CD7
CD7分子是一个含有40 kDa的单链糖蛋白分子,属于免疫球蛋白超家族。CD7分子是人体免疫细胞膜上一类重要的表面标志物,在淋巴细胞发育成熟过程中发挥协同刺激分子受体的作用。作为T细胞表面的高特异性靶点,CD7与大多数T细胞血液肿瘤的发生和发展息息相关,包括幼稚T细胞肿瘤(T-ALL/LBL/NKT细胞白血病)和成熟T细胞肿瘤(外周T细胞淋巴瘤、NKT细胞淋巴瘤、间变大细胞淋巴瘤)。CD7和抗体或者抗体衍生物结合后会迅速内化,这使得针对CD7分子的抗体非常适合作用药物运输工具。CD7分子被认为与疾病侵袭性、耐药性及不良预后密切相关。目前,CD7分子作为靶向抗肿瘤治疗的新靶点,将为CD7+复发/难治性血液系统恶性疾病治疗提供新的研究方向。
Recombinant Human CD7 活性蛋白实验验证数据
SDS-PAGE
(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
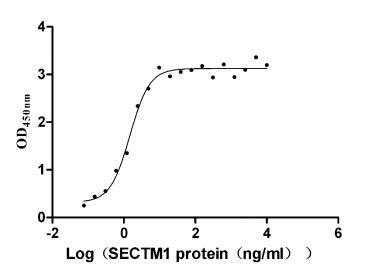
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized CD7 at 5 μg/ml can bind SECTM1 (CSB-MP819898HU), the EC50 is 1.236-1.773 ng/ml.
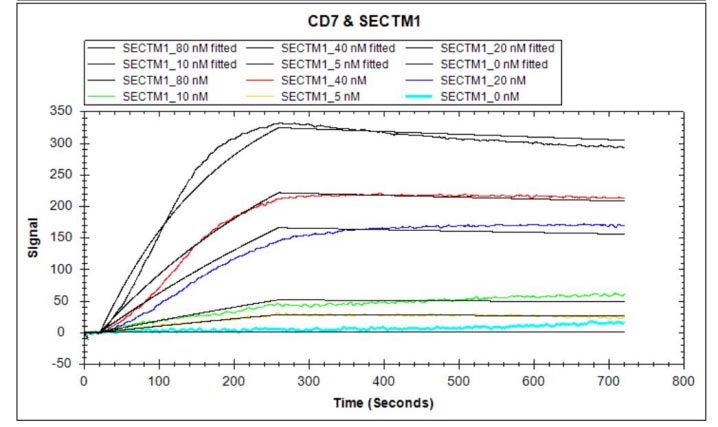
Human CD7 protein hFc and Myc tag (CSB-MP004953HU) captured on COOH chip can bind Human SECTM1 protein hFc tag (CSB-MP819898HU) with an affinity constant of 1.84 nM as detected by LSPR Assay.
CD7 Antibodies
CD7 for Homo sapiens (Human)
| 产品货号 | 产品名称 | 种属反应性 | 应用类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSB-PA004953YA01HU | CD7 Antibody | Human | ELISA, IHC |
| CSB-PA004953YC01HU | CD7 Antibody, FITC conjugated | Human | |
| CSB-PA004953YD01HU | CD7 Antibody, Biotin conjugated | Human | ELISA |
| CSB-PA004953ESR1HU | CD7 Antibody | Human | ELISA, IHC |
| CSB-PA005197 | CD7 Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA |
CD7 Proteins
CD7 Proteins for Mus musculus (Mouse)
| 产品货号 | 产品名称 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|
| CSB-YP004953MO1 CSB-EP004953MO1 CSB-BP004953MO1 CSB-MP004953MO1 CSB-EP004953MO1-B |
Recombinant Mouse T-cell antigen CD7 (Cd7), partial | Yeast E.coli Baculovirus Mammalian cell In Vivo Biotinylation in E.coli |
| CSB-CF004953MO | Recombinant Mouse T-cell antigen CD7 (Cd7) | in vitro E.coli expression system |
CD7 Proteins for Homo sapiens (Human)
| 产品货号 | 产品名称 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|
| CSB-YP004953HU | Recombinant Human T-cell antigen CD7 (CD7), partial | Yeast |
| CSB-EP004953HU | Recombinant Human T-cell antigen CD7 (CD7), partial | E.coli |
| CSB-BP004953HU CSB-EP004953HU-B |
Recombinant Human T-cell antigen CD7 (CD7), partial | Baculovirus In Vivo Biotinylation in E.coli |
| CSB-MP004953HUb1 | Recombinant Human T-cell antigen CD7 (CD7), partial (Active) | Mammalian cell |
| CSB-MP004953HU | Recombinant Human T-cell antigen CD7 (CD7), partial (Active) | Mammalian cell |











