR1B rs10830963/G variant is associated with gestational diabetes binary and glycemic traits in the Caucasian case-control study. PMID: 28072873
- the risk allele (G allele) of rs10830963 and (T allele) of rs1387153 in MTNR1B lead to a higher risk for gestational diabetes mellitus PMID: 26563312
- Our results provide the surprising insight that the MTNR1B risk allele influences dynamics of melatonin secretion, generating a novel hypothesis that the MTNR1B risk allele may extend the duration of endogenous melatonin production later into the morning and that early waking may magnify the diabetes risk conferred by the risk allele. PMID: 26868293
- Insomnia does not mediate or modify the association between MTNR1B risk variant rs10830963 and glucose levels. PMID: 26912228
- finding suggests that the MTNR1B-dependent vulnerability for elevated fasting plasma glucose levels is shared between bipolar disorder and schizophrenia PMID: 26991397
- For the first time, we show that Cry 2 rs2292910 and MTNR1B rs3781638 are associated with osteoporosis in a Chinese geriatric cohort. PMID: 26564225
- rs10830963 polymorphism was not associated with polycystic ovary syndrome in Han Chinese. PMID: 26519818
- s investigated the association between rs4753426 single nucleotide polymorphisms in the melatonin receptor 1B (MTNR1B) gene and the risk of developing gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). PMID: 26345809
- Increases in islet MTNR1B expression is associated with type 2 diabetes susceptibility. PMID: 26551672
- This systematic review was a comprehensive analysis of the currently available evidence, and found an overall significant association of rs4753426 polymorphism with the risk of--{REVIEW} PMID: 26431121
- results indicate, for the first time, the presence of a functional circadian clock in the human myometrium with the hMTNR1B gene as a clock controlled target. PMID: 25939854
- MTNR1B rs4753426 and MTNR1B rs10830963 polymorphisms are not obviously associated with risk of AIS in either Asian populations or Caucasian populations. PMID: 25898821
- rs10830963 MTNR1B polymorphism could be associated with individual differences in weight loss induced by a hypocaloric diet PMID: 25870980
- MTNR1B rs10830963 risk variant worsens the effect of melatonin on glucose tolerance PMID: 26440713
- these observations suggest a biologically plausible season-dependent association between SNPs at CRY1, CRY2 and MTNR1B and glucose homeostasis. PMID: 25707907
- It has been shown for the first time in obese youth that the MTNR1B variant is associated with an increased risk of IFG PMID: 25919927
- our study found that the genetic polymorphisms rs10830963 and rs1387153 in MTNR1B and rs1801278 in IRS1 were associated with an increased risk of developing GDM. PMID: 25146448
- Carriers of the G allele of MTNR1B rs10830963 are more likely to develop gestational diabetes than carriers of the C allele. PMID: 25982863
- results obtained are suggestive of MTNR1B role in T2D etiology, they need to be confirmed with much larger sample sizes PMID: 25922310
- cross-talk mediated via physical association of melatonin MT2 and 5-HT2C receptors into functional heteromers PMID: 25770211
- The extent of receptor internalization for the human MT2 receptor is independent of the intrinsic efficacy of agonists and provide novel insights into the controversial relationship between intrinsic agonist efficacy and agonist-induced internalization PMID: 25059758
- the association between the common MTNR1B rs10830963 variation and fasting plasma glucose levels in BH population. PMID: 24710643
- We conclude that variation in MTNR1B contributes to the absolute level of insulin secretion but not to differences in the temporal rate of change in insulin secretion. PMID: 24728128
- High expression for MT2 receptor is associated with gastric adenocarcinoma. PMID: 24142542
- 14 mutants with loss of Gi protein activation that associate with increased risk of type 2 diabete development (Review) PMID: 23798576
- Genetics of MTNR1B point to impact of the melatonin signalling pathway for BP and left ventricular function. PMID: 23611530
- GCKR rs780094 variant confers high cross-ethnicity risk for the development of T2DM, while significant associations between GCK, MTNR1B and G6PC2 variants and T2DM risk are limited to Caucasians. PMID: 23840762
- Our data indicate that variants in the circadian-related genes CRY2 and MTNR1B may affect long-term changes in energy expenditure, and dietary fat intake may modify the genetic effects. PMID: 24335056
- genetic association study in women in Finland: Data suggest that 2 SNPs in MTNR1B (rs10830963; rs1387153) are associated with gestational diabetes (and type 2 diabetes, as shown in previous studies); down-regulation of insulin secretion is related. PMID: 23761423
- The rs10830963 MTNR1B polymorphism is a risk factor for developing impaired glucose regulation and type 2 diabetes mellitus. (Meta-analysis) PMID: 23226241
- There is a strong association of rs1374645 polymorphism with low fasting blood glucose levels in the low BMI group compared to the high BMI group. PMID: 21558052
- Investigated whether genetic variants in MTNR1B were associated with delirium; none of the 5 single nucleotide polymorphisms tested were found to be associated with the occurrence of delirium. PMID: 22759724
- The MTNR1B is likely to be involved in the regulation of glucose homeostasis during pregnancy. PMID: 22768333
- These data showing the association of polymorphisms in the TPH2 and MTNR1B genes with the progressive subtypes of multiple sclerosis and disability suggest dysregulation in melatonin pathway PMID: 22698518
- This study confirms the association of gestational diabetes mellitus with the rs10830963 variant in a sample of the Greek population. PMID: 22450346
- Rare MTNR1B variants impairing melatonin receptor 1B function contribute to type 2 diabetes. PMID: 22286214
- Six SNP(rs7754840 in CDKAL1, rs391300 in SRR, rs2383208 in CDKN2A/2B, rs4402960 in IGF2BP2, rs10830963 in MTNR1B, rs4607517 in GCK)risk alleles of type 2 diabetes were associated with GDM in pregnant Chinese women. PMID: 22096510
- The results of this study suggested that the Single nucleotide polymorphisms MT(2) receptor gene influence the risk of recurrent depressive disorder. PMID: 21353709
- The rs10830963 polymorphism in MTNR1B was associated with increased fasting glucose and risk of impaired fasting glucose in Chinese children and adolescents. PMID: 21701235
- The G-allele of rs10830693 in the MTNR1B gene was significantly related to glucose levels, while an impact of this genetic variant on the changes in glucose metabolism in children participating in a lifestyle intervention was not observable. PMID: 21366812
- There is no effect by the common gene variant rs10830963 of the melatonin receptor 1B on the association between sleep disturbances and type 2 diabetes. PMID: 21380592
- There were significant associations between the two genetic variants (rs10830963 and rs1387153) of the melatonin receptor 1B gene and gestational diabetes mellitus. PMID: 21658282
- The rs3781637 A/G polymorphism of the MTNR1B gene is associated with type 2 diabetes, plasma, total cholesterol and LDL-C levels in the Han Chinese population. PMID: 21470412
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in retina and less in brain and hippocampus.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 7464
OMIM: 600804
KEGG: hsa:4544
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000257068
UniGene: Hs.569039
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-