CXADR Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA830526
-
规格:¥2024
-
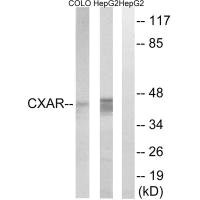
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) CXADR Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:P78310
-
基因名:CXADR
-
别名:CXADR; CAR; Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor; hCAR; CVB3-binding protein; Coxsackievirus B-adenovirus receptor; HCVADR
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from internal of Human CXADR.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:3000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Component of the epithelial apical junction complex that may function as a homophilic cell adhesion molecule and is essential for tight junction integrity. Also involved in transepithelial migration of leukocytes through adhesive interactions with JAML a transmembrane protein of the plasma membrane of leukocytes. The interaction between both receptors also mediates the activation of gamma-delta T-cells, a subpopulation of T-cells residing in epithelia and involved in tissue homeostasis and repair. Upon epithelial CXADR-binding, JAML induces downstream cell signaling events in gamma-delta T-cells through PI3-kinase and MAP kinases. It results in proliferation and production of cytokines and growth factors by T-cells that in turn stimulate epithelial tissues repair.; (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for adenovirus type C.; (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Coxsackievirus B1 to B6.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- EGF suppresses specifically CAR signaling mainly through transcriptional regulation and drives the xenobiotic response toward a pregnane X receptor (PXR)-mediated mechanism. PMID: 29269410
- The results pf this study demonstrated that CAR is expressed by mature neurons throughout the brain. In addition, we propose divergent roles for CAR in immature neurons, during neurogenesis, and at the mature synapse. PMID: 27629708
- data indicate that glycosylation of the extracellular CAR domain has only minor importance for the function of CAR as Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) receptor and that the D2 domain is not essential per se but contributes to receptor function by promoting the exposure of the D1 domain on the cell surface PMID: 27030267
- CAR expression has potential as a marker for monitoring and/or predicting the outcome of gene therapy, and increasing its expression levels may contribute to the upregulation of cellular sensitivity towards adenovirus infection. PMID: 27485384
- Membrane Dynamics and Signaling of the Coxsackievirus and Adenovirus Receptor. PMID: 26940522
- Glycan microarray, flow cytometry, surface plasmon resonance and ELISA analyses reveal that the terminal knob domain of the long fiber (52LFK) binds to CAR, and the knob domain of the short fiber (52SFK) binds to sialylated glycoproteins. PMID: 25674795
- Lovastatin enhances adenovirus-mediated TRAIL induced apoptosis by depleting cholesterol of lipid rafts and affecting CAR and death receptor expression of prostate cancer cells. PMID: 25605010
- Suggest that distinct forms of CAR play different roles in the undifferentiated state and tight junction formation of human embryos and embryonic stem cells. PMID: 25118298
- CAR might play a role in adipose tissue dysfunction, given its dual associations with adipogenic and inflammatory genes. PMID: 25459915
- Subsequent experiments also proved that both the rno-miR-466d and the human hsa-miR-466, which are orthologs of the miR-467 gene family, could effectively down-regulate the levels of rat and human CAR protein expression, respectively PMID: 25497012
- This study shows for the first time that lovastatin reduces the expression of CAR and subsequently the replication of CVB3 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. PMID: 24316867
- CAR regulates epithelial cell junction stability through control of E-cadherin trafficking. PMID: 24096322
- Kinetic analyses show that the apparent first-order rate constant for the inactivation of coxsackievirus B3 by soluble CAR (sCAR) at physiological temperatures varies nonlinearly with sCAR concentration. PMID: 24623425
- CAR substantially impacts the growth and survival of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells as a negative regulator of ROCK in vitro and in vivo. PMID: 23503462
- novel modifier of ventricular conduction and arrhythmia vulnerability in the setting of myocardial ischemia PMID: 24291282
- CAR belongs to the increasing list of cell surface molecules that undergo ectodomain shedding and that are substrates for -secretase-mediated RIP. PMID: 24015300
- The expression of CAR was detected in all normal organs, except in the brain. In malignancies, a high degree of variability was notable, ranging from significantly elevated CAR expression to decreased CAR expression. PMID: 24022195
- CAR expression in tumor tissues was significantly higher than that in normal lung tissues. CAR expression had a correlation with the histological grade of lung squamous cell carcinoma. PMID: 23307165
- CAR and ASIC3 co-immunoprecipitate only when co-expressed with PSD-95. PMID: 22809504
- Combined fiber modifications both to target alpha(v)beta(6) and detarget the coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor improve virus toxicity profiles in vivo but fail to improve antitumoral efficacy relative to adenovirus serotype 5. PMID: 22708837
- study suggests that CXADR and F2RL1 likely play important roles in BP and obesity variation, respectively; and these findings are consistent with those of other studies, so replication and functional analyses are necessary PMID: 22914544
- Sp1 is involved in regulation of CAR expression. PMID: 22190856
- high mRNA expression of Coxsackie-Adenovirus Receptor may support its role in regeneration of the damaged myocardium rather than having any role in viral mediated heart disease PMID: 21641134
- Results demonstrate that the increase in E-cadherin mobility is constitutively altered by the presence of CAR at FLCARMCF7 cell junctions. PMID: 21850251
- Adenoviral drifting motions upstream of internalization are mediated by CAR. PMID: 21843868
- ZEB1 represses CAR expression in both PANC-1 (pancreatic) and MDA-MB-231 (breast) human cancer cells. PMID: 21791114
- The mechanism of decreased cell migration, a prerequisite for metastasis and invasion, due to increased CAR expression may be explained by reduced alphavbeta3 integrin expression. PMID: 21712047
- identified a novel splice variant termed CAR4/6 that lacked exon 5 but retained exon 6 encoding the transmembrane domain; CAR4/6 was not expressed in normal cervical tissue but in 42% of CIN2/3 and in most cervical carcinomas PMID: 21431326
- The s found that DAF expression allowed attachment of both haemagglutinating and non-haemagglutinating echovirus 6 strains but was not sufficient for promoting echovirus 6 cell entry. PMID: 21420451
- CAR is a novel estrogen-responsive gene, which is involved in the E(2)-dependent proliferation of breast cancer cells. PMID: 21389059
- CAR facilitates complex effects during colon carcinogenesis: high CAR potentially prevents apoptosis in adenomas, loss of CAR at the plasma membrane promotes growth, dissemination of primary cancers; high membranous CAR may support distant metastases. PMID: 21468049
- Need for an efficient post-attachment internalisation signal for optimal Adenovirus 5 uptake and transport following surface binding mediated through FX. PMID: 20949078
- Transduction of brain dopamine neurons by adenoviral vectors is modulated by CAR expression. PMID: 20862245
- apical localization of CAR(Ex8) may be responsible for initiation of respiratory adenoviral infections and this localization appears to be regulated by interactions with PDZ-domain containing proteins PMID: 20361046
- The expression of CAR mRNA and protein in cancer tissue samples are significantly higher than that in the normal and paraneoplastic samples. PMID: 19615283
- The induction of expression of CAR by endothelial cells in dilated cardiomyopathy suggests that viruses targeting these receptors could more easily gain entry to heart cells after intravascular administration. PMID: 19957088
- Results suggested that loss of coxsackie and adenovirus receptor in human cancer cell lines under hypoxic conditions occurs in an HIF-1alpha-dependent manner. PMID: 19590529
- Review: Receptor for the group B coxsackieviruses and adenoviruses, CAR PMID: 11479928
- adenovirus serotype 30 fiber does not mediate transduction via the coxsackie-adenovirus receptor PMID: 11752156
- palmitylation is important for stable plasma membrane expression and biological activity of CAR but is not critical for adenovirus receptor performance. PMID: 12021372
- Since DAF is abundantly expressed in epithelial and endothelial cells, interaction of cardiotropic Coxsackie Virus B with the DAF coreceptor protein, in addition to CAR, could therefore be advantageous to the virus by enhancing viral entry into the heart. PMID: 12920584
- identified 3 CAR isoforms lacking the transmembrane domain and are the result of alternative RNA splicing events between exons IV and VII (CAR4/7), exons III and VII (CAR3/7), and exons II and VII (CAR2/7); CAR4/7 but not CAR2/7 binds to coxsackievirus B3 PMID: 14978041
- expression levels of CAR mRNA varies markedly between different tumor types PMID: 15173092
- CAR interacts with several distinct PDZ-domain-containing proteins and may exert its biological function through these interactions PMID: 15304526
- Results indicate that the coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor interacts with multi-PDZ domain protein 1 (MUPP1) and is involved in MUPP1 recruitment to the tight junction. PMID: 15364909
- Data suggest that modulating the expression of integrin subunits beta3/5 in human neurons may enhance adenoviral infectivity via the coxsackie-adenovirus receptor. PMID: 15456946
- interacts with a DAF binding Coxsackievirus B3 to induce A-particle formation PMID: 15596863
- the entire extracellular domain of CAR is of vital importance to the biology of this highly conserved and important protein PMID: 15778494
- swine vesicular disease virus isolates from early and recent outbreaks have been compared for their capacity to utilize the progenitor virus receptors coxsackie-adenovirus receptor and decay-accelerating factor PMID: 15831949
- Because the CVB3-specific siRNA is effective against other enteroviruses, siRNAs have potential for a universal anti-enterovirus strategy. PMID: 15956603
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Basolateral cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell junction, tight junction. Cell junction, adherens junction.; [Isoform 3]: Secreted.; [Isoform 4]: Secreted.; [Isoform 5]: Secreted.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in pancreas, brain, heart, small intestine, testis, prostate and at a lower level in liver and lung. Isoform 5 is ubiquitously expressed. Isoform 3 is expressed in heart, lung and pancreas. In skeletal muscle, isoform 1 is found at the neuromusc
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 2559
OMIM: 602621
KEGG: hsa:1525
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000284878
UniGene: Hs.627078
Most popular with customers
-
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-