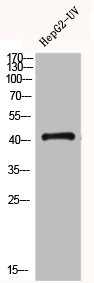
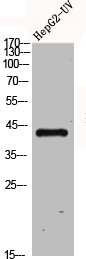
FFAR4 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA002756
-
规格:¥880
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:Q5NUL3
-
基因名:
-
别名:FFAR4; GPR120; GPR129; O3FAR1; PGR4; Free fatty acid receptor 4; G-protein coupled receptor 120; G-protein coupled receptor 129; G-protein coupled receptor GT01; G-protein coupled receptor PGR4; Omega-3 fatty acid receptor 1
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of Human GPR120.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:WB, IF, ELISA
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 IF 1:200-1:1000 ELISA 1:5000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:G-protein-coupled receptor for long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) with a major role in adipogenesis, energy metabolism and inflammation. Signals via G-protein and beta-arrestin pathways. LCFAs sensing initiates activation of phosphoinositidase C-linked G proteins GNAQ and GNA11 (G(q)/G(11)), inducing a variety of cellular responses via second messenger pathways such as intracellular calcium mobilization, modulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) production, and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). After LCFAs binding, associates with beta-arrestin ARRB2 that acts as an adapter protein coupling the receptor to specific downstream signaling pathways, as well as mediating receptor endocytosis. In response to dietary fats, plays an important role in the regulation of adipocyte proliferation and differentiation. Acts as a receptor for omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) at primary cilium of perivascular preadipocytes, initiating an adipogenic program via cAMP and CTCF-dependent chromatin remodeling that ultimately results in transcriptional activation of adipogenic genes and cell cycle entry. Induces differentiation of brown adipocytes probably via autocrine and endocrine functions of FGF21 hormone. Activates brown adipocytes by initiating intracellular calcium signaling that leads to mitochondrial depolarization and fission, and overall increased mitochondrial respiration. Consequently stimulates fatty acid uptake and oxidation in mitochondria together with UCP1-mediated thermogenic respiration, eventually reducing fat mass. Regulates bi-potential differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells toward osteoblasts or adipocytes likely by up-regulating distinct integrins. In response to dietary fats regulates hormone secretion and appetite. Stimulates GIP and GLP1 secretion from enteroendocrine cells as well as GCG secretion in pancreatic alpha cells, thereby playing a role in the regulation of blood glucose levels. Negatively regulates glucose-induced SST secretion in pancreatic delta cells. Mediates LCFAs inhibition of GHRL secretion, an appetite-controlling hormone. In taste buds, contributes to sensing of dietary fatty acids by the gustatory system. During the inflammatory response, promotes anti-inflammatory M2 macrophage differentiation in adipose tissue. Mediates the anti-inflammatory effects of omega-3 PUFAs via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. In this pathway, interacts with adapter protein ARRB2 and inhibits the priming step triggered by Toll-like receptors (TLRs) at the level of TAK1 and TAB1. Further inhibits the activation step when ARRB2 directly associates with NLRP3, leading to inhibition of proinflammatory cytokine release. Mediates LCFAs anti-apoptotic effects.; Receptor for LCFAs decoupled from G-protein signaling. May signal through beta-arrestin pathway. After LCFAs binding, associates with beta-arrestin ARRB2 that may act as an adapter protein coupling the receptor to specific downstream signaling pathways, as well as mediating receptor endocytosis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- An increased level of GPR120 in esophageal cancer tissues. PMID: 29901155
- Data suggest that cytokines TNFalpha and interleukin-1b markedly reduce GPR120/FFAR4 expression in adipocytes; in contrast, these cytokines induce expression of GPR84 and GPR41/FFAR3 in adipocytes. These studies were conducted in adipocytes cultured from subcutaneous adipose tissue. (GPR = G-protein coupled receptor; FFAR = free fatty acid receptor) PMID: 28835131
- Fatty acids are capable of directly acting on visceral adipocytes to modulate differently TNF-alpha, IL-6, IL-10 and adiponectin expression, with a different and greater effect in morbidly obese subjects. These effects are largely annulled when GPR120 expression was silenced, which suggests that they could be mediated by GPR120. PMID: 27299582
- The results of this study suggest that n-3 PUFA protect hepatic steatosis by activating FFA4 in hepatocytes, and its signaling cascade sequentially involves FFA4, Gq/11 proteins, CaMKK, AMPK, and SREBP-1c suppression. PMID: 29126901
- Studied action of linoleic acid (LA) on cell migration and neoplasm invasiveness of breast cancer cells. Findings show Akt2 activation requires EGFR and PI3K activity, whereas migration and invasion are dependent on FFAR4, EGFR and PI3K/Akt activity. PMID: 28456993
- Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents TNF-alpha-induced decrease of alpha-methylglucose uptake and AMPK phosphorylation in Caco-2 cells via GPR120 and AMPK activation. PMID: 28771713
- P.R270H of FFAR4 impairs Gq and Gi signalling of FFAR4 in vitro. PMID: 27068006
- G protein-coupled receptor 120 (GPR120) represents a promising target for the treatment of obesity-related metabolic disorders for its involvement in the regulation of adipogenesis, inflammation, glucose uptake, and insulin resistance. This review summarizes recent studies and advances regarding the systemic role of GPR120 in adipose tissue, including both white and brown adipocytes. [review] PMID: 28285320
- p.R270H variant of GPR120 modulates the risk of type 2 diabetes in interaction with dietary fat intake. PMID: 27212621
- These results indicated that GPR120 enhanced and GPR40 inhibited the cell motile activity of highly migratory osteosarcoma cells. PMID: 28159555
- LPA1 plays a critical role in EGF responses and that FFA4 agonists inhibit proliferation by suppressing positive cross-talk between LPA1 and the EGF receptor PMID: 27474750
- Ligands for FFAR4 comprise the family of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, suggesting that many of the long-known beneficial effects of these fats may be receptor mediated. (Review) PMID: 26827942
- It promotes the secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in the intestine, and also acts as a lipid sensor in adipose tissue to sense dietary fat and control energy balance.(review) PMID: 26028412
- demonstrated a GPR120-mediated novel anti-inflammatory pathway in specific intestinal epithelial cell types that could be of therapeutic relevance to intestinal inflammatory disorders PMID: 26791484
- GPR120 negatively and GPR40 positively regulate cellular functions during tumor progression in lung cancer cells. PMID: 26968637
- the low-frequency p.R270H variant which inhibits GPR120 activity might influence fasting glucose levels in a normal physiological range. PMID: 26025001
- GPR120 functions as a receptor for omega-3 fatty acid, involving in regulating the secretion of gastrointestinal peptide hormone, adipogenesis, adipogenic differentiation and anti-inflammatory process. [review] PMID: 26230883
- Characterizing pharmacological ligands to study the long-chain fatty acid receptors GPR40/FFA1 and GPR120/FFA4 PMID: 25131623
- Findings demonstrate the novel functional properties of GPR120 on human eosinophils and indicate the previously unrecognized link between nutrient metabolism and the immune system. PMID: 25790291
- These results suggest that distinct effects of GPR120 and GPR40 are involved in the acquisition of malignant property in pancreatic cancer cells. PMID: 26282200
- TNFa decreases GLP-2 expression by up-regulating GPR120 in Crohn disease PMID: 25447053
- Morbidly obese subjects had lower GPR120 mRNA and protein levels in visceral adipose tissue and a lower mRNA expression after a high-fat meal in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PMID: 24913719
- a significant interaction effect on alanine transaminase levels suggesting a driving effect of the PNPLA3 148M allele on liver injury in children with obesity carrying this variant. PMID: 25250621
- GPR120 is predominantly expressed in the microvillous membrane (MVM) of placenta and the expression level of this receptor in MVM is not altered by maternal body mass index PMID: 24844436
- GPR120 may have a positive role in the management of diabetes;GPR120 activation supports metabolic homeostasis by inhibiting inflammation in macrophages and regulating glucose and/or lipid metabolism in adipose, liver, and muscle tissues PMID: 25114508
- s show that oleic acid stimulates lipid droplet formation by activating the long-chain fatty acid receptor FFAR4, which signals through a pertussis-toxin-sensitive G-protein signalling pathway involving PI3-kinase, AKT and (PLD) activities. PMID: 24876224
- G protein-coupled receptor 120 (GPR 120) levels are reduced in pediatric obstructive sleep apnea and obesity (particularly when both are present) and may play a role in modulating the degree of insulin resistance PMID: 24790272
- Phosphorylation and structural elements within the C-terminal tail of FFA4 allow for the recruitment of arrestin-3. PMID: 24817122
- detailed mode of binding of both long-chain fatty acid and synthetic agonist ligands at FFA4 by integrating molecular modeling, receptor mutagenesis, and ligand structure-activity relationship approaches in an iterative format PMID: 24860101
- Free fatty acids and protein kinase C activation induce GPR120 phosphorylation. PMID: 24239485
- GPR120 is a nutrient sensor that is activated endogenously by both saturated and unsaturated long chain fatty acids. PMID: 24742677
- this study demonstrates the expression of GPR120 in pancreas and shows the distribution of GPR120 in human and rat pancreas. PMID: 23993698
- CD36 and GPR120 have nonoverlapping roles in taste bud cell signaling during orogustatory perception of dietary lipids; these are differentially regulated by obesity. PMID: 24412488
- Basal and heterologous phosphorylation of FFA4 is mediated by protein kinase C. PMID: 24412271
- these results demonstrate that GPR120 functions as a tumor-promoting receptor in colorectal carcinoma and, therefore, shows promise as a new potential target for cancer therapeutics. PMID: 23851494
- Our results show that EPA, DHA and AA elicit the same signalling events, but with different kinetics and efficiency through GPR120 in Caco-2 cells. PMID: 23849180
- Our data suggest that the combination of common genetic variations in the GPR120 gene and dietary fat intake is a possible determinant of body mass index. PMID: 23594480
- GPR120 may participate in human gustatory fatty acid perception. PMID: 21868624
- agonist-stimulated GPR120S and GPR120L receptors both recruited beta-arrestin2 and underwent robust internalization. PMID: 22282525
- GPR120 expression in adipose tissue is significantly higher in obese individuals than in lean controls; GPR120 exon sequencing in obese subjects reveals a deleterious non-synonymous mutation (p.R270H) that inhibits GPR120 signalling activity PMID: 22343897
- Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) PMID: 20677014
- These are the first results which demonstrate specific phosphorylation of GPR120 isoforms upon agonism by free fatty acids and the first which distinguish the phosphorylation profiles of the two GPR120 isoforms. PMID: 20471368
- possible significance of the alternate splice variant of GPR120 in human is discussed PMID: 19723586
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Lysosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.; [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Lysosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection, cilium membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
-
组织特异性:[Isoform 2]: The predominant isoform in human tissues. Expressed in adipose tissue, pancreatic islets, lung and brain. Expressed in alpha cells of pancreatic islets. Expressed in primary cilia of perivascular preadipocytes of white adipose tissue (at prot
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 19061
OMIM: 607514
KEGG: hsa:338557
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000360538
UniGene: Hs.661022
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-