CDKL5 Antibody
-
中文名称:CDKL5兔多克隆抗体
-
货号:CSB-PA005085LA01HU
-
规格:¥440
-
促销:
-
图片:
-
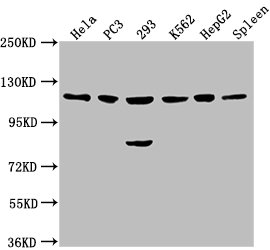
Western Blot
Positive WB detected in: Hela whole cell lysate, PC3 whole cell lysate, 293 whole cell lysate, K562 whole cell lysate, HepG2 whole cell lysate, Rat spleen tissue
All lanes: CDKL5 antibody at 1:2000
Secondary
Goat polyclonal to rabbit IgG at 1/50000 dilution
Predicted band size: 116, 108 kDa
Observed band size: 116 kDa
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) CDKL5 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:O76039
-
基因名:CDKL5
-
别名:Cdkl5 antibody; CDKL5_HUMAN antibody; Cyclin dependent kinase 5 transcript antibody; Cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 antibody; EIEE2 antibody; ISSX antibody; Serine/threonine kinase 9 antibody; Serine/threonine-protein kinase 9 antibody; Stk9 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human, Rat
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 protein (790-921AA)
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
本页面中的产品,CDKL5 Antibody (CSB-PA005085LA01HU),的标记方式是Non-conjugated。对于CDKL5 Antibody,我们还提供其他标记。见下表:
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:1000-1:5000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Mediates phosphorylation of MECP2. May regulate ciliogenesis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- mutations in the CDKL5 gene in complex genotypes associated with West syndrome with variable phenotype PMID: 28780406
- The genetic etiology of Rett syndrome (RTT) without MECP2, CDKL5, and FOXG1 mutations is heterogeneous, overlaps with other NDDs, and complicated by a high mutation burden. Dysregulation of chromatin structure and abnormal excitatory synaptic signaling may form two common pathological bases of RTT. PMID: 27171548
- Although abilities were markedly impaired for the majority with the CDKL5 disorder, some females and a few males had better functional abilities. This variability may be related to underlying gene variants, with females with a late truncating variant having better levels of ability than those with no functional protein. PMID: 27528505
- We have characterised the predominant brain isoform of CDKL5, a 9.7 kb transcript comprised of 18 exons with a large 6.6 kb 3'-untranslated region (UTR), which we name hCDKL5_1. In addition we describe new exonic regions and a range of novel splice and UTR isoforms PMID: 27315173
- In the asymptomatic mother, the mutated copy of the CDKL5 gene was inactivated in 90% of blood cells. We also identified a premature stop codon (p.Arg926*) in IQSEC2 in a patient with a Rett-like phenotype. Finally, exome sequencing enabled us to characterize a heterozygous de novo missense (p.Val408Ala) in KCNA2 in a girl with infantile-onset seizures variant of Rett syndrome (RTT) PMID: 27062609
- The results suggested the mutant CDKL5 was responsible for the Rett syndrome disease. PMID: 27265524
- Rett syndrome with early epilepsy and the congenital variant are mainly due to variations in the CDKL5 and FOXG1 genes, respectively PMID: 26239053
- Mutations in exon 8 of cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 gene were determined to be disease-causing in epileptic encephalopathy. PMID: 26701947
- study presents the genotype of 2 sisters, a CDKL5 mutation c. 283-3_290del, but different phenotype PMID: 25762588
- Data suggest that the increased dosage of cyclin dependent kinase like 5 protein(CDKL5) might have affected interactions of this kinase with its substrates, leading to perturbation of neurodevelopmental and neurobehavioral abnormalities. PMID: 25315662
- It was indicated that CDKL5 controls excitatory synaptic transmission and the conditions associated with CDKL5 deviation in man indicates synaptic abnormalities. PMID: 25864828
- CDKL5 gene mutations accounted for 5.4% of boys with early onset epileptic encephalopathy PMID: 25266480
- CDKL5 gene is not useful in practical molecular diagnosis of atypical Rett syndrome. PMID: 23756444
- Its mutation causes Rett syndrome.(review) PMID: 24738188
- Mutations in the CDKL5 gene associtaed with Hanefield variants of Rett syndrome and early-onset epileptic encephalopathies. PMID: 24564546
- study described the clinical condition and characterization of two first Brazilian patients with CDKL5 mutations, including the first Brazilian case of atypical Rett related to abnormalities in this gene PMID: 23828526
- CDKL5 mutations cause severe epilepsy in infancy with subsequent epileptic encephalopathy. PMID: 22832775
- aberrations of CDKL5 and ARX combined are an important consideration in the genetic forms of early-onset epilepsy in boys PMID: 23583054
- 3 known & 3 new (V966Im A1911V, H589H)mutations in the C-terminal domain of CDKL5 were found in Indian patients with Rett syndrome negative for MECP2. PMID: 23242510
- study examines the presence of breathing and sleep abnormalities in a small series of patients with CDKL5 mutations PMID: 23151060
- This review surveys the current state of CDKL5 research with emphasis on the clinical symptoms associated with mutations in CDKL5, the different mechanisms regulating its functions, and the connected molecular pathways. PMID: 22779007
- a functional axis between MYCN and CDKL5 governing both neuron proliferation rate and differentiation. PMID: 22921766
- CDKL5 is localized at excitatory synapses and contributes to correct dendritic spine structure and synapse activity. PMID: 22922712
- The importance of CDKL5 mutations as etiological factors in neurodevelopmental disorders was shown. The CDKL5 gene sequence and its rearrangements should be thoroughly analyzed in females with Rett syndrome, severe encephalopathy and epilepsy. PMID: 22867051
- Identification of eleven novel sequence variations including four pathogenic mutations in the CDKL5 gene. PMID: 23064044
- Recurrent mutations in the CDKL5 gene in patients with epileptic encephalopathies can be associated with either a milder or a more severe phenotype. PMID: 22678952
- The patients with clinical features of Rett syndrome, with epileptic encephalopathy before 6 months of age, regardless the presence of genetic abnormalities (mutations in MeCP2 or CDKL5 or both) or even in their absence. PMID: 22430159
- A novel CDKL5 mutation is identified in an ambulatory girl who had severe mental retardation and multiple types of seizures without Rett-like features. PMID: 21775177
- sought to determine the historic, clinical, and prognostic features of epilepsy secondary to CDKL5 mutations. all children developed infantile spasms. All children demonstrated developmental delay and visual impairment. PMID: 22264704
- This study present clinical phenotype of 5 girls having a mutation in the CDKL5 gene PMID: 21765152
- female CDKL5-mutated iPSCs maintain X-chromosome inactivation and clones express either the mutant CDKL5 allele or the wild-type allele that serve as an ideal experimental control. PMID: 21750574
- CDKL5 deficit may induce changes in synaptic plasticity in the patient's brain. PMID: 21107515
- mutations in early onset epileptic encephalopathy PMID: 21770923
- Two patients (one female, one male) with CDKL5 mutations have epileptic spasms after tonic seizures but never present infantile spasms as the main seizure type or hypsarrhythmia in electroencephalography. PMID: 20493745
- A novel CDKL5 exon and pathogenic mutations in patients with severe mental retardation, early-onset seizures and Rett-like features. PMID: 21318334
- We report the first case of an exonic deletion of CDKL5 in a male and emphasize the importance of underappreciated mosaic exonic copy number variation in patients with early-onset seizures and RTT-like features of both genders. PMID: 21293276
- the distinctive hypermotor-tonic-spasms sequence is a feature of CDKL5 epileptic encephalopathy. PMID: 21502606
- CDKL5 exon 16b should now be considered in the genetic screening of patients presenting with a CDKL5-related disease profile. PMID: 21124335
- Infants with CDKL5-related early epileptic encephalopathy can present in the first year of life with an unusual. PMID: 21309761
- CDKL5 mutation is associated with epileptic encephalopathy. PMID: 20602487
- Data indicate that MEF2C missense de novo mutations in severe mental retardation showed diminished MECP2 and CDKL5 expression. PMID: 20513142
- seven polymorphic variations and four de novo mutations of the CDKL5 gene were identified, and in all instances of the latter the clinical phenotype was that of an epileptic encephalopathy. PMID: 20397747
- a novel p.Arg970X mutation in the last exon of the CDKL5 gene resulting in late onset seizure disorder. PMID: 19428276
- We found CDKL5 mutations in 8.2% (4 of 49) of patients and genomic deletions in 8.2% (4 of 49). Overall, abnormalities of the CDKL5 gene accounted for 16.3% (8 of 49) of patients. PMID: 19780792
- CDKL5 is involved in pre-mRNA processing, by controlling splicing factor dynamics. PMID: 19740913
- CDKL5 mutations are associated with epilepsy, X-linked mental retardation and a clinical phenotype that overlaps Rett syndrome. PMID: 15492925
- A proportion of Rett syndrome atypical cases may result from mutations in CDKL5. (review) PMID: 15635068
- demonstrate that MeCP2 and CDKL5 interact both in vivo and in vitro and that CDKL5 is indeed a kinase, which is able to phosphorylate itself and to mediate MeCP2 phosphorylation PMID: 15917271
- novel pathogenic CDKL5 mutations were identified in three girls, two of whom had initially been diagnosed with the early onset seizure variant of Rett Syndrome (RTT) and the other with early onset seizures and some features of RTT PMID: 16015284
- Patients with the CDKL5 mutation have an early onset, epileptic encephalopathy in infancy that evolves into myoclonic seizures in childhood with a unique EEG pattern. PMID: 16326141
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 2 (EIEE2)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, cilium basal body. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CDC2/CDKX subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed in brain, lung, kidney, prostate, ovary, placenta, pancreas and testis.; [Isoform 2]: Predominant transcript in brain.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 11411
OMIM: 300203
KEGG: hsa:6792
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000369325
UniGene: Hs.659851
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-