DRD4 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA695604
-
规格:¥1100
-
图片:
-
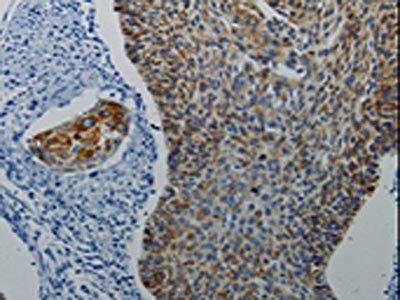
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human cervical cancer tissue using CSB-PA695604(DRD4 Antibody) at dilution 1/5, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
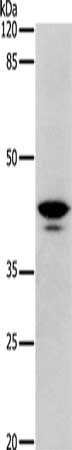
Gel: 10%SDS-PAGE, Lysate: 30 μg, Lane: Mouse skeletal muscle tissue, Primary antibody: CSB-PA695604(DRD4 Antibody) at dilution 1/350, Secondary antibody: Goat anti rabbit IgG at 1/8000 dilution, Exposure time: 1 minute
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P21917
-
基因名:
-
别名:DRD4; D(4 dopamine receptor; D(2C dopamine receptor; Dopamine D4 receptor
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse
-
免疫原:Synthetic peptide of Human DRD4
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen affinity purification
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:-20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB,IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution ELISA 1:500-1:5000 WB 1:500-1:1000 IHC 1:5-1:20 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Dopamine receptor responsible for neuronal signaling in the mesolimbic system of the brain, an area of the brain that regulates emotion and complex behavior. Activated by dopamine, but also by epinephrine and norepinephrine, and by numerous synthetic agonists and drugs. Agonist binding triggers signaling via G proteins that inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Modulates the circadian rhythm of contrast sensitivity by regulating the rhythmic expression of NPAS2 in the retinal ganglion cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Mothers who carry the long allele of DRD4 and experienced more adverse life events are less sensitive in interactions with their children. PMID: 30035571
- The presence of the DRD4 7-repeat allele was associated with less disorganized attachment and the effect of the DRD4 genotype may be moderated by infant birth weight and by maternal depression. PMID: 29149620
- genetic association studies in population of young adults in Columbia: Data suggest that genetic polymorphisms in DRD4 and SLC6A3 are associated with overweight/obesity in the population studied; DRD4 4/4 genotype is associated with lower BMI and SLC6A3 10/10 genotype is associated with higher BMI. (DRD4 = dopamine receptor D4; SLC6A3 = solute carrier family 6 member 3) PMID: 29145734
- data imply that enhanced D4 receptor-mediated dopaminergic control of corticostriatal transmission constitutes a vulnerability factor of ADHD and other neuropsychiatric disorders. PMID: 28097219
- These data suggest that the DRD4 polymorphisms are associated with localized brain activity and specific functional connections, including abnormality in the frontal-striatal-cerebellar loop. PMID: 29564731
- These results showed that C-allele carriers were associated with a higher erousal from sleep, decreased gray matter volume and functional connectivity density in the pregenual anterior cingulate cortex; children with primary nocturnal enuresis carrying the C allele exhibit decreased gray matter volume and functional connectivity density in the thalamus. PMID: 28450726
- Results suggest that alterations in the glutamate and dopamine system (GRIN2B and DRD4) in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder may contribute to abnormalities in local functional connectivity and its dynamic repertoire in the superior parietal area, and these abnormalities would be related to dysfunction in sustained and divided attention. PMID: 28258362
- There is significant interaction effects of the GIT1 and DRD4 gene variants on impulsivity in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. PMID: 28948080
- The DRD4 and 5HTR2A genes are co-expressed in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells during antipsychotic administration. Despite a correlation between the studied biogenic amine indicators and the psychopathological status of patients, reliable biomarkers of treatment response could not be determined. PMID: 29221470
- heterozygotes at the DRD4 locus are more risk averse than either homozygotes PMID: 27905471
- We report an interaction between birth weight status and DRD4 gene in predicting respiratory sinus arrhythmia, such that DRD4 long carriers had the highest and lowest resting respiratory sinus arrhythmia depending on whether they were born normal or extremely low birth weight, respectively. PMID: 28727140
- DRD4 haplotypes may play a role in general psychopathology in patients with eating disorders PMID: 29455021
- Results indicated that DRD4 L carriers with a sexual trauma history reported significantly more severe suicidal ideation than DRD4S homozygotes. PMID: 27267123
- DRD4 x Positive peer affiliation interaction on the right fusiform gyrus (rFG) activation during successful inhibition. PMID: 27170266
- over-suppression of NMDAR function may underlie the role of hD4.7 in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder PMID: 27475724
- nine ADHD candidate single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in seven genes were tested for association with PD in 5333 cases and 12,019 healthy controls. No significant association was observed. PMID: 28176268
- Study analyzed the effects of DRD4 and DAT1, prenatal exposure to alcohol and smoking and their interactions on attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder severity, response inhibition and brain activity; found no significant gene x environment interaction effects. PMID: 28234207
- this study determined crystal structures of the D4 dopamine receptor in its inactive state bound to the antipsychotic drug nemonapride, with resolutions up to 1.95 angstroms. PMID: 29051383
- Egyptian attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) children had a significant presence of DRD4 2-repeat allele with an absence of 7-repeat allele. Genotype-phenotype correlation indicated that DRD4 2-repeat and 4-repeat alleles were associated with significant inattention and hyperactivity whereas 3-repeat allele was associated with mild ADHD symptoms. PMID: 27821512
- We investigated genetic associations with reflexive attention measures in infancy and childhood in the same group of children. Performance on the infant task was associated with SLC6A3. In addition, several genetic associations with an analogous child task occurred with markers on CHRNA4, COMT, and DRD4. PMID: 26613685
- The results demonstrate Interaction between DBH gene variants and low enzymatic activity in male ADDH probands. The data obtained may partly answer the male biasness of ADDH Significant male preferential transmission of Dopamine receptor D4 was also observed. PMID: 23881560
- Children who carried DRD4 GA/AA genotypes (rs752306) were less likely than those who carried the DRD4 GG genotype to have attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. PMID: 29054088
- Many children who carry the 7R allele of DRD4 appear to be more in fl uenced by maternal sensitivity asit relates to overweight/obesity risk. PMID: 27726127
- Parenting and DRD4 variants GxE interaction in ADHD. PMID: 28138806
- Higher levels of antenatal maternal anxiety symptoms are associated with more frequent fetal movements among fetuses carrying a 7R allele, but not among fetuses carrying shorter DRD4 alleles. PMID: 27195896
- youth without the DRD4-7R allele were particularly affected by the school environment. PMID: 27786532
- C allele of SNP rs1800955 associated with cigarette smoking PMID: 28103253
- Infants carrying the DRD4 7R allele showed greater effects of maternal insensitivity than non-carriers for behavioral problems at 18-months. PMID: 27494520
- DRD4 exon 3 VNTR polymorphism is related to attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder in Chinese children. PMID: 28282463
- Adolescent rule-breaking is stronger for DRD4 non-long carriers. PMID: 27268567
- these findings suggest that in part genetically determined peer selection (carriers of the DRD4 seven-repeat allele tend to associate with peers who have more favorable attitudes toward drinking and greater alcohol use) and peer socialization (carriers' subsequent drinking behaviors are more strongly associated with their peer drinking norms) may differ across adolescent developmental stages. PMID: 26902782
- Results found that frequency of those carrying the DRD4 7 repeat allele continuously increased with age in a Caucasian population of Hungarians until age 75, and this was found preferentially for females. For the older groups, a decrease in 7 repeat carriers was noted which might be a result of a gene environment interaction. PMID: 27992450
- Mothers with long alleles for AVPR1a and DRD4 engaged in more mother-oriented social cognition, which in turn predicted less sensitive maternal behavior. There were no significant direct effects of AVPR1a or DRD4 on maternal sensitivity (beta = 0.02, P = .73 and beta = -0.10, P = .57, respectively). PMID: 27581946
- Parent and child dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) genotypes jointly moderate the transactional relations between parenting practices and child self-regulation. PMID: 27548745
- dopamine D4 receptor carboxyl-terminal palmitoylation is required for surface expression, endocytosis, and signaling PMID: 27659709
- GxE interaction between DRD4 7R and family SES/neighborhood poverty, and the frequency of voluntary and involuntary job changes through educational achievement. PMID: 27077527
- the results of the present study demonstrated that elevated DRD4 promoter methylation was associated with AD risk in males. PMID: 27485706
- The results indicate that epigenetic regulation of the DRD4 gene in the form of increased methylation is associated with the cognitive/attentional deficits in ADHD. PMID: 26897359
- DRD4 antagonist has an antimelanogenic effect that is related to downregulation of MITF transcription through the activation of the ERK PMID: 26782007
- DRD4 7-repeat carriers with ADHD showed the least striatal activation during reward anticipation when exposed to high maternal warmth, but the most when exposed to low warmth. PMID: 27045841
- DRD4 gene expression reduction in breast cancer patients after spiritual intervention PMID: 26597879
- Polymorphisms of the DRD4 gene appear to be associated with SSRI treatment response in Chinese MDD patients. PMID: 25854875
- Community disadvantage interacted with parental DRD4 status to predict low levels of protective parenting. Protective parenting, in turn, interacted with youth DRD4 status to forecast increases in youth's planful future orientations, a proximal influence on changes in risk behavior. PMID: 26189764
- DRD4 and SLC6A3 gene polymorphisms may have a role in food intake and nutritional status in children in early stages of development PMID: 26350252
- There may be a specific molecular pathway by which the DRD4-521T genotype alters ACC electrophysiology and thereby predicts the level of problematic substance use in undergraduates. PMID: 26601911
- There were no significant interactions for DRD4 with parental support and psychological control with respect to development of adolescent delinquency. PMID: 26595468
- In contrast to previous results, we observed no significant interactions between DRD4 and childhood adversity in the etiology of alcohol dependence symptoms during emerging and young adulthood. PMID: 26595480
- findings thus reveal unreported structural determinants of the mutated DRD4 receptor and provide a robust framework for design of effective novel drugs. PMID: 26680992
- present findings suggest that DRD4L may be involved in the development of an intermediate phenotype specific to substance abuse. PMID: 26688118
- the putative involvement of DAT1 and DRD4 genes in the aetiology of Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder with a main role in modulation of key dimensions of the disorder PMID: 25555995
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in retina. Detected at much lower levels in brain, in amygdala, thalamus, hypothalamus, cerebellum and pituitary.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 3025
OMIM: 126452
KEGG: hsa:1815
UniGene: Hs.99922
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-