Recombinant Mouse Excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (Slc1a2), partial
Promotion-
中文名称:小鼠Slc1a2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP021433MO
-
规格:¥1836
-
促销:
-
图片:
-
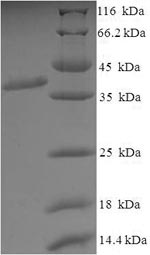
(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
-
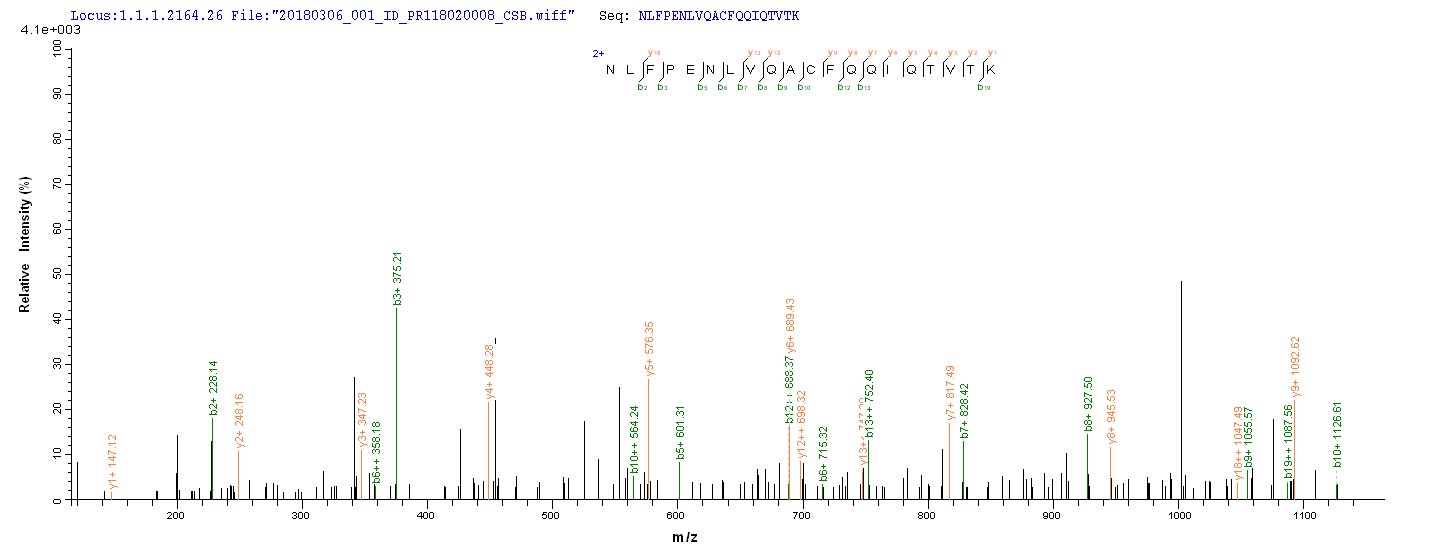
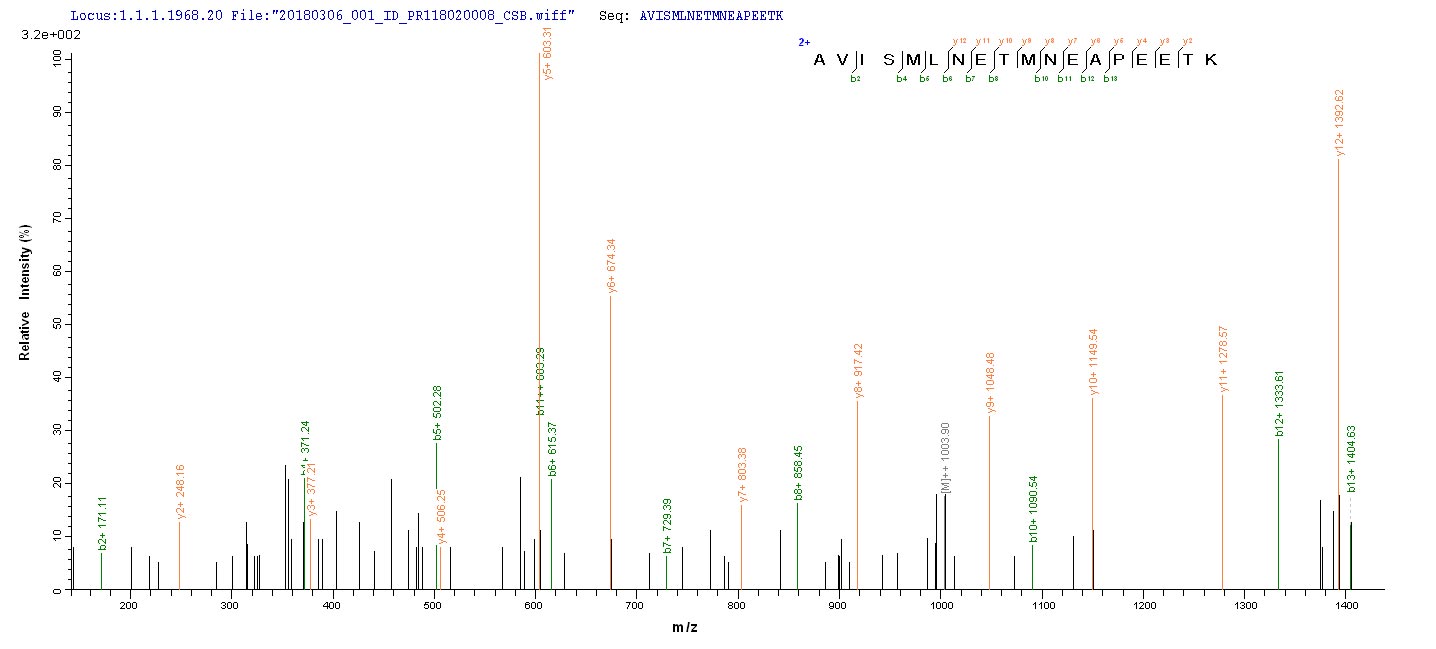
Based on the SEQUEST from database of E.coli host and target protein, the LC-MS/MS Analysis result of CSB-EP021433MO could indicate that this peptide derived from E.coli-expressed Mus musculus (Mouse) Slc1a2.
-
Based on the SEQUEST from database of E.coli host and target protein, the LC-MS/MS Analysis result of CSB-EP021433MO could indicate that this peptide derived from E.coli-expressed Mus musculus (Mouse) Slc1a2.
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Slc1a2; Eaat2; Glt1Excitatory amino acid transporter 2; GLT-1; Sodium-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter 2; Solute carrier family 1 member 2
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:partial
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:37.6kDa
-
表达区域:143-238aa
-
氨基酸序列HPGNPKLKKQLGPGKKNDEVSSLDAFLDLIRNLFPENLVQACFQQIQTVTKKVLVAPPSEEANTTKAVISMLNETMNEAPEETKIVIKKGLEFKDG
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal GST-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Sodium-dependent, high-affinity amino acid transporter that mediates the uptake of L-glutamate and also L-aspartate and D-aspartate. Functions as a symporter that transports one amino acid molecule together with two or three Na(+) ions and one proton, in parallel with the counter-transport of one K(+) ion. Mediates Cl(-) flux that is not coupled to amino acid transport; this avoids the accumulation of negative charges due to aspartate and Na(+) symport. Essential for the rapid removal of released glutamate from the synaptic cleft, and for terminating the postsynaptic action of glutamate.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Selective deletion of GLT1 in the diencephalon, brainstem and spinal cord reproduces the phenotypes (excess mortality, lower body weight, and lethal spontaneous seizure) of the global GLT1 knockout mice. By contrast, dorsal forebrain-specific GLT1 knockout mice showed nonlethal spontaneous seizures at the limited period from P12 to 14 and selective neuronal death in cortical layer II/III and the hippocampus. PMID: 29214672
- Study shows that high-fat feeding induces metabolic disorders and disrupts lactate metabolism in the hippocampus. Glial glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT-1 may contribute to the high-fat diet induced abnormalities of the hippocampal lactate metabolism. PMID: 29051084
- Interaction of the IgG-AQP4 complex with FcgammaRs triggers coendocytosis of the excitatory amino acid transporter 2. PMID: 28461494
- GLT1 deletion in spinal cord causes motor deficits. GLT1 deletion in spinal cord induces spinal motor neuron loss. GLT1 deletion in spinal cord induces gliosis in the ventral horn. PMID: 29458024
- s demonstrated that the upregulation of GLT1 corrected Purkinje cell firing and motor incoordination in myotonic dystrophy. PMID: 28658620
- suggest that VGluT2 and GLT-1 may be differentially involved in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis via abnormal glutamate homeostasis at the presymptomatic stage and end stage of disease, respectively PMID: 28526579
- Immunoreactivity of vGluT1 in continuous theta-burst stimulation (iTBS; cTBS) repeated session (RS) decreased, while GLT-1 increased in cTBS SS and cTBS RS, compared to control PMID: 27623095
- Decreased glial and synaptic glutamate uptake due to low GLT-1 expression has been found in the striatum of HIV-1 gp120 transgenic mice. PMID: 26567011
- interactions of NF-kappaB and N-myc with GLT-1/EAAT2 promoter sequences was significantly elevated in the ipsi-lateral cortex of both adult and old Traumatic brain injury mice. PMID: 26081154
- infection of co-cultures with shRNA directed against recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J, a Notch effector, also reduces endothelia-dependent increases in enhanced green fluorescent protein and GLT-1 PMID: 28771710
- Mutation of the caspase-3 cleavage site in the astroglial glutamate transporter EAAT2 delays disease progression and extends lifespan in the SOD1-G93A mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis PMID: 28342750
- The upregulation of GLT-1 induced by transplanted neural precursor cells was found to rely on the secretion of VEGF by neural precursor cells PMID: 27733606
- We demonstrate that the R6/1 transgenic mouse model of HD has lower basal levels of cystine, and showed depressive-like behaviors in the forced-swim test. Administration of NAC reversed these behaviors. This effect was blocked by co-administration of the system xc(-) and GLT-1 inhibitors CPG and DHK, showing that glutamate transporter activity was required for the antidepressant effects of NAC PMID: 27179791
- Consistent with glutamate dysregulation, analysis of neurons reveal changes in morphology including a reduction in dendritic spines, VGlut1 and NeuN immunoreactivity PMID: 27281462
- A significant initial increase in dorsal hippocampal GLT1 immunoreactivity and protein levels were observed 1day post epilepsy and followed by a marked downregulation at 4 and 7days post epilepsy with a return to near control levels by 30days post epilepsy. PMID: 27155358
- These results demonstrate that focal restoration of GLT1 expression in the superficial dorsal horn is a promising target for treating chronic neuropathic pain following SCI. PMID: 26496514
- Lipid raft integrity, ensured by DHCR24, plays a crucial role in the ischemic brain by guaranteeing EAAT2-mediated uptake of glutamate excess. PMID: 26628388
- Findings suggest that focal restoration of glutamate transporter 1,expression in astrocytes of the cervical spinal cord using adeno-associated virus delivery is not an effective therapy for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PMID: 25818008
- we have demonstrated for the first time that DOR receptor activation induces astrocytic expression of EAAT1 and EAAT2 PMID: 25052197
- neuronal GLT-1 but not astrocytic GLT-1 contributed significantly to glutamate uptake. astrocytic GLT-1 performs critical functions required for normal weight gain, resistance to epilepsy, and survival. PMID: 25834045
- data indicate that the surface expression and function of EAAT2b can be rapidly modulated through the disruption of its interaction with DLG1 by CaMKII activation. PMID: 25834051
- Inhibition of L-glutamate transport reveals increases in EAAt2 cell surface expression in astrocytes. PMID: 24095695
- results provide evidence that disrupting glutamate transporter GLT-1 in habenular astrocytes increases neuronal excitability and depressive-like phenotypes in behaviors and sleep. PMID: 25471567
- Results show that a fraction of EAAT2 undergoes SUMO1 conjugation under physiological conditions; sumoylated EAAT2 localizes to intracellular compartments, whereas non-sumoylated EAAT2 resides on the plasma membrane PMID: 24753081
- conclude that the association between GLT-1 and mitochondria is modest, is driven by synaptic activity and dependent on polymerized actin filaments. PMID: 24814819
- IL-1beta treatment of AEG-1-overexpressing astrocytes significantly lowered expression of excitatory amino acid transporter 2 PMID: 24855648
- Study suggests that there is a remarkable subcellular heterogeneity of GLAST and GLT-1 expression in the developing hippocampus PMID: 23939750
- GLT1 overexpression exacerbates neuronal damage and increases respiratory impairment following cervical spinal cord injury. PMID: 24872566
- TBI affects expression of Kir4.1 and GLT-1 genes in age- and time dependent manner and it may lead to accumulations of more K(+) and glutamate early in the synapse of old mice as compared to adult PMID: 24026668
- Pharmacological enhancement of EAAT2 translation may be a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. PMID: 24569372
- GLT-1 plays a role in glutamate homeostasis in the neocortex PMID: 24224925
- Proteome analysis and conditional deletion of the EAAT2 glutamate transporter provide evidence against a role of EAAT2 in pancreatic insulin secretion in mice. PMID: 24280215
- Unitary current amplitudes of EAAT5 anion channels turned out to be approximately twice as high as single-channel amplitudes of GLT-1c. PMID: 24307171
- FMRP positively regulates translational expression of mGluR5 in astroglial cells, and FMRP-dependent down-regulation of mGluR5 underlies GLT1 dysregulation in fmr1(-/-) astrocytes PMID: 23396537
- EAAT2 expression in astrocytes, regulated by adenosine signaling, controls ethanol drinking in mice. PMID: 23032072
- Astrocyte GLT1 plays a role in limiting secondary cell death following spinal cord injury; compromise of key astrocyte functions has significant effects on outcome following traumatic spinal injury. PMID: 21882244
- Amyloid-beta peptide Abeta1-42 markedly prolongs the extracellular lifetime of synaptically released glutamate by reducing GLT-1 surface expression in mouse astrocytes. PMID: 23516295
- Data indicate that direct miR-124a transfection significantly and selectively increases protein expression levels of GLT1 in cultured astrocytes. PMID: 23364798
- GLT-1 activation appears to play a key role in the preventive effect of beta-lactam antibiotics on cannabinoid tolerance. PMID: 21536061
- These findings demonstrate that GltI and Glast negatively regulate calcium-dependent proliferation in vitro and that their upregulation after injury is associated with decreased proliferation after brain trauma. PMID: 22092549
- Spatial and temporal alterations in GLT1 expression observed after spinal cord injury result from both astrocyte death and gene expression changes in surviving astrocytes. PMID: 21488085
- glutamine synthetase was coexpressed with GLT-1 in islets, which suggests that, as with liver and brain, one possible role of GLT-1 in the pancreas is to support glutamine synthesis PMID: 22114258
- Evidence against cellular internalization in vivo of NMO-IgG, aquaporin-4, and excitatory amino acid transporter 2 in neuromyelitis optica. PMID: 22069320
- This study demonistrated that in cerebral ischemia in mice down regulation the GLT-1. PMID: 21911209
- deficits in lgt1 function compound the effects of familial amyloid-beta protein precursor and presenilin-1 mutant transgenes in younger animals and thus may contribute to early occurring pathogenic processes associated with Alzheimer's disease PMID: 21677376
- These data imply a glutamate cycle in which glutamate is carried into the granules by VGLUT3 and carried out by EAAT2. PMID: 21853059
- GLT1 is a new player in glutamate homeostasis and signaling in the islet of Langerhans; beta-cells critically depend on its activity to control extracellular glutamate levels and cellular integrity PMID: 21335552
- these results suggest that A1 receptor-mediated signaling regulates EAAT2 expression in astrocytes. PMID: 21291865
- Early treatment with ceftriaxone prior to the onset of epilepsy increased expression of astrocyte glutamate transporters, decreased extracellular glutamate levels, neuronal death, and seizure frequency, and improved survival in Tsc1(GFAP)CKO mice. PMID: 20045054
- SOD1-G93A transgene and HO-1 are preferentially over-expressed in the lumbar spinal cord and GLT-1 are down-regulated. PMID: 20303959
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Dicarboxylate/amino acid:cation symporter (DAACS) (TC 2.A.23) family, SLC1A2 subfamily
-
组织特异性:Detected in brain. Detected in embryonic forebrain, especially in globus pallidus, perirhinal cortex, lateral hypothalamus, hippocampus, and on fimbria and axonal pathways connecting the neocortex, basal ganglia and thalamus (at protein level). Isoform GL
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:20511
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000079100
UniGene: Mm.267547
Most popular with customers
-
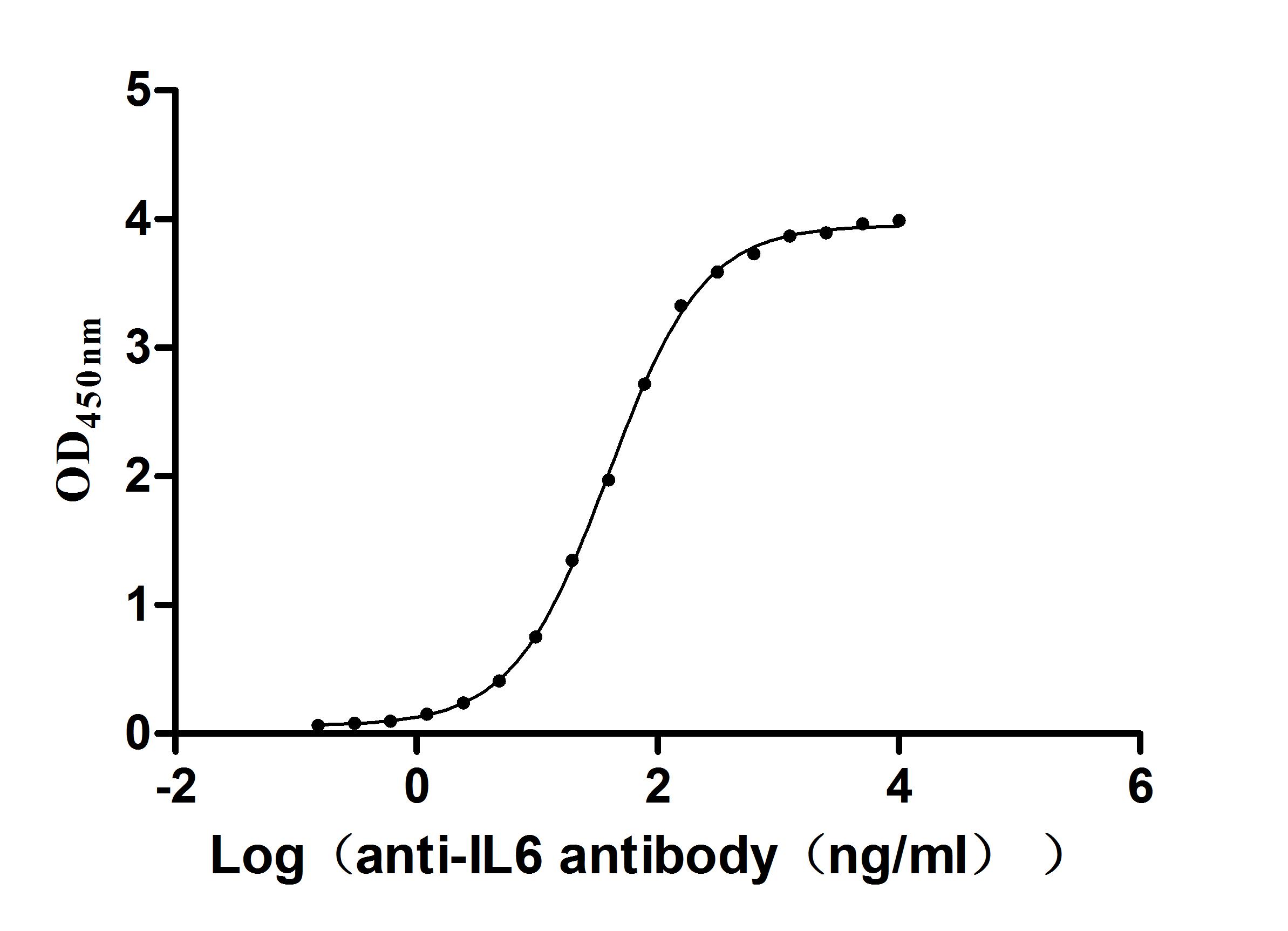
Recombinant Human Semaphorin-4D (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
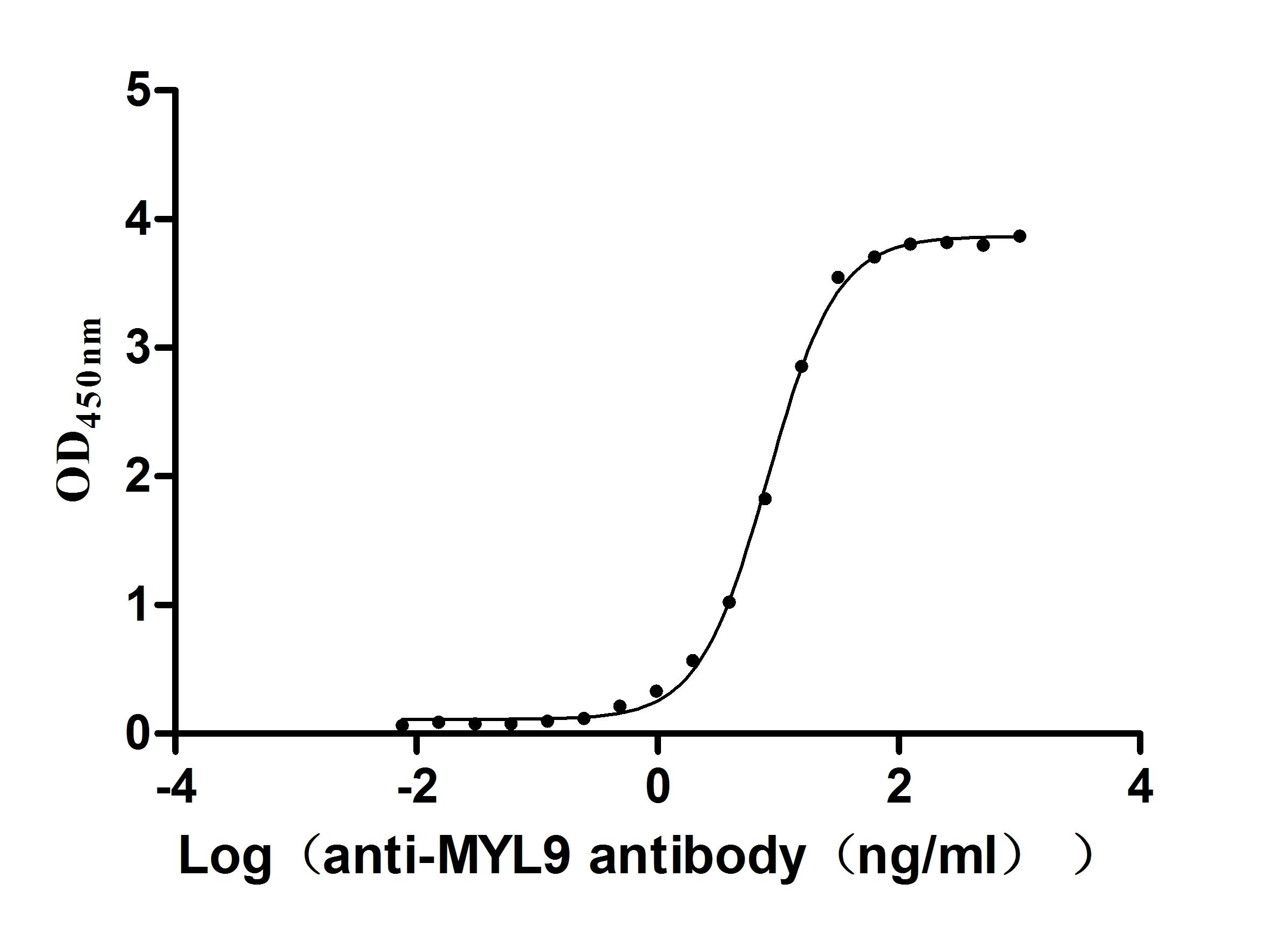
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B(MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
-
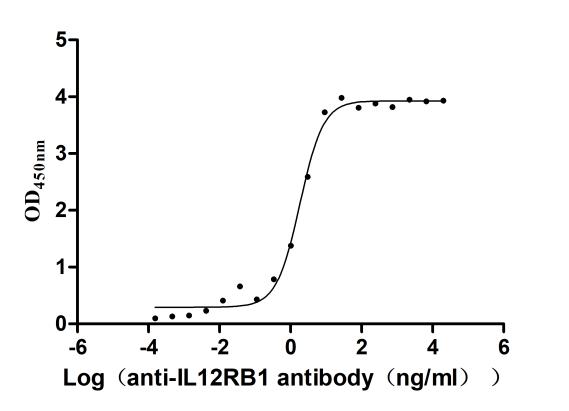
Recombinant Human Interleukin-12 receptor subunit beta-1(IL12RB1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)