CENPF Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA230952
-
规格:¥1100
-
图片:
-
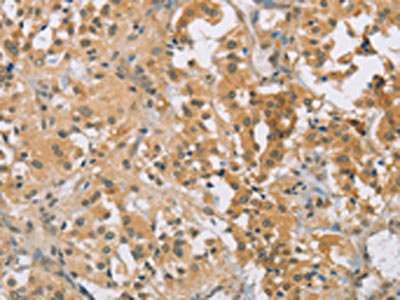
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human thyroid cancer tissue using CSB-PA230952(CENPF Antibody) at dilution 1/30, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
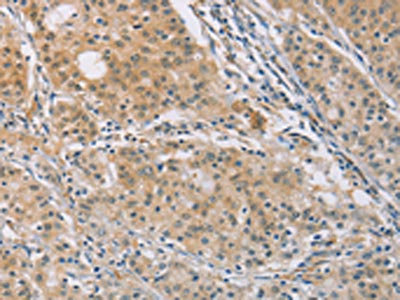
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human gastric cancer tissue using CSB-PA230952(CENPF Antibody) at dilution 1/30, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P49454
-
基因名:
-
别名:AH antigen antibody; Cell cycle dependent 350K nuclear protein antibody; CENF antibody; CENP F antibody; CENP F kinetochore protein antibody; CENP-F antibody; CENPF antibody; CENPF kinetochore protein antibody; CENPF_HUMAN antibody; Centromere protein F 350/400ka antibody; Centromere protein F antibody; Centromere protein F, 350/400kDa antibody; CILD31 antibody; Hcp 1 antibody; Hcp1 antibody; Kinetochore protein CENP F antibody; Kinetochore protein CENPF antibody; Mitosin antibody; PRO1779 antibody; STROMS antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Synthetic peptide of Human CENPF
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen affinity purification
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:-20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution ELISA 1:1000-1:5000 IHC 1:25-1:100 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Required for kinetochore function and chromosome segregation in mitosis. Required for kinetochore localization of dynein, LIS1, NDE1 and NDEL1. Regulates recycling of the plasma membrane by acting as a link between recycling vesicles and the microtubule network though its association with STX4 and SNAP25. Acts as a potential inhibitor of pocket protein-mediated cellular processes during development by regulating the activity of RB proteins during cell division and proliferation. May play a regulatory or permissive role in the normal embryonic cardiomyocyte cell cycle and in promoting continued mitosis in transformed, abnormally dividing neonatal cardiomyocytes. Interaction with RB directs embryonic stem cells toward a cardiac lineage. Involved in the regulation of DNA synthesis and hence cell cycle progression, via its C-terminus. Has a potential role regulating skeletal myogenesis and in cell differentiation in embryogenesis. Involved in dendritic cell regulation of T-cell immunity against chlamydia.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- This is the second case report identifying CENPF mutation as the cause of Stromme syndrome PMID: 28407396
- s suggest that CENP-F might act as a transporter of mitochondria and other cellular cargoes by attaching them to dynamic microtubule ends during both polymerization and depolymerization of tubulin. PMID: 28701340
- Tumors with higher topoisomerase IIalpha and/or mitosin expression have a higher risk of recurrence after initial treatment, and these patients may benefit from adjuvant treatment and closer radiological follow-up PMID: 28301542
- We show for the first time that Stromme syndrome is an autosomal-recessive disease caused by mutations in CENPF that can result in a wide phenotypic spectrum. PMID: 26820108
- Miro and Cenp-F promote anterograde mitochondrial movement and proper mitochondrial distribution in daughter cells. PMID: 26259702
- Mitosin and pHH3 immunostaining predict poorer survival in astrocytomas WHO grades II and III. PMID: 26188054
- Our data identify CENPF as a new centriolar disease gene implicated in severe human ciliopathy and microcephaly related phenotypes PMID: 25564561
- the increased expression of CENPF plays an important role in the progression of PCa. PMID: 25647485
- N-terminal microtubule-binding domain of CENP-F prefers curled oligomers of tubulin relative to microtubule walls by approximately fivefold, suggesting it may contribute to the firm bonds between kinetochores and flared plus ends of dynamic microtubules PMID: 26101217
- FOXM1 and CENPF function synergistically to promote tumor growth by coordinated regulation of target gene expression and activation of key signaling pathways associated with prostate cancer malignancy. PMID: 24823640
- CENP-F may serve as valuable molecular marker for predicting prognosis of ESCC patients. data indicate potential benefit of combining ZOL with cisplatin in ESCC; CENP-F expressionmay have therapeutic implications. PMID: 23163484
- data suggest that CENPF is frequently overexpressed in HCC and plays a critical role in driving HCC tumorigenesis PMID: 23791740
- Data suggest that ASUN promotes perinuclear enrichment of dynein at G2/M that facilitates BICD2- and CENP-F-mediated anchoring of dynein to nuclear pore complexes. PMID: 23097494
- Coincidently amplified CDK13, GMNN, and CENPF genes can play a role as common cancer-driver genes in human cancers. PMID: 22912832
- Rab5 forms a complex with a subset of CENP-F in mitotic cells and regulates the kinetics of release of CENP-F from the nuclear envelope and its accumulation on kinetochores. PMID: 21987812
- Centromere protein F and survivin are malignant behaviour markers for colorectal gastrointestinal stromal tumours. PMID: 21613637
- Data identified Cenp-F as a potential new molecular target for NBPs in tumour cells. PMID: 20015195
- Cenp-F plays a role in organization of interphase chromatin through association and possibly regulation of DNA-PK. PMID: 20978035
- Data suggest that CENP-F protein is a valuable marker of nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression, and CENP-F expression is associated with poor overall survival of patients. PMID: 20828406
- Mitosin did not predict patient survival in this series of cutaneous melanomas. PMID: 20398247
- These results uncover a novel role of CENP-F in regulation of epigenetic modification on histone H3. PMID: 20213041
- Data show that the post-anaphase, KEN-box-dependent degradation of Cenp-F requires it to be farnesylated, a post-translational modification usually linked to membrane association. PMID: 20053638
- Data suggest that farnesylation of Cenp-F is required not only for its localisation to the nuclear envelope and kinetochores but also for timely progression through G2/M and its degradation after mitosis. PMID: 12154071
- Data show that mitosin associates preferentially with kinetochores of unaligned chromosomes. PMID: 12974617
- CENP-F expression presents a theoretical advantage for the analysis of the precise cell cycle of G2 to M cells, compared to Ki-67. PMID: 14720137
- Results suggest that mitosin is a negative regulator of ATF4 in interphase through direct interaction. PMID: 15677469
- Mitosin is therefore essential for full chromosome alignment, possibly by promoting proper kinetochore attachments through modulating CENP-E and dynein functions PMID: 15870278
- In addition to regulating kinetochore-microtubule interactions, Cenp-F might be required to protect centromeric cohesion prior to anaphase commitment. PMID: 16219694
- Data show that the absence of nuclear CENP-F does not affect cell cycle progression in S and G2, and that CENP-F is crucial for efficient assembly of a stable microtubule-kinetochore interface. PMID: 16252009
- REVIEW: involvement in mitotic control, microtubule dynamics, transcriptional regulation, and muscle cell differentiation. PMID: 16456711
- CENP-F is a novel microtubule-binding protein that possesses two microtubule-binding domains at opposite ends of the molecule. The C-terminal microtubule-binding domain was found to stimulate microtubule polymerization in vitro. PMID: 16601978
- CENP-F upregulation was significantly associated breast cancer PMID: 17205517
- Ndel1, Nde1, and Lis1 localize to kinetochores in a Cenp-F-dependent manner. PMID: 17600710
- high expression levels of the CENP-F appeared to be the molecular background of higher proliferative activity, and they were correlated with high SUV (standardized uptake value) in breast cancer PMID: 19102762
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Stromme syndrome (STROMS)
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Nucleus matrix. Chromosome, centromere, kinetochore. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle. Note=Relocalizes to the kinetochore/centromere (coronal surface of the outer plate) and the spindle during mitosis. Observed in nucleus during interphase but not in the nucleolus. At metaphase becomes localized to areas including kinetochore and mitotic apparatus as well as cytoplasm. By telophase, is concentrated within the intracellular bridge at either side of the mid-body.
-
蛋白家族:Centromere protein F family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 1857
OMIM: 243605
KEGG: hsa:1063
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000355922
UniGene: Hs.497741
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-