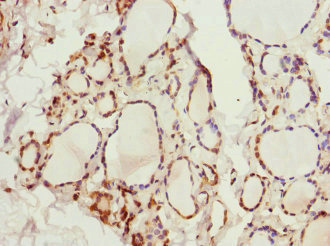
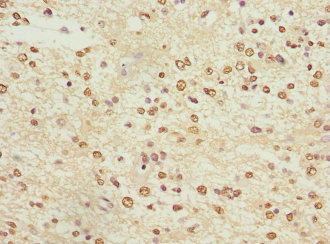
KCNA3 Antibody
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) KCNA3 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:P22001
-
基因名:KCNA3
-
别名:KCNA3; HGK5; Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 3; HLK3; HPCN3; Voltage-gated K(+ channel HuKIII; Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv1.3
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 3 protein (486-575AA)
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen Affinity Purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC 1:20-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Mediates the voltage-dependent potassium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a potassium-selective channel through which potassium ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- T-cell dependency on Kv1.3 or KCa3.1 might be irreversibly modulated by antigen exposure. PMID: 28248292
- Kv1.3 methylation may serve as diagnostic and prognostic markers in colorectal cancer. PMID: 28472608
- the tertiary structure of the C-terminal domain of Kv1.3 is necessary and sufficient for Kv1.3- KCNE4 interaction. PMID: 27802162
- results identify a caveolin-binding domain in Kv1 channels and highlight the mechanisms that govern the regulation of channel surface localization during cellular processes PMID: 26931497
- we report that Kv1.3-NPs reduced NFAT activation and CD40L expression exclusively in CD45RO(+) T cells. Furthermore, Kv1.3-NPs suppressed cytokine release and induced a phenotype switch of T cells from predominantly memory to naive. PMID: 26994905
- The implication of Kv1.3 in a wide repertoire of human pathologies indicates this channel is an important therapeutic target. PMID: 26634786
- Results contribute to the characterization of leukemic B cells, as it shows that upregulation of Kv1.3 in pathologic B lymphocytes is linked to the oncogenic B-RAF signaling. PMID: 26393354
- Data suggest that C-terminus is necessary for Kv1.3-induced cell proliferation; the mechanism involves accessibility of key docking sites at the C terminus; phosphorylation of Tyr-447 by MAP kinase signal cascade appears crucial. PMID: 26655221
- concluded that Kv1.3 may stimulate macrophage migration through the activation of ERK. PMID: 26748289
- The inhibition of Kv1.3 channels might be involved in antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects of the compounds observed in cancer cell lines expressing these channels. PMID: 25688010
- Kv1.3 channels modulate human vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation independently of mTOR signaling pathway. PMID: 25208915
- actin dynamics regulates the membrane motility of Kv1.3 channels. PMID: 25739456
- The increment and decrement of the basic residue number in a positively charged S4 sensor of Kv1.3 channel yields conductance-voltage relationship curves in the positive direction by approximately 31.2 mV and 2-4 mV PMID: 25944908
- the association between Kv1.3 and the COPII cargo adaptor subunit isoform Sec24a PMID: 26156069
- Findings reveal that alpha-defensins are endogenous inhibitors of potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 3 (Kv1.3) with distinct interaction mechanisms. PMID: 26148969
- This study demonstrated that Potassium channel Kv1.3 is highly expressed by microglia in human Alzheimer's disease. PMID: 25362031
- These results demonstrate that Kv1.3 channels are primarily localized in the nucleus of several types of cancer cells and human brain tissues where they are capable of regulating nuclear membrane potential and activation of transcription factors PMID: 25829491
- the small molecule Kv1.3 blocker PAP-1 dose-dependently inhibited proliferation and suppressed IL-2 and IFN-gamma production. PMID: 25175978
- Treatment with Acacetin for 24 h significantly inhibited Kv1.3 protein expression. PMID: 25301362
- results revealed that the deficient expression of Kv1.3 channel would cause the less Ca2+ signal, leading to the less efficiency in secretion PMID: 24594979
- Targeting the ion channel Kv1.3 with scorpion venom peptides engineered for potency, selectivity, and half-life PMID: 24939846
- We show the structure of the T1 domain derived from the voltage-dependent potassium channel K(v)1.3 of Homo sapiens sapiens at 1.2 A resolution crystallized under near-physiological conditions. PMID: 24114469
- s show the helical transmembrane S3b-S4 hairpin ("paddle") of a voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel, a critical region of the Kv voltage sensor, forms in the ribosomal vestibule. PMID: 24055377
- CMYA5 is a new potential substrate of Kcna3 in human heart PMID: 23335746
- diseases. Our present results indicate a critical role for Kv1.3 in the conversion of CD8+ T cells into potential pathogenic effector cells with cytotoxic function. PMID: 23382885
- role of Kv1.3 in modulating cholesterol-metabolism-associated molecules in human acute monocytic leukemia cell-derived macrophages (THP-1 macrophages) and human monocyte-derived macrophages exposed to oxidized LDL PMID: 23099443
- Diclofenac can significant down-regulate the expression of Kv1.3 and Kir2.1 channels in human macrophages, lower their membrane potential and inhibit the process of foam cell formation. PMID: 22931594
- MMP23-PD suppresses the voltage-gated potassium channel KV1.3, but not the closely related KV1.2 channel, by trapping the channel intracellularly. PMID: 23300077
- GrB released from T cells induced neurotoxicity by interacting with the membrane bound Gi-coupled PAR-1 receptor and subsequently activated Kv1.3 and Notch-1 PMID: 22952817
- and immunocytochemistry experiments revealed an association between K(v)1.5, K(v)beta1.3, the receptor for activated C kinase (RACK1), PKCbetaI, PKCbetaII, and PKCtheta. PMID: 22547057
- Selective knockdown of protein kinase A 1(PKAI) eliminates modulation of Kv1.3 channels by PKAI activation. PMID: 22378744
- Data suggest that rituximab induces apoptosis of malignant B lymphocytes by stimulating FcgammaRIIB receptors and inhibiting Kv1.3 channels. PMID: 22192444
- CD4+CD28null T cells expressed small numbers of the voltage-gated Kv1.3 and intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel KCa3.1 when quiescent, but increased Kv1.3 expression 4-fold with little change in KCa3.1 levels upon activation. PMID: 22169811
- expression of Kv1.5 and Kv1.3 increased in skeletal muscle tumorigenesis in a close relationship with malignancy. PMID: 22360360
- hypoxia disrupts AP1/clathrin-mediated forward trafficking of Kv1.3 from the trans-Golgi to the plasma membrane thus contributing to decreased Kv1.3 surface expression in T lymphocytes. PMID: 22134923
- Functional blockade of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 mediates reversion of T effector to central memory lymphocytes through SMAD3/p21cip1 signaling. PMID: 22110135
- Our findings provide the first evidence that KCNA3 is associated with autoimmune pancreatitis and suggest that KCNA3 may influence the risk for autoimmune pancreatitis PMID: 22045429
- PDZ binding domain-dependent interactions affect both Kv1.3 localization (plasma membrane vs. golgi complex) and electrophysiological function. PDZ interactions affect localization and function via independent mechanisms. PMID: 21726550
- regulatory switch of Kv1.3 activity in peripherally induced Tregs may constitute an important contributing factor in the signaling rewiring associated with the development of these cells PMID: 21834013
- findings are not supportive of a role for Kv1.3 in the modulation of peripheral insulin sensitivity PMID: 21586699
- A mutation in Kv1.3 (A413C) doubles the stoichiometry of emopamil but not verapamil for blocking the channel. PMID: 21220411
- K(V)1.3 potassium channels are functional in proliferating mouse and human vascular smooth muscle cells and have positive effects on cell migration. Blockers of the channels may be useful as inhibitors of neointimal hyperplasia. PMID: 20884640
- treatment with short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against Kv1.3, significantly blocked A549 cells' proliferation PMID: 21087602
- higher expression on major T-lymphocyte subsets of newborns compared to adult ones except for T(h)1 lymphocytes PMID: 20601376
- increased impact on T-lymphocyte activation in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients PMID: 20603149
- Kv1.3 contributes an unusual nonconducting role - the detection of metabolic state. PMID: 20865378
- role of this channel in the sequence of events leading to Bax-induced cytochrome c release PMID: 20114030
- A comparison of the expression patterns of Kv1.3 and Kv1.5 in the human fetus. PMID: 20798505
- trafficking abnormalities contribute to defective signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus T cells PMID: 19959227
- Given that glutamate is present in plasma and that both mGluRs and K(V)1.3 channels regulate T-lymphocyte responsiveness, our finding may account for the presence of immune-associated alterations in AD. PMID: 19850126
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Potassium channel family, A (Shaker) (TC 1.A.1.2) subfamily, Kv1.3/KCNA3 sub-subfamily
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6221
OMIM: 176263
KEGG: hsa:3738
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000358784
UniGene: Hs.169948