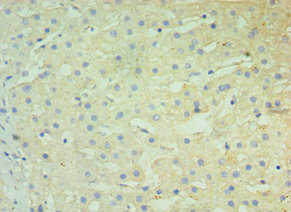
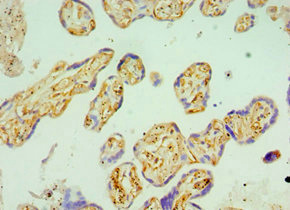
BST2 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA606010DSR2HU
-
规格:¥440
-
促销:
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) BST2 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q10589
-
基因名:BST2
-
别名:Bone marrow stromal antigen 2 antibody; Bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 antibody; Bone marrow stromal cell antigen antibody; BST 2 antibody; BST-2 antibody; BST2 antibody; BST2_HUMAN antibody; CD 317 antibody; CD317 antibody; CD317 antigen antibody; HM1.24 antigen antibody; NPC A 7 antibody; Tetherin antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Bone marrow stromal antigen 2 protein (49-161AA)
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen Affinity Purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC 1:20-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:IFN-induced antiviral host restriction factor which efficiently blocks the release of diverse mammalian enveloped viruses by directly tethering nascent virions to the membranes of infected cells. Acts as a direct physical tether, holding virions to the cell membrane and linking virions to each other. The tethered virions can be internalized by endocytosis and subsequently degraded or they can remain on the cell surface. In either case, their spread as cell-free virions is restricted. Its target viruses belong to diverse families, including retroviridae: human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2), simian immunodeficiency viruses (SIVs), equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV), feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV), prototype foamy virus (PFV), Mason-Pfizer monkey virus (MPMV), human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1), Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) and murine leukemia virus (MLV), flavivirideae: hepatitis C virus (HCV), filoviridae: ebola virus (EBOV) and marburg virus (MARV), arenaviridae: lassa virus (LASV) and machupo virus (MACV), herpesviridae: kaposis sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), rhabdoviridae: vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), orthomyxoviridae: influenza A virus, paramyxoviridae: nipah virus, and coronaviridae: SARS-CoV. Can inhibit cell surface proteolytic activity of MMP14 causing decreased activation of MMP15 which results in inhibition of cell growth and migration. Can stimulate signaling by LILRA4/ILT7 and consequently provide negative feedback to the production of IFN by plasmacytoid dendritic cells in response to viral infection. Plays a role in the organization of the subapical actin cytoskeleton in polarized epithelial cells. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 are both effective viral restriction factors but have differing antiviral and signaling activities. Isoform 2 is resistant to HIV-1 Vpu-mediated degradation and restricts HIV-1 viral budding in the presence of Vpu. Isoform 1 acts as an activator of NF-kappa-B and this activity is inhibited by isoform 2.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The primary role of the S(52,56) residues of Vpu in antagonism of CD4, GaLV Env, and BST-2/tetherin is to recruit the SCF/betaTrCP ubiquitin ligase. PMID: 30347660
- Studied role of bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 (BST2) in gastric cancer (GC); results show BST2 is overexpressed in GC tissues and BST2 silencing inhibits cell proliferation and migration, partly by regulating NF-kappaB signaling. PMID: 29774441
- The results establish tetherin as a key effector of the intrinsic immune defense against HIV-1, and they demonstrate that Vpu-mediated tetherin antagonism is critical for efficient viral spread during the initial phase of HIV-1 replication. PMID: 29324226
- findings support the notion that NAbs can induce ADCC. They highlight that while BST2 antagonism by HIV promotes ADCC evasion, strategies aimed at restoring BST2 restriction could improve anti-HIV responses and potentially provide a means to eliminate reactivated cells in latent reservoirs. PMID: 27853288
- BST2 likely mediates platinum resistance in nasopharyngeal cancer via NF-kappaB signaling PMID: 28617432
- These data collectively suggest that the human parainfluenza virus type 2 V protein inhibits tetherin expression induced by several external stimuli. PMID: 28455649
- These results suggest that tetherin antagonism by V proteins is common among the genus Rubulavirus. PMID: 28466381
- High BST2 expression is associated with Esophageal, Gastric, or Colorectal Cancer. PMID: 26832883
- Two additional regulators of BST2 constitutive ubiquitylation and sorting to the lysosomes: the E3 ubiquitin ligases NEDD4 and MARCH8, are reported. PMID: 28320822
- Coimmunoprecipitation studies indicated that non-glycosylated tetherin is stabilized through the formation of a ternary SGTA/Vpu/tetherin complex. Although the results do not provide support for a physiological function of SGTA in HIV-1 replication, they demonstrate that SGTA overexpression regulates tetherin expression and stability, thus providing insights into the function of SGTA in endoplasmic reticulum translocation PMID: 27103333
- Importantly, the s demonstrate for the first time that the HIV-2 Env induces NF-kappaB activation in HEKappa293T cells. Furthermore, the anti-BST-2 activity of the HIV-2 Env is not sufficient to completely inhibit NF-kappaB activity. PMID: 29028477
- Data revealed that under a nutrient deficient condition, CD317 functions as an anti-apoptotic factor through AIF-mediated caspase and autophagy-independent manner. PMID: 27444183
- findings lead us to believe that BISPR and BST2 may regulate egress of HEV virions into bile in vivo. This system may also be used to scale up virus production in vitro PMID: 29091957
- a non-canonical autophagy pathway reminiscent of LC3-associated phagocytosis contributes to Vpu counteraction of BST2 restriction. PMID: 27880899
- Ebola virus GP1,2, the Ebola virus matrix protein VP40, and BST2 are at least additive with respect to the induction of NF-kappaB activity. PMID: 28878074
- Studied the mechanism of viral budding and tethering mediated by human BST-2/tetherin using a model of BST-2 embedded in a membrane and used steered molecular dynamics to simulate the transition from the host cell membrane associated form to the cell-virus membrane bridging form. PMID: 28779494
- Disruption of BST-2 dimerization offers a potential therapeutic approach for breast cancer. PMID: 28300825
- identified WDR81 as a novel gene required for tetherin trafficking and degradation in both the presence and absence of Vpu PMID: 27126989
- Among 32 HIV-2 ROD Env mutants tested, the s demonstrated that the asparagine residue at position 659 located in the gp36 ectodomain is mandatory to exert the anti-tetherin function. PMID: 27754450
- Despite the influence of rs919266 and rs9576 on BST2 expression being still undetermined, a preventive role by BST2 polymorphisms was found during HIV-1 infection. PMID: 26885809
- The s demonstrated that BST2 restricts the release of Japanese encephalitis virus whose budding occurs at the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment, and in turn, Japanese encephalitis virus downregulates BST2 expression via envelope protein E. PMID: 28710958
- These results suggest that BST2 plays an important role in the progression of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), and, because BST2 is expressed on the cell membrane, BST2 is a good therapeutic target for RCC. PMID: 28551621
- findings show that BST-2 upregulation by IFN-beta and interleukin-27 (IL-27) also increases the surface expression of Env and thus boosts the ability of CD4mc to sensitize HIV-1-infected cells to ADCC by sera from HIV-1-infected individuals. PMID: 28331088
- study found that tetherin expression on hematopoietic cells resulted in the specific reduction of Moloney murine leukemia virus cell-free plasma viremia but not the number of infected hematopoietic cells PMID: 28381565
- The s show that orthobunyaviruses viruses with human tropism (Oropouche virus and La Crosse virus) are restricted by sheep BST-2 but not by the human orthologue, while viruses with ruminant tropism (Schmallenberg virus and others) are restricted by human BST-2 but not by the sheep orthologue. PMID: 28628828
- Thus, efficient human immunodeficiency virus type 1 release from infected cells seems to play an important role in the spread of the virus in the human population and requires a fully functional Vpu protein that counteracts human tetherin. PMID: 27531907
- BST-2 restricts influenza A virus release and is countered by the viral M2 protein. PMID: 28087685
- IL8 might play an important role in the enhancement of BST2 and be involved in HBsAg eradication. PMID: 28363866
- Antagonism of BST-2 is a conserved function of the env glycoprotein of primary HIV-2 isolates. PMID: 27681141
- These data present the first example of an HIV-1 group O Vpu that efficiently antagonizes human tetherin and suggest that counteraction by O-Nefs may be suboptimal. PMID: 28077643
- This is in contrast to the pandemic HIV-1 group M-specified BST2 countermeasure Vpu. PMID: 27581991
- The s show that while the conserved transmembrane-proximal Vpu hinge region residues have no intrinsic activity on the cellular distribution of Vpu in the absence of BST2, they regulate the ability of Vpu to bind to BST2 and, consequently, govern both BST2-dependent trafficking properties of the protein as well as its co-localization with BST2. PMID: 28288652
- In this study, we addressed this question by analysing sLex expression together with two glycoproteins (BST-2 and LGALS3BP).Concomitant high expression of BST-2 with sLex defined a sub-group of patients with ER-negative tumours displaying higher risks of liver and brain metastasis and a 3-fold decreased survival rate PMID: 27176937
- Studies demonstrate that the interaction Bst-2 and MT1-MMP, actually happens and the cytoplasmic tails, both the N-terminal domain of Bst-2 and the C-terminal domain of MT1-MMP, play crucial roles in the interaction. The interaction between Bst-2 and MT1-MMP is important in MT1-MMP regulating the tetherin activity of Bst-2 and also in Bst-2 regulating the activity of the MT1-MP/proMMP2/MMP2 pathway. PMID: 27240342
- BST-2 and HIV-2 Env proteins interact through their ectodomain but residues involved are not clearly defined. In this study, we demonstrated the importance of the asparagine residue at position 659 in the HIV-2 gp36 ectodomain for the anti-tetherin function. This study also demonstrated the involvement of the HIV-2 Env cytoplasmic tail in this antagonistic role. PMID: 27754450
- results herein demonstrated that IMB-LA could specifically inhibit the degradation of BST-2 induced by Vpu, and impair HIV-1 replication in a BST-2 dependent manner PMID: 26669976
- BST-2 inhibits the the release of Hepatitis B virus particles. [review] PMID: 27396167
- Combining these results suggests an important role for the Ebola virus glycoprotein glycan cap and membrane spanning domain in tetherin antagonism. PMID: 26516900
- BST2 showed significantly elevated plasma levels and overexpression of BST2 in CRC tissues that correlated with poor survival of colorectal cancer patients. PMID: 26494939
- Human parainfluenza virus type 2 V protein antagonizes tetherin by binding it and reducing its presence at the cell surface. PMID: 26675672
- studies suggest that Vpu hijacks the FLNa function in the modulation of tetherin to neutralize the antiviral factor tetherin. PMID: 26742839
- Using viral tethering, amino acid level insights into the function of BST-2 were identified. PMID: 26789136
- BST-2 restricts Hepatitis B virus production at intracellular multivesicular bodies. PMID: 26119070
- results shed light on the interaction between HIV-2 Env and tetherin, suggesting a physical interaction that maps to the ectodomains of both proteins and indicating a strong selection pressure to maintain an anti-tetherin activity in the HIV-2 Env PMID: 26248668
- This study shows that through a targeted regulation of surface BST2, Vpu promotes HIV-1 release and limits plasmacytoid dendritic cells antiviral responses upon sensing of infected cells PMID: 26172439
- The early evolution of antiviral activity together with the high topology conservation but low sequence homology suggests that restriction of virus release is the primary function of tetherin. PMID: 26401043
- Our results suggest that CD317 expression might be of prognostic significance for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia PMID: 25973046
- These findings support BST2 as a genetic susceptibility factor for HIV-1 acquisition by identifying a novel single nucleotide polymorphism association for rs13189798. PMID: 25985399
- Vpu-mediated enhancement of HIV-1 release is uncoupled from Vpu-mediated tetherin degradation. PMID: 25360760
- Our study suggests that the DNA methylation pattern and expression of BST-2 may play a role in disease pathogenesis and could serve as a biomarker for the diagnosis of breast cancer. PMID: 25860442
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network. Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor, GPI-anchor. Membrane raft. Cytoplasm. Apical cell membrane.
-
蛋白家族:Tetherin family
-
组织特异性:Predominantly expressed in liver, lung, heart and placenta. Lower levels in pancreas, kidney, skeletal muscle and brain. Overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells. Highly expressed during B-cell development, from pro-B precursors to plasma cells. Highly exp
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 1119
OMIM: 600534
KEGG: hsa:684
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000252593
UniGene: Hs.118110
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-