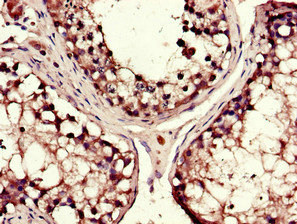
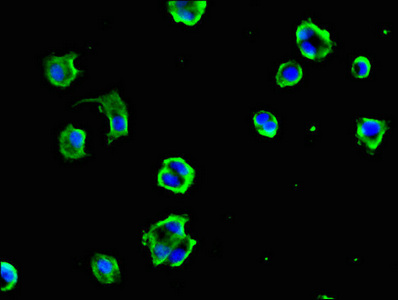
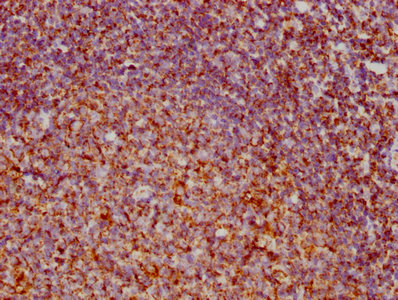
DYNC1H1 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA613491LA01HU
-
规格:¥440
-
促销:
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) DYNC1H1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q14204
-
基因名:DYNC1H1
-
别名:DYNC1H1 antibody; DHC1 antibody; DNCH1 antibody; DNCL antibody; DNECL antibody; DYHC antibody; KIAA0325Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 antibody; Cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain 1 antibody; Dynein heavy chain antibody; cytosolic antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 protein (12-66AA)
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
本页面中的产品,DYNC1H1 Antibody (CSB-PA613491LA01HU),的标记方式是Non-conjugated。对于DYNC1H1 Antibody,我们还提供其他标记。见下表:
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, IHC, IF
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC 1:20-1:200 IF 1:50-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Cytoplasmic dynein 1 acts as a motor for the intracellular retrograde motility of vesicles and organelles along microtubules. Dynein has ATPase activity; the force-producing power stroke is thought to occur on release of ADP. Plays a role in mitotic spindle assembly and metaphase plate congression.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Taken together, these results demonstrate DYNC1H1 as a strong candidate and RTP1 as a potential candidate on the onset of epileptic encephalopathies. PMID: 28325891
- Here, the s use quantitative imaging and laser ablation to show that NuMA targets dynactin to spindle microtubule minus-ends, localizing dynein activity there. PMID: 29185983
- Structural and functional mutations and hotspots for DYNC1H1. PMID: 28455235
- This observation offers an explanation for the dominant effects of DYNC1H1 mutations in vivo. PMID: 28196890
- This cohort demonstrates that mutations in DYNC1H1 can mimic a congenital myopathy. PMID: 28554554
- These results suggest that cytoplasmic dynein 1 binds to BRCA2 through the latter's centrosomal localization signal and BRCA2 mediates the cohesion between centrosomes during the S phase, potentially serving as a cell-cycle checkpoint. PMID: 27433848
- A novel de novo mutation (c.2327C > T, p.P776L) in the DYNC1H1 gene identified and confirmed it as the causal variant of Spinal muscular atrophy with lower extremity predominance. PMID: 26846447
- Our findings suggest that DYNC1H1 variants can cause not only lower, but also upper motor neuron disease. PMID: 26100331
- The mutations in DYNC1H1 increase the interaction with its adaptor BICD2. PMID: 25512093
- These findings also reveal a possible new target for Amblyomin-X, i.e., dynein, and may serve as a tool for investigating tumor cell death associated with proteasome inhibition. PMID: 25479096
- These results reveal that conformational changes involving hexon hypervariable region 1 are the basis for a novel viral mechanism controlling capsid transport to the nucleus by dynein. PMID: 25355895
- Report expands the clinical spectrum of DYNC1H1-related spinal muscular atrophy to include generalized arthrogryposis PMID: 25609763
- s propose that Snapin connects chlamydial inclusions with the microtubule network by interacting with both Chlamydia psittaci IncB and dynein. PMID: 24751478
- s find that pharmacological or small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated inhibition of cytoplasmic dynein or the kinesin 1 heavy chain KIF5B delays HIV-1 uncoating. PMID: 25231297
- single dynein molecules in the cell are autoinhibited through intramolecular head-head stacking PMID: 25266423
- Our results expand the set of pathological mutations in DYNC1H1, reinforce the role of cytoplasmic dynein in disorders of neuronal migration, and provide evidence for a syndrome including spinal nerve degeneration and brain developmental problems. PMID: 24307404
- This study demonistrated that DYNC1H1 mutation alters transport kinetics and ERK1/2-cFos signalling in a mouse model of distal spinal muscular atrophy. PMID: 24755273
- It focus on cytoplasmic dynein, which is required for a myriad of cellular functions in interphase, mitosis and meiosis, ranging from transport of organelles and functioning of the mitotic spindle to chromosome movements in meiotic prophase. PMID: 24256283
- In conclusion, association with microtubules and the translocation activity of dynein motor complexes are required to achieve efficient retrovirus restriction by TRIM5alpha. PMID: 24600008
- This study demonistrated that Dynein mutations associated with hereditary motor neuropathies impair mitochondrial morphology and function with age. PMID: 23742762
- Data indicate that dynein- and astral microtubule-mediated transport of Galphai/LGN/nuclear mitotic apparatus (NuMA) complex from cell cortex to spindle poles. PMID: 23389635
- The cytoplasmic Dynein Heavy Chain 1 (DHC) was found to interact with NF1 along microtubules in vesicular structures identified to be melanosomes. PMID: 23583712
- Dynein forms distinct complexes requiring specific recruiters and activators to promote orderly progression through mitosis. PMID: 23589491
- this study has demonstrated that the same DYNC1H1 mutation could cause spinal muscular atrophy as well as distal neuropathy, indicating pleotropic effects of the mutation. PMID: 22847149
- analysis of reconstitution of the human cytoplasmic dynein complex PMID: 23213255
- study demonstrates that mutations in the tail domain of the heavy chain of cytoplasmic dynein (DYNC1H1) cause spinal muscular atrophy and provide experimental evidence that a DYNC1H1 mutation disrupts dynein complex assembly and function PMID: 22459677
- Mutations in DYNC1H1 can lead to a broad phenotypic spectrum, confirming the importance of DYNC1H1 in both central and peripheral neuronal functions. PMID: 22368300
- Exome sequencing of three affected individuals separated by eight meioses identified a single shared novel heterozygous variant, c.917A>G, in DYNC1H1, which encodes the cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain 1. PMID: 21820100
- In an in vitro MT gliding assay, both dynein-1 and dynein-2 showed minus-end-directed motor activities. PMID: 21723285
- mediates the perinuclear aggregation of phagocytosed melanosomes, participates in the formation of the supranuclear melanin cap or "microparasol" and serves as a mechanism to help protect the nucleus from ultraviolet-induced DNA damage. PMID: 14632200
- these results suggest that complexes of dynein, Lis1 and CLIP-170 crosslink and slide microtubules within the spindle, thereby producing an inward force that pulls centrosomes together. PMID: 19020519
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 2O (CMT2O); Mental retardation, autosomal dominant 13 (MRD13); Spinal muscular atrophy, lower extremity-predominant 1, autosomal dominant (SMALED1)
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton.
-
蛋白家族:Dynein heavy chain family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 2961
OMIM: 158600
KEGG: hsa:1778
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000348965
UniGene: Hs.614080
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
-
-
-
-
-
VDAC1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat