Grin2b Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA191146
-
规格:¥2024
-
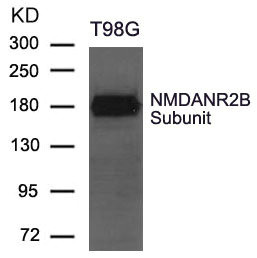
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Rattus norvegicus (Rat) Grin2b Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q00960
-
基因名:
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around aa.1250-1254(N-L-Y-D-I) derived from Human NMDANR2B Subunit.
-
免疫原种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic peptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific peptide.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:1000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
靶点详情
-
功能:Component of NMDA receptor complexes that function as heterotetrameric, ligand-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Channel activation requires binding of the neurotransmitter glutamate to the epsilon subunit, glycine binding to the zeta subunit, plus membrane depolarization to eliminate channel inhibition by Mg(2+). Sensitivity to glutamate and channel kinetics depend on the subunit composition (Probable). In concert with DAPK1 at extrasynaptic sites, acts as a central mediator for stroke damage. Its phosphorylation at Ser-1303 by DAPK1 enhances synaptic NMDA receptor channel activity inducing injurious Ca2+ influx through them, resulting in an irreversible neuronal death. Contributes to neural pattern formation in the developing brain. Plays a role in long-term depression (LTD) of hippocampus membrane currents and in synaptic plasticity.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- CaMKIIa-GluN2B interaction had an important role in the development of L-dopa-induced dyskinesia. PMID: 30142538
- Peptides specifically disrupting the interaction between GluN2B and AP-2 complex not only blocked endocytosis of GluN2B induced by NMDA treatment but also abolished NMDA-induced excitotoxicity PMID: 28326942
- the BDNF-Fyn-GluN2B signaling cascade in the spinal dorsal horn may constitute a key mechanism underlying central sensitization and neuropathic pain development after peripheral nerve injury PMID: 28497343
- Pharmacological inactivation and antagonism study suggests that oflactory span capacity in rats depends on GluN2B-containing NMDA receptor-dependent interactions between the medial prefrontal cortex and dorsomedial striatum. PMID: 28916627
- APP intracellular domain increase in mature neurons, as reported in Alzheimer's disease, alters synaptic NMDAR composition to an immature-like GluN2B-rich profile. This disrupts synaptic signal integration, via over-activation of SK channels, and synapse plasticity. PMID: 28682239
- Findings provide a new insight for the role of GluN2B in memory storage in adult hippocampus. The unique mechanism, by which GluN2B is training-strength-dependently involved in memory formation, suggests that GluN2B can flexibly participate in memory formation through a rapid change in its membrane expression following individual experience. PMID: 27487820
- An appetitive experience after fear memory destabilization attenuates fear retention. Blocking GluN2B-NMDA receptors in basolateral amygdala, prevented the fear reduction caused by the appetitive experience. Results suggest that the expression of a fear memory can be dampened by an unrelated appetitive experience, as long as memory destabilization is achieved during reactivation. PMID: 27531837
- This study demonstrated that high anxiety restraint rats had decreased GR/GluN2B density in cortical areas and basolateral amygdala. PMID: 27865917
- Transgenic rats with over-expressed GluN2B-subunits in the forebrain exhibited a relatively higher susceptibility to morphine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) and naloxone-induced place aversion than their wild-type littermates did, while they retained the similar sensitivity as wild-type rats to CPP induced by natural reinforcers (food and sucrose). PMID: 27217103
- Overexpression of EphB2 also rescued the ADDLs-induced depletion of the expression of EphB2 and GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors trafficking in cultured hippocampal neurons. PMID: 28358367
- Results are consistent with a role of GluN2B diheretomers in long-term depression, a role of both GluN2B- and GluN2D- containing NMDARs in short-term potentiation and a role of GluN2A/B triheteromers in long-term potentiation. PMID: 27523302
- single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites in the rat GRIN2B promoter region were screened. PMID: 25917873
- While low-frequency stimulation -depotentiation clearly required N-Methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor activation, GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors were not involved in this form of depotentiation. PMID: 26881126
- Data show that 17beta estradiol recruits a causal role for GluN2B-containing NMDARs and ERK signaling in the induction of long-term potentiation PMID: 26190171
- activity-dependent regulation of STEP61 and its substrates GluN2B and GluA2 may contribute to homeostatic stabilization of excitatory synapses. PMID: 26391783
- Results show that monomeric Abeta1-42 application induces an increase of the Ca2+-response and of the membrane expression of the extrasynaptic subunit of the NMDA receptor GluN2B in PC12 cells, while the opposite effects were observed in cultured neurons PMID: 26401567
- The NR2B-CREB-CRTC1 signaling pathway may play a crucial role in circadian rhythm of pain PMID: 26440419
- The pronociception induced by systemic cholecystokinin, which is vagal afferent-dependent, requires activation of central amygdala NR2B-containing N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. PMID: 26197883
- The adaptive changes in AMPAR and NMDAR subunit mRNA might dictate the regenerative fate of FMNs in response to the peripheral axotomy and thereby play a unique role in the pathogenesis of facial nerve injury and regeneration. PMID: 26343542
- Study reported that in the developing rat cortex, migration of presumptive layer II/III neurons to their deserved destination was regulated by NMDA receptors with GluN2B subunit PMID: 25838242
- Auditory cortex NR2B mRNA and protein were upregulated in salicylate-treated rats. expression returning to normal levels 14 days after cessation of treatment or after GM1 administration. PMID: 26554229
- results revealed that the phosphorylation change of GluN2B at Tyr-1070 accompanied the Tyr-1472 phosphorylation and Fyn associated with GluN2B in synaptic plasticity induced by both chemical and contextual fear learning. PMID: 26229100
- Results suggest that the pre-synaptic facilitator NR2B subunit may contribute to epileptogenesis by triggering hyper-excitability and, in general, NMDARs containing NR2B may modulate an ERK 1/2-mediated NR2A over-expression PMID: 22824136
- Lovastatin downregulates excessive NR2B expression accompanied by increased expression of ERK signaling cascade. The effect of NR2B in upregulating pERK1/2 maybe due, at least in part, to inactivation of CaMKII/SAP102/SynGAP signaling cascade. PMID: 24718106
- increased after stress, and decreased in the CLF. NMDAR2B were increased in the hippocampus of CLF and CHF. In the amygdala, there was a decrease in the NMDAR2B for stress in the CLF and CHF. PMID: 25772108
- Here we have used single molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer (smFRET) to investigate the cleft closure conformational states that the glycine-binding domain of the NMDA receptors PMID: 25404733
- Study demonstrates that hippocampal NR2B receptors play an important role in the enhanced LTP and visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome-like rats and that activities of NR2B-NMDARs are mainly regulated by tyrosine kinase PMID: 24824341
- the late adolescent acquisition of GluN2B function provides a mechanism for dopamine D1-mediated regulation of PFC responses in an input-specific manner. PMID: 24041503
- GluN2B subunits are moderately expressed at primary afferent synapses on lamina I NK1R+ neurons, but play more important roles for polysynaptic NMDA EPSCs driven by primary afferents following disinhibition PMID: 25122884
- In addition, PNS significantly increased the levels of GSK-3alpha, beta and NR2B, but reduced hippocampal cell proliferation during fear extinction. PMID: 24631206
- The specific temporospatial distribution pattern of CaMKII with NR2B might be related to the different physiological functions during postnatal development PMID: 22906554
- the developmental increase in synaptic expression of PSD95 obstructs the synaptic clustering of NR2B-NMDARs, and thereby restricts reactivation of dendritic branching. PMID: 24705401
- GluN2B receptor subtype decreases in the perirhinal cortex of methamphetamine induced-memory deficit animals. PMID: 24120858
- gp120 injures neurons via an increase of NR2B and a decrease of PSD-95 expressions PMID: 24491052
- s uncover a non-canonical mechanism by which GluN2B-NMDAR surface dynamics plays a critical role in the plasticity of maturing synapses through a direct interplay with CaMKII. PMID: 24591565
- Released Ca(2+) dissociates preformed CaMKIIalpha from mGluR5 and meanwhile promotes active CaMKIIalpha to bind to the adjacent NMDAR GluN2B subunit, which enables CaMKIIalpha to phosphorylate GluN2B at a CaMKIIalpha-sensitive site. PMID: 24032403
- Disrupting NR2B-Cdk5 interaction via a small interfering peptide (siP) increases NR2B surface levels, facilitates synaptic transmission, and improves memory formation in vivo. PMID: 24607229
- Data indicate that Wnt-5a signaling is related to nitric oxide (NO) production, which in turn increases the the GluN2B subunit of the NMDA receptor (NMDAR) trafficking to the cell surface. PMID: 24440698
- we used immunoblotting to investigate the role of an NMDAR subpopulation on the phosphorylation level of the GluN2B subunit at the Y1336 and Y1472 sites in rat brain slices after NMDA treatment. PMID: 23585298
- Prenatal activation of maternal TLR3 receptors by viral-mimetic poly(I:C) modifies GluN2B expression in embryos and sonic hedgehog in offspring in the absence of kynurenine pathway activation. PMID: 23981041
- Activation of NR2B receptors increases excitatory postsynaptic potentials in glycoprotein (gp)120-treated macrophages. PMID: 23660833
- increased expression as a key mechanisms for long-term synaptic plasticity in visceral pain hypersensitivity rats PMID: 24487031
- Increased expression of NR2B in the hippocampus is associated with amelioration of impaired fear extinction in stressed rats. PMID: 23584669
- Serine residue (Ser1166) in the carboxy-terminal tail Of GluN2B is a functional target of protein kinase A phosphorylation. PMID: 24431445
- Artificial food colors and additives led to an increase in NR2B and nAChR beta2 receptor subunits in male rats and led to decrease in NR2B subunits in female rats. PMID: 23429044
- NR2B-specific small interfering (si)RNA was neuroprotective against an animal model of Parkinson's disease. PMID: 22377595
- We find that synaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor stimulation in neurons leads to activation of PP1 through a mechanism involving inhibitory phosphorylation at Thr320 by Cdk5. PMID: 24189275
- results implied that NR2B-, not NR2A-, containing NMDARs showed pathological high expression in AD-like rat hippocampus PMID: 22359056
- In the dyskinetic striatum, striatal GluN2B subunits tonically inhibit striato-nigral projections. PMID: 23611155
- synapses in chronically epileptic tissue can undergo an long-term potentiation enhancement due to an NR2B up-regulation in CA1 pyramidal neurons PMID: 23313317
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Late endosome. Lysosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton.
-
蛋白家族:Glutamate-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.10.1) family, NR2B/GRIN2B subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed in the hippocampus including the dentate gyrus (at protein level). Detected in adult olfactory bulb, brain cortex, hippocampus, striatum, thalamus, superior colliculus, with much lower levels in inferior colliculus, midbrain and cerebellum.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: rno:24410
STRING: 10116.ENSRNOP00000011697
UniGene: Rn.9711
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-