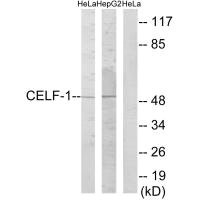
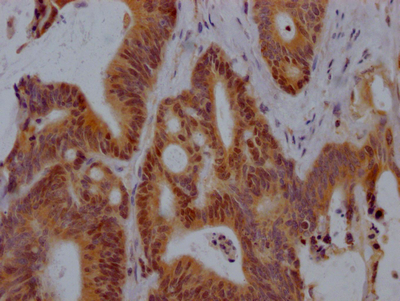
CELF1 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA991834
-
规格:¥2024
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) CELF1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q92879
-
基因名:CELF1
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from internal of Human CELF-1.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:3000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:RNA-binding protein implicated in the regulation of several post-transcriptional events. Involved in pre-mRNA alternative splicing, mRNA translation and stability. Mediates exon inclusion and/or exclusion in pre-mRNA that are subject to tissue-specific and developmentally regulated alternative splicing. Specifically activates exon 5 inclusion of cardiac isoforms of TNNT2 during heart remodeling at the juvenile to adult transition. Acts as both an activator and repressor of a pair of coregulated exons: promotes inclusion of the smooth muscle (SM) exon but exclusion of the non-muscle (NM) exon in actinin pre-mRNAs. Activates SM exon 5 inclusion by antagonizing the repressive effect of PTB. Promotes exclusion of exon 11 of the INSR pre-mRNA. Inhibits, together with HNRNPH1, insulin receptor (IR) pre-mRNA exon 11 inclusion in myoblast. Increases translation and controls the choice of translation initiation codon of CEBPB mRNA. Increases mRNA translation of CEBPB in aging liver. Increases translation of CDKN1A mRNA by antagonizing the repressive effect of CALR3. Mediates rapid cytoplasmic mRNA deadenylation. Recruits the deadenylase PARN to the poly(A) tail of EDEN-containing mRNAs to promote their deadenylation. Required for completion of spermatogenesis. Binds to (CUG)n triplet repeats in the 3'-UTR of transcripts such as DMPK and to Bruno response elements (BREs). Binds to muscle-specific splicing enhancer (MSE) intronic sites flanking the alternative exon 5 of TNNT2 pre-mRNA. Binds to AU-rich sequences (AREs or EDEN-like) localized in the 3'-UTR of JUN and FOS mRNAs. Binds to the IR RNA. Binds to the 5'-region of CDKN1A and CEBPB mRNAs. Binds with the 5'-region of CEBPB mRNA in aging liver. May be a specific regulator of miRNA biogenesis. Binds to primary microRNA pri-MIR140 and, with CELF2, negatively regulates the processing to mature miRNA.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- results underscore novel roles of CELF1 in melanoma, illustrating tumor type-restricted functions of mRNA binding proteins in cancer. PMID: 29269732
- These data present an 11-component genetic pathway, invisible to transcriptional profiling approaches, in which the CELF1 protein functions as a central node controlling translational activation of genes driving EMT and ultimately tumour progression. PMID: 27869122
- High CELF1 expression is associated with aberrant splicing in Type 1 diabetes. PMID: 28512194
- CELF1 globally regulates the alternative splicing. PMID: 28733224
- Findings indicate that IGF2R expression is controlled posttranscriptionally by two factors that associate with Igf2r mRNA and suggest that miR-195 and CUGBP1 dampen IGF signaling by inhibiting IGF2R translation. PMID: 28716948
- In the course of these studies, we found that RNA binding protein CUGBP1 is a new tumor suppressor protein which is reduced in all HBL samples. Therefore, we generated CUGBP1 KO mice and examined HBL signatures in the liver of these mice. Micro-array studies revealed that the HBL-specific molecular signature is developed in livers of CUGBP1 KO mice at very early ages PMID: 28535186
- Results show that CELF1 is a potential target of TUG1 interaction and could be negatively regulated by TUG1 RNA. PMID: 27485439
- CUG-binding protein 1 regulates HSC activation and liver fibrogenesis. PMID: 27853137
- High expression of CUGBP1 is associated with recurrence in lung adenocarcinoma. PMID: 26728670
- CUG-BP1 affected the calcium release activity in single myofibers and the extent of atrophy was significantly reduced upon gene silencing of CUG-BP1 in atrophic muscle. PMID: 26531141
- these data provided a comprehensive view of the CELF1 mRNA regulatory network in oral cancer PMID: 26498364
- forced expression of miR-214-3p enhances the sensitivity of esophageal cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. This effect is abrogated with rescue expression of survivin or CUG-BP1 PMID: 26234674
- Expression of several genes within the CELF1 locus, including MTCH2, were highly correlated with one another and were associated with Alzheimer's disease status. PMID: 26919393
- CUGBP1 and HuR negate each other's effects in regulating E-cadherin translation by altering the recruitment of E-cadherin mRNA to PBs and play important roles in the regulation of intestinal barrier integrity. PMID: 26491048
- CUGBP1 promotes cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis via down-regulating C-EBPalpha in human non-small cell lung cancers. PMID: 25701464
- The results indicate that the cellular level of miR-122 is determined by the balance between the opposing effects of GLD-2 and PARN/CUGBP1 on the metabolism of its 3'-terminus. PMID: 26130707
- CELF1 dysfunction in malignant T cells led to the up-regulation of a subset of GRE-containing transcripts that promote cell growth and down-regulation of another subset that suppress cell growth PMID: 26249002
- Celf1 has a role in vegetal RNA localization during Xenopus oogenesis PMID: 26164657
- These results demonstrate the importance of CUGBP1 in the biological and pathological functions of NSCLC and indicate its potential as a therapeutic target for NSCLC. PMID: 25619475
- The result is consistent with the hypothesis that MBNL proteins are trapped by expanded CUG repeats and inactivated in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) and that CELF1 is activated in DM1. PMID: 25403273
- CUGBP1 has a critical role in modulating cell growth and apoptosis PMID: 25077823
- the size and the number of colonies formed in gastric cancer MGC-803 cells were markedly reduced in the absence of CUGBP1 PMID: 24818870
- CUGBP1 seems to play a role in classic DM1 but not in DM2 PMID: 24376746
- The Alzheimer's disease single nucleotide polymorphism rs10838725 (pAD = 1.1 x 10(-08)) at the locus CELF1 is also genome-wide significant for obesity. PMID: 24788522
- Data suggest a model for RNA binding protein CELF1/CUGBP1-mediated regulation of alternative polyadenylation (APA). PMID: 25123787
- CUGBP1 was expressed in 85.7% hepatocellular carcinoma specimens compared with 50% in normal liver specimens. CUGBP1 silencing remarkably decreased the proliferation of HepG2 cells. PMID: 24502807
- High CUGBP1 expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. PMID: 23359188
- CELF1 depletion induces apoptosis in tumor cells, but not in normal cells. PMID: 23324604
- CUGBP1 represses occludin translation by increasing occludin mRNA recruitment to P-bodies. PMID: 23155001
- study suggests that regulation of CUGBP1 and MBNL1 is essential for accurate control of destabilization of a broad spectrum of mRNAs as well as of alternative splicing events PMID: 22355723
- The results suggest that CUG-BP1 binds to nucleotides 51-100 of the human albumin 3'UTR. In human cells CUG-BP1 binding may thus play a role in regulation of albumin expression and, additionally, it may have a function in post-transcriptional control in CHO cells. PMID: 22982313
- CUG-BP1 is overexpressed in oesophageal cancer cell lines and human oesophageal cancer specimens. CUG-BP1 associates with the 3'-untranslated region of survivin mRNA. PMID: 22646166
- CUG-binding protein represses translation of p27Kip1 mRNA through its internal ribosomal entry site PMID: 21508681
- CUGBP1 binding to certain GRE-containing target transcripts decreased following T cell activation through activation-dependent phosphorylation of CUGBP1. PMID: 22117072
- Stress granules component CUGBP1 was identified as a factor required for p21 mRNA stabilization. PMID: 21637851
- Data show that crystal structures of CUGBP1 RRM1 and tandem RRM1/2 domains bound to RNAs containing tandem UGU(U/G) elements. PMID: 20947024
- Overexpression of CUGBP1 in mouse skeletal muscle reproduces features of myotonic dystrophy type 1. PMID: 20603324
- identified 613 putative mRNA targets of CUGBP1 and found that the UGUUUGUUUGU GU-rich elements (GREs) sequence and a GU-repeat sequence were both highly enriched in the 3' UTRs of these targets PMID: 20547756
- These results strongly support a role for CUGBP1 up-regulation in myotonic dystrophy type 1 pathogenesis. PMID: 20051426
- CUGBP1 directly controls CD9 expression. PMID: 20227387
- CUG-BP and Xenopus EDEN-BP have very similar RNA-binding specificities; it is suggested that the CUG expansion associated with Type 1 myotonic dystrophy can affect the function of CUG-BP, leading to a trans-dominant effect on normal RNA processing PMID: 12799066
- Data show that epidermal growth factor receptor signaling results in phosphorylation of CUG-BP1, and leads to increased binding of CUG-BP1 to CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta (C/EBP beta) mRNA and elevated expression of the C/EBPbeta LIP isoform. PMID: 15082764
- The results of this study suggest that the CUG expansion may bind to complementary sequences within the CUGBP1 mRNA and that this molecular interaction may affect CUGBP1 mRNA expression in DM1. PMID: 15099703
- CUG-BP, therefore, is the first RNA-binding protein shown to directly recruit a deadenylase to an RNA substrate.CUG-BP interacts with PARN in extracts by coimmunoprecipitation, and this interaction can be recapitulated using recombinant proteins PMID: 16601207
- coordinated physical and functional interactions between hnRNP H, CUG-BP1 and MBNL1 dictate IR splicing in normal and DM1 myoblasts PMID: 16946708
- transcription of Cugbp1 gene in muscle is regulated by myogenin and E proteins PMID: 17531403
- Insertional disruption of the CUGBP1 gene is associated with leukemogenesis PMID: 17854664
- Data show that expression of DMPK-CUG-repeat RNA results in hyperphosphorylation and stabilization of CUGBP1, and suggest that inappropriate activation of the PKC pathway contributes to the pathogenic effects of a noncoding RNA. PMID: 17936705
- CUG-BP1 specifically recognized UG repeats, probably through cooperative binding of RNA recognition motifs at both ends of the protein. PMID: 18039683
- These results demonstrate the dynamic behavior of CUGBP-1 during stress response and that the linker region, in concert with RRMs, plays a significant role in defining its subcellular localization and dynamics. PMID: 18164289
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Note=RNA-binding activity is detected in both nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments.
-
蛋白家族:CELF/BRUNOL family
-
组织特异性:Ubiquitous.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 2549
OMIM: 601074
KEGG: hsa:10658
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000435926
UniGene: Hs.595333
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-