E2F4 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA290646
-
规格:¥2024
-
图片:
-
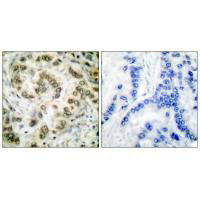
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung carcinoma tissue using E2F4 antibody.
-
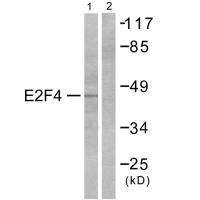
Western blot analysis of extracts from COS7 cells, using E2F4 antibody.
-
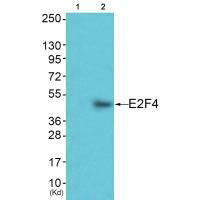
Western blot analysis of extracts from JK cells (Lane 2), using E2F4 antiobdy. The lane on the left is treated with synthesized peptide.
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) E2F4 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q16254
-
基因名:
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from Human E2F4.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB,IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:3000 IHC 1:50-1:100 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription activator that binds DNA cooperatively with DP proteins through the E2 recognition site, 5'-TTTC[CG]CGC-3' found in the promoter region of a number of genes whose products are involved in cell cycle regulation or in DNA replication. The DRTF1/E2F complex functions in the control of cell-cycle progression from G1 to S phase. E2F4 binds with high affinity to RBL1 and RBL2. In some instances can also bind RB1. Specifically required for multiciliate cell differentiation: together with MCIDAS and E2F5, binds and activate genes required for centriole biogenesis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- E2f4 forms apical cytoplasmic organizing centres for assembly and nucleation of deuterosomes. Using genetically altered mice and E2F4 mutant proteins we demonstrate that centriole amplification is crucially dependent on these organizing centres and that, without cytoplasmic E2f4, deuterosomes are not assembled, halting multiciliogenesis PMID: 28675157
- Studied expression of E2F4 in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy; found target gene-based signature of E2F4 can be used to predict neoadjuvant response. PMID: 28464832
- The s found that phosphorylation of residues S650 and S975 in p107 weakens the E2F4 transactivation domain binding. PMID: 27567532
- E2F4 gene expression in glioblastoma. PMID: 27983535
- This study found evidence that the number of triplet AGC repeats in the E2F4 gene may play a role in the susceptibility to early-onset colorectal cancer. PMID: 26343152
- PHF8 reduces the H3K9me2 level at the E2F4 transcriptional start site, demonstrating a direct function of PHF8 in endothelial E2F4 gene regulation PMID: 26751588
- s show that BRCA1 and RAD17 genes, whose derived proteins play a pivotal role in DNA damage repair, are transcriptional targets of gain-of-function mutant p53 proteins. PMID: 25650659
- E2F4 promoter occupancy is globally associated with p53-repression targets, but not with p53 activation targets. PMID: 24096481
- cancer-associated E2F4 mutations enhance the capacity of colorectal cancer cells to grow without anchorage, thereby contributing to tumor progression. PMID: 24100580
- Short alleles (<13 repeats) of (AGC)n in E2F4 were less frequent in women with breast cancer than in the control sample. PMID: 23015403
- the loss of CDH1/E2F4 may be associated with worse clinical and pathological findings in mammary ductal carcinoma. PMID: 23007606
- In terminally differentiated cells, common KDM5A and E2F4 gene targets were bound by the pRB-related protein p130, a DREAM complex component. PMID: 23093672
- Silica could induce the high expression of cyclin D1 and CDK4 and the low expression of E2F-4, resulting in the cell cycle changes by AP-1/cyclin D1 pathway in human embryonic lung fibroblasts. PMID: 22357515
- data demonstrate that enforced E2F4 expression in Burkitt lymphoma (BL) cells not only diminishes E2F1 levels, but also reduces selectively the tumorigenic properties and proliferation of BL cells PMID: 22475873
- Our data indicate that E2F4 is required for cardiomyocyte proliferation and suggest a function for E2F4 in mitosis PMID: 19955219
- E2F4, PHACTR3, PRAME family member and CDH12 most probably play important role in non-small-cell lung cancer geneses PMID: 19473719
- regulation of expression of p130, p107 and E2F-4 in human cells PMID: 12006580
- data point to Tat as an adaptor protein that recruits cellular factors such as E2F-4 to exert its multiple biological activities PMID: 12055184
- Mutations in E2F-4 gene is associated with hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer PMID: 12148576
- EBV LMP1 blocks p16INK4 pathway by promoting nuclear export of E2F-4. PMID: 12860972
- E2F-a and E2F-c binding sites are involved in the TCR-induced down-regulation of ICBP90 gene transcription PMID: 15964557
- E2F4 is a transcriptional regulator of the cell cycle genes. PMID: 16135806
- Hypoxia induces substantial p130 dephosphorylation and nuclear accumulation, leading to the formation of E2F4/p130 complexes and increased occupancy of E2F4 and p130 at the RAD51 and BRCA1 promoters. PMID: 17001309
- in response to radiation, E2F4 becomes active in the nucleus, enforces a stable G(2) arrest by target gene repression, and thus provides increased cell survival ability by minimizing propagation of cells that have irreparable DNA damage PMID: 17043659
- Evolutionarily conserved multisubunit protein complex that contains p130 and E2F4 mediates the repression of cell cycle-dependent genes in quiescence. PMID: 17531812
- deregulated nuclear E2F4 expression induces apoptosis via multiple pathways in normal intestinal epithelial cells but not in colon cancer cells. PMID: 17656449
- E2F4, binding sites are located within 2 kb of a transcription start site, in both normal and tumor cells PMID: 17908821
- Cell cycle genes are the evolutionarily conserved targets of the E2F4 transcription factor PMID: 17957245
- FBI-1 is the first transcriptional repressor shown to act as a dual regulator in adipogenesis exerting repressor activities on target genes by both, direct and indirect mechanisms. PMID: 18368381
- E2F4 may be determinant in the promotion of proliferation of human intestinal epithelial crypt cells and colorectal cancer cells. PMID: 19562678
- By interacting with p130, E2F4 plays a key role in the maintenance of a stable G2 arrest. Increased E2F4 levels and its translocation to the nucleus following genotoxic stress result in downregulation of mitotic genes. PMID: 17507799
- Increased E2F4/p130 complex formation seen after irradiation depended on increased nuclear E2F4, dissociation of p130 from Cdk2, and p130 dephosphorylation. E2F4 siRNA prevented p130/E2F4 formation and sensitized cells to radiation-induced apoptosis. PMID: 15231644
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:E2F/DP family
-
组织特异性:Found in all tissue examined including heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and pancreas.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 3118
OMIM: 600659
KEGG: hsa:1874
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000368686
UniGene: Hs.108371
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-