CLIC1 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA005545ESR1HU
-
规格:¥440
-
促销:
-
图片:
-
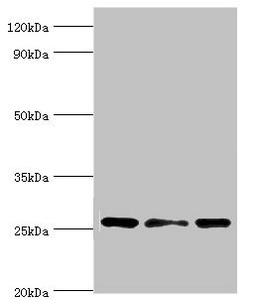
Western blot
All lanes: Chloride intracellular channel protein 1 antibody at 4μg/ml
Lane 1: Hela whole cell lysate
Lane 2: Jurkat whole cell lysate
Lane 3: MCF-7 whole cell lysate
Secondary
Goat polyclonal to rabbit IgG at 1/10000 dilution
Predicted band size: 27 kDa
Observed band size: 27 kDa -
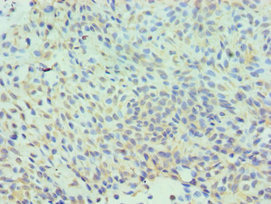
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer using CSB-PA005545ESR1HU at dilution of 1:100
-
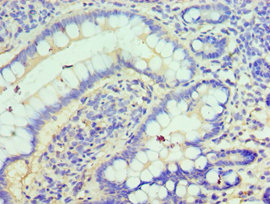
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human small intestine tissue using CSB-PA005545ESR1HU at dilution of 1:100
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) CLIC1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:O00299
-
基因名:CLIC1
-
别名:CLIC1; G6; NCC27; Chloride intracellular channel protein 1; Chloride channel ABP; Nuclear chloride ion channel 27; Regulatory nuclear chloride ion channel protein; hRNCC
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Chloride intracellular channel protein 1 protein (42-241AA)
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen Affinity Purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, WB, IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:5000 IHC 1:20-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Can insert into membranes and form chloride ion channels. Channel activity depends on the pH. Membrane insertion seems to be redox-regulated and may occur only under oxydizing conditions. Involved in regulation of the cell cycle.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- After CLIC1 knockdown, the expression levels of ITGalpha3, ITGalphav, ITGbeta1 and Bcl-2 mRNA and protein were decreased significantly in gastric cancer cells, as well as AKT-phosphorylation, ERK-phosphorylation and p38-phosphorylation, were reduced in vivo. PMID: 29669336
- The current study provides the first statistically convincing evidence that downregulation of miR-372 may occur in gallbladder cancer tissues, which may be associated with aggressive and progressive tumor behavior by affecting CLIC1 expression. PMID: 28944858
- The CLIC1-mediated drug resistance is achieved through positive regulation of MRP1 in choriocarcinoma.CLIC1 is highly expressed in chemoresistant choriocarcinoma. PMID: 27983917
- Proteomic analysis indicates that CLIC1 promotes tumorgenesis in epithelial ovarian cancer. PMID: 27825122
- CLIC1 is a possible tumor marker for ovarian cancer. Dendritic cells pulsed with MtHsp70-CLIC1 can enhance antitumor immunity against ovarian cancer, providing a novel immune therapeutic strategy. PMID: 29061300
- Either dysfunction or downregulation of CLIC1 can partially decrease the antineoplastic effects of metformin. PMID: 28378944
- The expression of CLIC1 might be closely related to the carcinogenesis, clinical biological behaviors, and prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. PMID: 27461670
- Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of CLIC1 protein is a novel mechanism for the regulation of glioblastoma growth. PMID: 26429879
- Results indicate that CLIC1 is an important contributor to tumor invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis. PMID: 25205595
- CLIC1 acts as a putative oncogene in pancreatic cancer. PMID: 25920608
- Data show that glutamate 85 and glutamate 228 are pH-sensor residues of chloride intracellular channel protein CLIC1 and contribute to the pH-response stability in different ways. PMID: 25209805
- CLIC1 and CLIC4 are overexpressed in specific tumor types or their corresponding stroma and change localization and function from hydrophilic cytosolic to integral transmembrane proteins. (Review) PMID: 25546839
- CLIC1 may be a potential sensitive and specific molecular biomarker for early diagnose for serous epithelial ovarian cancers metastasis. PMID: 25582317
- It participates in migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting maspin. PMID: 24989236
- The expression of CLIC1 is closely related to the progression of gall bladder cancer and may be used as an effective marker for predicting the prognosis of this disease. PMID: 25227665
- Data indicate the chloride channel protein CLIC1 as the most penetrant receptor. PMID: 24661138
- Results indicate that CLIC1 could regulate prostate cancer cell proliferation and migration by regulating the(MAPK)/ERK pathway. PMID: 25279971
- CLIC1 protein is involved in the metastasis of colon cancer LOVO cells via regulating the ROS/ERK pathway in the hypoxia-reoxygenation process PMID: 24587680
- Mutation of the two charged amino acids (K37 and R29) in the putative transmembrane region of CLIC1 alters the biophysical properties of the ion channel in both artificial bilayers and cells. PMID: 24058583
- our results are consistent with a model of CLIC function in which covalent binding of glutathione does not occur spontaneously but requires interaction with another protein to stabilise the GSH binding site and/or transfer of the ligand PMID: 24089665
- We have identified a cation-pi interaction involving Lys37. Although this residue is not required for folding, membrane binding, or insertion, it does facilitate CLIC1 transmembrane domain self-association. PMID: 24328417
- In addition to CLIC1 and TPM1, which were the proteins initially discovered in a xenograft mouse model, CLIC4, TPM2, TPM3, and TPM4 were present in ovarian cancer patient sera at significantly elevated levels compared with controls. PMID: 23792823
- Reduced gliomagenesis after CLIC1 targeting in tumoral stem/progenitor cells and the finding that CLIC1 expression is inversely associated with patient survival suggest CLIC1 as a potential target and prognostic biomarker. PMID: 24115360
- increased CLIC1 protein expression is associated with clinicopathological factors and a poor prognosis of hepatic tumors. PMID: 23593969
- cholesterol dependent behaviour of CLIC1 PMID: 23457643
- the first evidence that CLIC1 expression might play an important role in the regulation of aggressiveness in human gliomas PMID: 22578365
- High CLIC1 expression can efficiently inhibit proliferation and enhance apoptosis, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells in vitro. PMID: 22791942
- knockdown of PA28beta could enhance tumor invasion and metastasis, at least in part, through up-regulation of CLIC1 in gastric adenocarcinoma PMID: 22173998
- CLIC1 regulates the migration and invasion of colon cancer cells. PMID: 22426742
- Both histidine (His)74 and His185 are involved in triggering pH changes to the conformational stability of wild-type CLIC1 via their protonation, which stabilizes the intermediate state. PMID: 22242893
- Intermolecular FRET data suggest that (1) N-terminal domain of CLIC1 inserts into bilayer as extended alpha-helix, (2) CLIC1 forms oligomer upon oxidation in presence of membranes, and (3) CLIC1 inserts into bilayer as oligomer of 6-8 subunits. PMID: 22082111
- Data show that the expression of HSP27 and CLIC1 was strongly positive in 61 (59.2%) and 49 cases (47.6%), respectively. PMID: 21858536
- Suppression of CLIC1 contributes to acquisition of the radioresistance phenotype of laryngeal cancer cells via inhibition of reactive oxygen species production. PMID: 20461716
- Consistent with previous findings, the N-terminal domain of CLIC1 is likely to insert into the lipid bilayer, while the C-domain remains in solution on the extravesicular side of the membrane PMID: 20507120
- statistical analysis of CLIC1 level in plasma shows that CLIC1 could be applied as a marker for early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma PMID: 19845400
- CLIC1 may play a role in the regulation of osteoblastic differentiation from mesenchymal progenitors, although its physiologic role in osteoblasts remains to be determined. PMID: 19703605
- on oxidation CLIC1 undergoes a reversible transition from a monomeric to a non-covalent dimeric state due to the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond (Cys-24-Cys-59) PMID: 14613939
- insulin induces the proteasome-dependent degradation of SRp20 as well as the subnuclear relocalization of CLIC1 PMID: 15827065
- In certain polarized columnar epithelia, CLIC1 may play a role in apical membrane recycling. PMID: 17326840
- Data showed that CLIC1 and CLIC5, but not CLIC4, were strongly and reversibly inhibited (or inactivated) by F-actin. PMID: 18028448
- CLIC1 and TPD52 were significantly (P<0.05) up-regulated in all cases of colorectal cancer investigated, irrespective of localization, pTNM stage and grade of colon cancer. PMID: 18710659
- Acid-induced destabilization and partial unfolding of CLIC1 involve helix alpha1 which is the major structural element of the transmembrane region. PMID: 18850721
- Overexpression of CLIC1 promoted cell motility & invasion of gallbladder carcinoma cell lines in vitro, while RNA interference of CLIC1 remarkably decreased these. CLIC1 might play an important role in metastasis of gallbladder carcinoma. PMID: 19299076
- Amyloid-b stimulation of neonatal rat microglia increases CLIC1 protein and functional expression of CLIC1 chloride conductance. Blocking CLIC1 or reducing it by siRNA in amyloid-b treated microglia cocultured with neurons inhibits neurotoxicity PMID: 15190104
- Soluble E. coli-derived recombinant CLIC1 moves from solution into artificial bilayers and forms chloride-selective ion channels with essentially identical properties to those observed in CLIC1-transfected CHO cells. PMID: 11978800
- The structure of oxidized CLIC1 has been determined. The oxidized CLIC1 dimer maintains its ability to form chloride ion channels in artificial bilayers and vesicles, whereas a reducing environment prevents the formation of ion channels by CLIC1 PMID: 14613939
- By selectively tagging either N- or C-termini of NCC27 (CLIC1) and varying the side of the membrane from which channel activity is recorded, NCC27 can be seen to be a TM protein forming part of an ion channel. PMID: 10834939
- NCC27 (CLIC1) is a 27 kDa intracellular ion channel localized to the nucleus and cytoplasm that exists in both a soluble and integral membrane form PMID: 9139710
- NCC27 (CLIC1) is broadly expressed and highly conserved. NCC27 blockers led to arrest of CHO-K1 cells in the G2/M stage of the cell cycle, the same stage at which this ion channel is selectively expressed on the plasma membrane PMID: 11195932
- The soluble form of CLIC1 has been determined at 1.4-A resolution. The protein is monomeric and structurally homologous to the glutathione S-transferase superfamily, and it has a redox-active site resembling glutaredoxin. PMID: 11551966
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Nucleus membrane; Single-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasm. Cell membrane; Single-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Chloride channel CLIC family
-
组织特异性:Expression is prominent in heart, placenta, liver, kidney and pancreas.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 2062
OMIM: 602872
KEGG: hsa:1192
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000364934
UniGene: Hs.414565
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
-
-
-
-
-
-