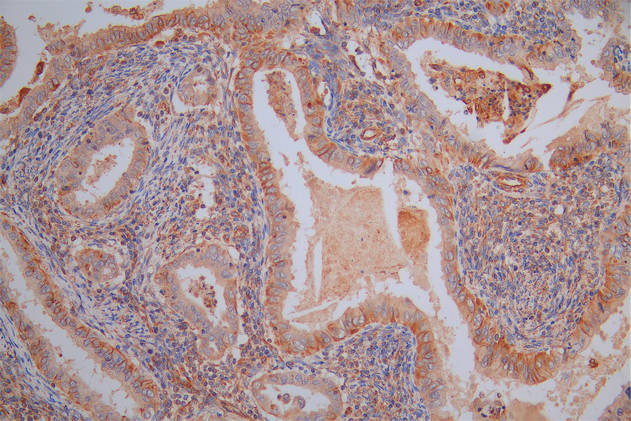
IGHD Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA367346
-
规格:¥880
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P01880
-
基因名:IGHD
-
别名:IGHD antibody; Immunoglobulin heavy constant delta antibody; Ig delta chain C region antibody; Ig delta chain C region NIG-65 antibody; Ig delta chain C region WAH antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Synthetic peptide from Human protein at AA range: 111-160
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit serum by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:PBS, pH 7.4, containing 0.02% sodium azide as Preservative and 50% Glycerol.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:IHC,ELISA
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC IHC-p:1:50-300 ELISA 1:10000-20000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Constant region of immunoglobulin heavy chains. Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are membrane-bound or secreted glycoproteins produced by B lymphocytes. In the recognition phase of humoral immunity, the membrane-bound immunoglobulins serve as receptors which, upon binding of a specific antigen, trigger the clonal expansion and differentiation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulins-secreting plasma cells. Secreted immunoglobulins mediate the effector phase of humoral immunity, which results in the elimination of bound antigens. The antigen binding site is formed by the variable domain of one heavy chain, together with that of its associated light chain. Thus, each immunoglobulin has two antigen binding sites with remarkable affinity for a particular antigen. The variable domains are assembled by a process called V-(D)-J rearrangement and can then be subjected to somatic hypermutations which, after exposure to antigen and selection, allow affinity maturation for a particular antigen. IgD is the major antigen receptor isotype on the surface of most peripheral B-cells, where it is coexpressed with IgM. The membrane-bound IgD (mIgD) induces the phosphorylation of CD79A and CD79B by the Src family of protein tyrosine kinases. Soluble IgD (sIgD) concentration in serum below those of IgG, IgA, and IgM but much higher than that of IgE. IgM and IgD molecules present on B cells have identical V regions and antigen-binding sites. After the antigen binds to the B-cell receptor, the secreted form sIgD is shut off. IgD is a potent inducer of TNF, IL1B, and IL1RN. IgD also induces release of IL6, IL10, and LIF from peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Monocytes seem to be the main producers of cytokines in vitro in the presence of IgD.
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform 1]: Secreted.; [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 5480
OMIM: 147170
UniGene: Hs.510635
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-