EPHB4 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA277115
-
规格:¥2024
-
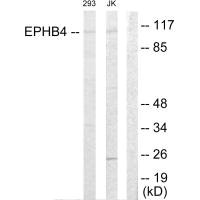
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) EPHB4 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:P54760
-
基因名:EPHB4
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from internal of Human EPHB4.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:3000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Receptor tyrosine kinase which binds promiscuously transmembrane ephrin-B family ligands residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Together with its cognate ligand/functional ligand EFNB2 it is involved in the regulation of cell adhesion and migration, and plays a central role in heart morphogenesis, angiogenesis and blood vessel remodeling and permeability. EPHB4-mediated forward signaling controls cellular repulsion and segregation from EFNB2-expressing cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- miR-454 promotes the proliferation and invasion of trophoblast cells by inhibiting EPHB4 expression. PMID: 30138897
- EphB4 expression is associated with colorectal cancer cell proliferation and vascularization. PMID: 29368976
- functional expression of EphB4 is considered a promising differentiating characteristic, preferentially determined by non-invasive in vivo imaging, which may improve personalized theranostics of malignant melanoma. PMID: 29462967
- The identified endothelial signalling pathway of CCM3-DLL4/Notch-EphB4-Erk1/2 may provide an insight into mechanism of CCM3-ablation-mediated angiogenesis. PMID: 28371279
- EphB4 overexpression is associated with resistance to dasatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. PMID: 29096333
- this study uncovered the character of EPHB4-regulating endothelial activation in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia PMID: 27553867
- HOXA9 transcriptionally regulated EPHB4 expression to modulate trophoblasts migration and invasion, which may suggest a contribution of HOXA9-EPHB4 in the poor placentation in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. PMID: 28292467
- EPHB4 mutations were identified in patients with multifocal capillary malformation with arteriovenous malformations. PMID: 28687708
- EPHB4 is a critical regulator of early lymphatic vascular development; mutations in the gene can cause an autosomal dominant form of lymphatic-related hydrops fetalis that is associated with a high mortality rate PMID: 27400125
- The expression of EPHB4 was increased in gastric cancer and increased EPHB4 expression was correlated with poor survival. Knockdown of EPHB4 promoted adhesion and exerted diverse effects on migration of gastric cancer cells. PMID: 28739744
- EphB4 protein acts as a tumour promoter associated with proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis, and may be used as a potential colorectal cancer (CRC) therapeutic target. PMID: 27072105
- Study illustrates that aberrant activation of EphB4/ephrinB2 may mediate chronic myeloid leukemia resistance involved in cytoskeletal proteins. PMID: 27226777
- both EphA2 and EphB4 show potential as target for image-guided colorectal cancer surgery, but EphB4 seems to have the best characteristics with respect to tumor/normal mucosa distribution. PMID: 28165374
- Enhanced EphB4 expression was significantly associated with Thyroid Lesions. PMID: 26220827
- LISA method may be considered rapid and sensitive enough to detect even low levels of total and phosphorylated EphB4 Cost-effectiveness of this method for the detection of differential expression of EphB4 proteins in clinics is also noticeable. PMID: 27072235
- EphB4 facilitates stromal-mediated support of hematopoiesis in hematopoietic stem cells. PMID: 26033476
- N-(2,4)-dinitrophenyl-L-arginine Interacts with EphB4 and Functions as an EphB4 Kinase Modulator. PMID: 25581780
- Stimulation of Eph-B4 function may be a candidate strategy for translation to human clinical trials designed to inhibit venous neointimal hyperplasia. PMID: 25446283
- EPHB4 oncogenomic network provides a molecular basis for its role in tumor progression and points to EPHB4 as a potential tumor aggressiveness biomarker and drug target in gastroesophageal cancers PMID: 26414866
- Novel EPHB4 receptor tyrosine kinase mutations have been found in lung cancer patients. PMID: 26073592
- Suggest role for EphB4/IGF1R signaling in regulation proliferation/migration of breast cancer cells. PMID: 26191333
- Results indicate EphB4 receptor as a critical mediator of erythropoietin-induced tumor progression. PMID: 26481148
- EphB4 regulates integrin Beta8 expression and integrin Beta8 plays a role in prostate cancer cells. PMID: 25886373
- EPHB4 expression is associate with progression of HNSCC from normal tissue to dysplasia and to cancer. PMID: 25391996
- Decreased EphB4 expression is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. PMID: 24764074
- EphB4 contains two nuclear localization signal sequences and localises to the nucleus. PMID: 25724901
- Venous Eph-B4 expression diminished (p = .002), Ephrin-B2 expression was not induced (p = .268), and expression of osteopontin (p = .002) was increased with exposure to arterial magnitudes of shear stress. PMID: 25191151
- Silencing of EPHB4 significantly reduced the transmigration of synovial sarcoma cells. PMID: 25274141
- our study revealed the important function and regulation of EphB4 in the progression of ESCC and suggested EphB4 as a novel target for the treatment of ESCC. PMID: 24771266
- The recombinant plasmid can inhibit the expression of EphB4 mRNA and protein in PANC-1 cells, as well as cell growth and migration. PMID: 25051915
- levels of EphB4, mTOR and Akt were distinctly lower than those in other groups. It was concluded that suppression of EphB4 may inhibit the growth of ovarian cancer cells by downregulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. PMID: 22684558
- EphB4 activation can differentially inhibit breast cancer cells at post confluent state. PMID: 24427781
- High EphB4 expression is associated with glioma. PMID: 24121831
- These results are the first to identify EphB4 and its cross-talk with PDGFRbeta as unexpected vital determinants of tumor cell survival in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. PMID: 24733895
- Our data suggests EphB4 as an upstream regulator of ER-alpha in human breast cancer cells by modulating ER-alpha transcription. The results also suggest Akt as a relevant downstream signaling molecule in this novel EphB4-ER-alpha pathway. PMID: 23725356
- The EphB4 receptor tyrosine kinase promotes lung cancer growth. PMID: 23844053
- EphB4 was overexpressed in 72% of mesothelioma tissues PMID: 23721559
- Compared gene expression profiles in CRC patients treated with bevacizumab who responded to the treatment with those that did not respond. Found EPHB4 expression significantly increased in nonresponders and high levels associated with decreased survival. PMID: 23579861
- HAb47-Cy5.5 successfully imaged the decreased EphB4 expression. PMID: 23211050
- Data indicate that the reduced vimentin expression in response to EPHB4, WIPF2 and MTHFD2 silencing was observed at mRNA and protein levels. PMID: 23295955
- molecular classification of breast cancer is based upon the expression of ESR, PGR and HER2; the expression of EPOR, membrane receptor GPER and EPHB4 may be considered as an additional classification factor in breast cancer PMID: 23314808
- EphB4 receptor expresion is correlated to the initiation, progression and tumor angiogenesis. PMID: 23079712
- verify amplification and/or deletion in the ACHE, BCHE, EPHB4 and MME genes in 32 samples of sporadic breast cancer PMID: 23063927
- expression of EphB4 was significantly upregulated in clinical glioma samples; overexpression of EphB4 in glioma cell lines accelerated cell growth and tumorigenesis; downregulation of EphB4 inhibited cell growth PMID: 23138393
- EphB4 is robustly expressed and potentially serves as a novel biomarker for targeted therapy in esophageal cancers PMID: 23100466
- EphB4 plays an important role in the progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma by stimulating cell migration and EphB4 might be a potential therapeutic target in papillary thyroid carcinoma. PMID: 22528941
- EphB4 protein expression is significantly increased in non-small- cell lung cancer and corresponds to progression and severity of the disease. PMID: 22684742
- EphB4/EphrinB2 expression has closed related to gennesis and progression of hepatoblastoma. PMID: 22024229
- High EphB4 is associated with malignant urogenital tissue. PMID: 19272799
- Ephb4 was over-expressed and localized to the cytoplasm of gastric cancer cells. Moreover, Ephb4 protein was observed as being significantly related to tumor size and regional lymph nodes category. PMID: 20686847
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Hydrops fetalis, non-immune, and/or atrial septal defect (HFASD)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, Ephrin receptor subfamily
-
组织特异性:Abundantly expressed in placenta but also detected in kidney, liver, lung, pancreas, skeletal muscle and heart. Expressed in primitive and myeloid, but not lymphoid, hematopoietic cells. Also observed in cell lines derived from liver, breast, colon, lung,
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 3395
OMIM: 600011
KEGG: hsa:2050
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000350896
UniGene: Hs.437008
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-