Recombinant Mouse Syndecan-4 (Sdc4)
-
货号:CSB-CF020891MO
-
规格:
-
来源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
其他:
产品详情
-
基因名:Sdc4
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Sdc4; Syndecan-4; SYND4; Ryudocan core protein
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:24-198
-
氨基酸序列ESIRETEVIDPQDLLEGRYFSGALPDDEDAGGSDDFELSGSGDLDDTEEPRPFPEVIEPLVPLDNHIPENAQPGIRVPSEPKELEENEVIPKRAPSDVGDDMSNKVSMSSTAQGSNIFERTEVLAALIVGGVVGILFAVFLILLLVYRMKKKDEGSYDLGKKPIYKKAPTNEFYA
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Cell surface proteoglycan that bears heparan sulfate. Regulates exosome biogenesis in concert with SDCBP and PDCD6IP.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- SDC4 antagonizes the activation of RIG-I in a CYLD-mediated deubiquitination-dependent process, thereby balancing antiviral signalling to avoid deleterious effects on host cells. PMID: 27279133
- Cell-extracellular matrix and cell-cell adhesion are linked by syndecan-4. PMID: 27751945
- Syndecan-4 is essential for the compensated hypertrophy and the maintenance of cardiac function during the process of heart failure following pressure overload. PMID: 28395201
- This study demonstrates that the shedding of synd4 from Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) plays a key role in advanced glycation end products-mediated dysfunction of EPC migration and homing. PMID: 27662820
- Syndecan-4 therapy also induces a marked immunomodulation in the tissues, increasing the polarization of macrophages toward the M2 phenotype. PMID: 26891081
- SDC4 thus controls flow-induced lymphatic endothelial cell polarization via regulation of VANGL2 expression. PMID: 27789626
- loss of N-sulfation leads to the disruption of the pattern of distribution of Sdc-4 within the glomeruli of Ndst1-/- mutants PMID: 26936875
- Sdc4 has been identified as a mycobacterial attachment receptor on alveolar epithelial cells. PMID: 27279134
- Synd4 shedding from vascular endothelial cells played an important role in the diabetes-related impairment of angiogenesis. PMID: 27018253
- the present study demonstrated that synd4 was involved in the chemotactic migration of ECs in vitro and in vivo. PMID: 27541034
- Shedding of syndecan-4 promotes immune cell recruitment and mitigates cardiac dysfunction after lipopolysaccharide challenge in mice. PMID: 26449522
- SDC4 plays an important role in asthma induction. Disturbed SDC4 signalling leads to an impaired motility and directional migration of antigen-presenting dendritic cells. PMID: 26165408
- Syndecan-4 exerts a dual role in collagen cross-linking, one involving its cytosolic domain and calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T-cells signalling leading to collagen PMID: 25587045
- Locally generated Sdc4 may play a role in regulating TRPC6 channels, and may contribute to glomerular pathology. PMID: 26193076
- Sdc4 contributes to the development of collagen induced arthritis by promoting germinal center formation and autoantibody production through its regulation of SDF-1-mediated B cell migration. PMID: 25989265
- binding interaction between syndesmos and syn4(cyto) was characterized as a low-affinity interaction (Kd = 62 muM) by surface plasmon resonance and nuclear magnetic resonance PMID: 26100207
- the crucial role of SDC-4 for neuron density, neurite length, and branches. PMID: 25757361
- SDC4 participates in amelogenesis, and FGF10 may modulate dental epithelial cell behaviors through the regulation of SDC4 expression. PMID: 25174688
- Data show that endothelial cells (ECs) from the thoracic aortas of syndecan 4 (S4-/-) mice were poorly aligned in the direction of the flow. PMID: 25404299
- Sdc4 is required for cell surface targeting of transglutaminase 2 and the development of kidney fibrosis in chronic kidney disease. PMID: 24357671
- The results indicate that syndecan-4 may play an important role in beta-cell function and that the cell-surface HS proteoglycans may be the missing link to maintaining islet longevity after isolation. PMID: 22872317
- Results indicate that the DC-HIL/syndecan-4 (SD-4) pathway regulates autoimmune responses by mediating the T cell suppressor function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). PMID: 24516197
- Angiopoietin-2 secretion by endothelial cell exosomes: regulation by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and syndecan-4/syntenin pathways. PMID: 24235146
- Sdc4 has a dynamic expression pattern during development and is detected in tissues, including the neural tube during and following closure, the hindgut and the cochlea. Co-expression with Vangl2 is consistent with a possible role for Sdc4 in Wnt/PCP signaling during morphogenesis. PMID: 23760952
- PGE2-induced activation of angiogenesis is mediated via syndecan-4-dependent activation of PKCalpha. PMID: 23525101
- syndecan-4 is important for the differentiation of cardiac fibroblasts into myofibroblasts in the pressure-overloaded heart. PMID: 23178899
- A deletion or knockdown of the Syndecan 4 effector molecule PKCalpha led to a similar reduction in phosphorylation of Thr308 while overexpression of myristoylated PKCalpha rescued AktThr308 phosphorylation in endothelial cells lacking Syndecan 4. PMID: 22975683
- Alpha-actinin interaction with syndecan-4 has a role in stabilising cell-matrix adhesion. PMID: 22940199
- Our results demonstrate that syndecan 4 is functionally involved in endochondral ossification and that its loss impairs fracture healing, due to inhibition of compensatory mechanisms under inflammatory conditions. PMID: 23233348
- Arf6 is responsible for alpha5beta1-integrin recycling and thereby completes the cycle of syndecan-4-regulated integrin trafficking. PMID: 22790193
- SD-4, as the T-cell ligand of DC-HIL, is a potent inhibitor of allo-reactive T cells responsible for GVHD and a potentially useful target for treating this disease. PMID: 23113638
- Macrophages and epithelial cells treated with LPS had increased expression of syndecan-4. PMID: 22427536
- Reduced Syndecan-4 is associated with severe colitis in IL-10 knockout mice. PMID: 21987406
- Syndecan-4 is essential for development of concentric myocardial hypertrophy via stretch-induced activation of the calcineurin-NFAT pathway PMID: 22164265
- The proteoglycan syndecan 4 regulates transient receptor potential canonical 6 channels via RhoA/Rho-associated protein kinase signaling in glomerular permeability. PMID: 22155451
- Interception of the Sdc4 pathway enhances infarct expansion and hypertrophic remodelling during early infarct healing in ischaemic-reperfusion injury. PMID: 21632883
- Disruption of syndecan-4 or caveolin, gene disruption of RhoG in mice was found to retard closure of dermal wounds due to a migration defect of the fibroblasts and keratinocytes of RhoG null mice. PMID: 21982645
- inhibits T-cell activation by employing CD148 protein tyrosine phosphatase activity PMID: 21469128
- Syn4 plays an important role in the inflammatory response and granulation tissue formation, thereby preventing cardiac rupture and dysfunction after myocardial infarct PMID: 21493899
- Syn4 deficiency limits neointimal formation after vascular injury by regulating vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and vascular progenitor cell mobilization. PMID: 21330609
- A new houttuyfonate derivative can inhibit the proliferation of NIH3T3 cell and the expression of syndecan-4 protein induced by TNF-alpha in vitro. PMID: 20518314
- RGD-independent cell adhesion via a tissue transglutaminase 2-fibronectin matrix promotes fibronectin fibril deposition and requires syndecan-4/2 and {alpha}5{beta}1 integrin co-signaling. PMID: 20929862
- Loss of syndecan-4 do not organize alpha-smooth muscle actin into bundles. PMID: 20154082
- demonstrate the ability of syndecan-4 molecules to support cell attachment and spreading without the direct extracellular binding of integrins PMID: 20080785
- Syndecan4 has a role in regulation of microvascular homeostasis by carrying heparan sulfate PMID: 12074629
- role of syndecan-4 in focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation PMID: 12087088
- Syndecan-4 mRNA transcripts are expressed by reactive astrocytes in the region surrounding the necrotic brain tissue, exhibiting peak levels at day 7 after cryo-injury. PMID: 12112370
- enhanced syndecan-4 expression in mouse cardiac endothelial cells results in preferential augmentation of fibroblast growth factor 2 but not VEGF-A(165)-induced NO release PMID: 12543640
- This protein is synthesized together with syndecan 1 by mouse mammary gland epithelial cells and bears heparan sulfate chains that are apparently structurally indistinguishable. PMID: 12571251
- augmentation of TGF-beta function by induced syndecan-4 was suggested as a mechanism of the suppressive action of syndecan-4 against endotoxin shock PMID: 12975610
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Syndecan proteoglycan family
-
组织特异性:Ubiquitous. Highest levels in liver, kidney and lung.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:20971
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000017153
UniGene: Mm.3815
Most popular with customers
-
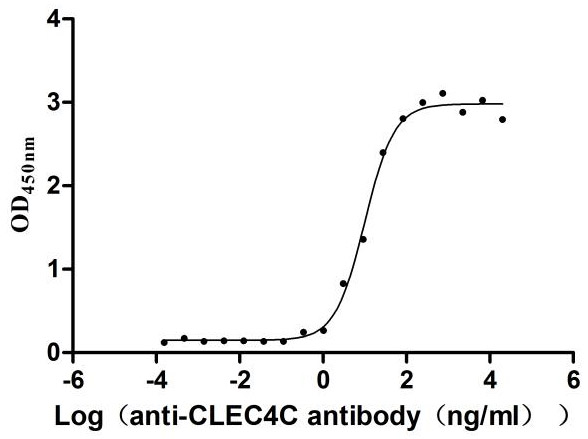
Recombinant Human C-type lectin domain family 4 member C (CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
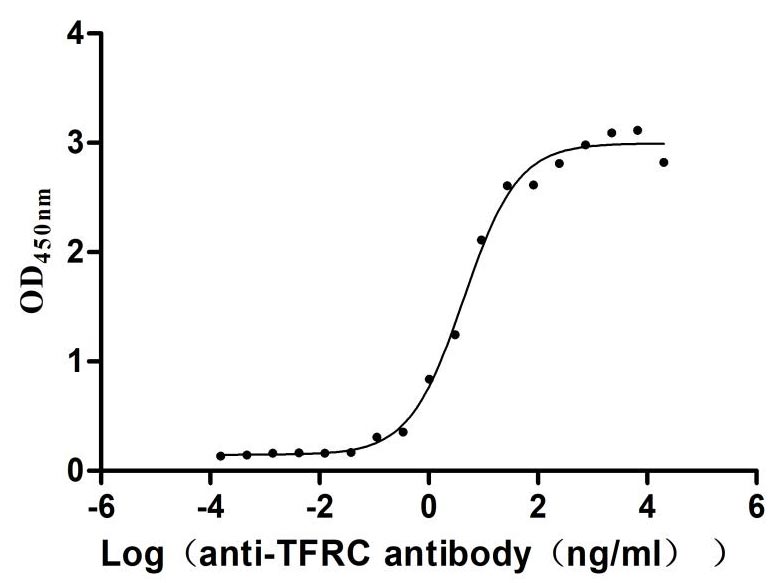
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
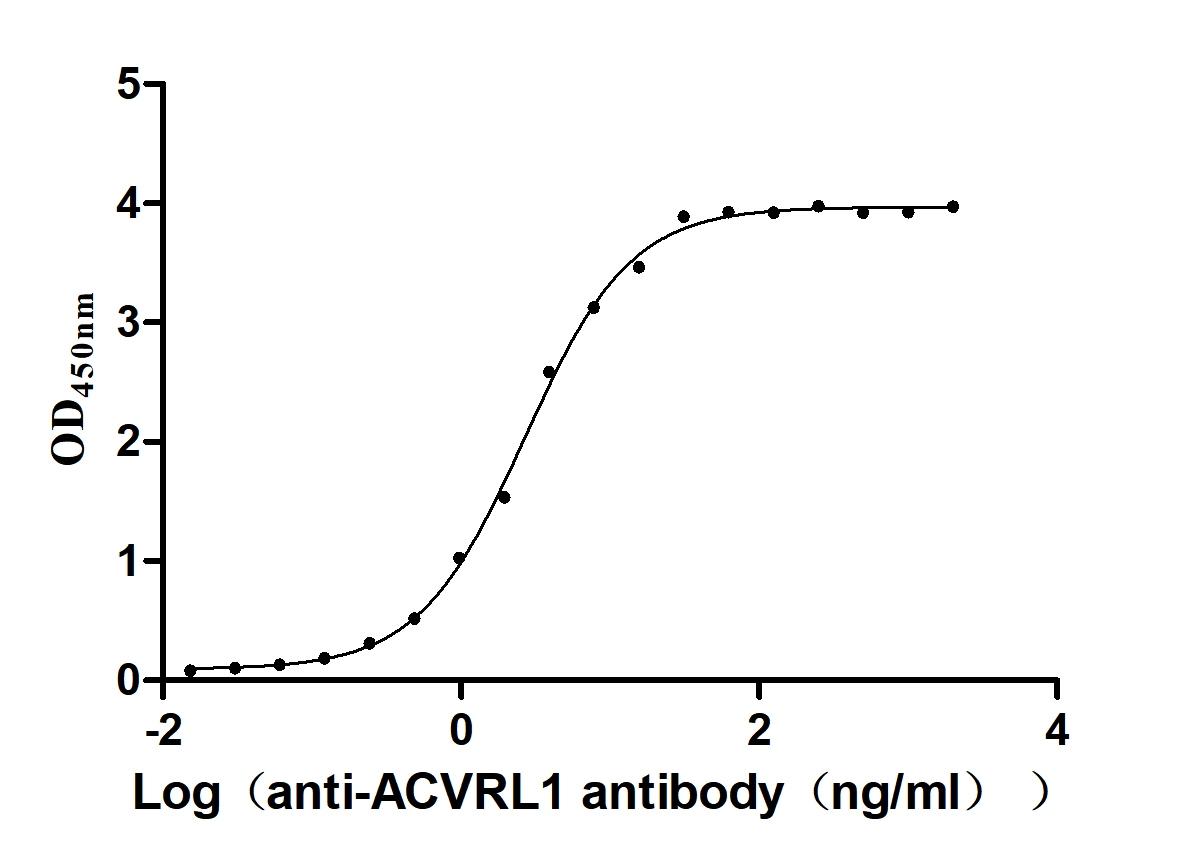
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
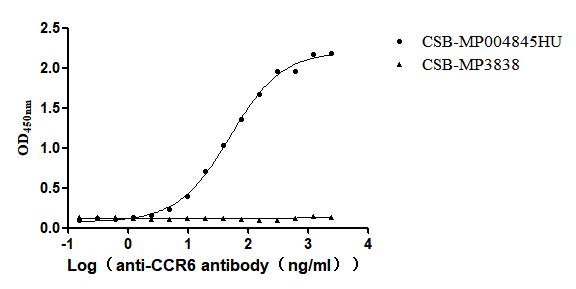
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)