Recombinant Mouse Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (Srebf1)
-
货号:CSB-CF896228MO
-
规格:
-
来源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
其他:
产品详情
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Srebf1; Srebp1; Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; SREBP-1; Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-480
-
氨基酸序列MDELAFGEAALEQTLAEMCELDTAVLNDIEDMLQLINNQDSDFPGLFDAPYAGGETGDTG PSSPGANSPESFSSASLASSLEAFLGGPKVTPAPLSPPPSAPAALKMYPSVSPFSPGPGI KEEPVPLTILQPAAPQPSPGTLLPPSFPAPPVQLSPAPVLGYSSLPSGFSGTLPGNTQQP PSSLPLAPAPGVLPTPALHTQVQSLASQQPLPASAAPRTNTVTSQVQQVPVVLQPHFIKA DSLLLTAVKTDAGATVKTAGISTLAPGTAVQAGPLQTLVSGGTILATVPLVVDTDKLPIH RLAAGSKALGSAQSRGEKRTAHNAIEKRYRSSINDKIVELKDLVVGTEAKLNKSAVLRKA IDYIRFLQHSNQKLKQENLTLRSAHKSKSLKDLVSACGSGGGTDVSMEGMKPEVVETLTP PPSDAGSPSQSSPLSFGSRASSSGGSDSEPDSPAFEDSQVKAQRLPSHSRGMLDRSRLAL
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Precursor of the transcription factor form (Processed sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1), which is embedded in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Low sterol concentrations promote processing of this form, releasing the transcription factor form that translocates into the nucleus and activates transcription of genes involved in cholesterol biosynthesis and lipid homeostasis.; Key transcription factor that regulates expression of genes involved in cholesterol biosynthesis and lipid homeostasis. Binds to the sterol regulatory element 1 (SRE-1) (5'-ATCACCCCAC-3'). Has dual sequence specificity binding to both an E-box motif (5'-ATCACGTGA-3') and to SRE-1 (5'-ATCACCCCAC-3'). Regulates the promoters of genes involved in cholesterol biosynthesis and the LDL receptor (LDLR) pathway of sterol regulation.; Isoform expressed only in select tissues, which has higher transcriptional activity compared to SREBP-1C. Able to stimulate both lipogenic and cholesterogenic gene expression. Has a role in the nutritional regulation of fatty acids and triglycerides in lipogenic organs such as the liver. Required for innate immune response in macrophages by regulating lipid metabolism.; Predominant isoform expressed in most tissues, which has weaker transcriptional activity compared to isoform SREBP-1A. Primarily controls expression of lipogenic gene. Strongly activates global lipid synthesis in rapidly growing cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Adenosine 2A receptor (AZAR) can directly suppress hepatocyte fat deposition, which is attributable to the effects of A2AR on repressing SREBP1c expression under fasted states and on suppressing SREBP1c transcription activity. PMID: 29315766
- our findings suggest that Cidea is highly associated with alcoholic fatty liver disease and Cidea expression is specifically induced by acetaldehyde, and this up-regulation is most likely mediated by SREBP1c. PMID: 29352167
- disruption of SREBP-1a phosphorylation resulted in massive alteration of cellular processes, including signs for loss of targeting lipid pathways. PMID: 29587401
- Depletion of SREBP-1 had no impact on liver IRS1Y612, AktS473, and downstream effectors GSK3alphaS21 and FoxO1S256 during the fed state. Reduced levels of these molecules were observed under fasting conditions. The contribution of SREBP-1 to maintain insulin signal transduction in liver is modest. PMID: 29723221
- Data (including data from studies in transgenic/knockout mice) suggest that Kdm1a-mediated attenuation of Srebf1 transcriptional activities functions as underlying mechanism for suppression of de novo lipogenesis by oxidative stress in white adipose tissue. [Kdm1a = lysine (K)-specific demethylase-1A; Srebf1 = sterol-regulatory element-binding transcription factor-1] PMID: 29618580
- Tlr4-mutant mice are resistant to acute alcohol-induced hepatic SREBP-1 activation and hepatic lipid accumulation. PMID: 27627966
- LncARSR promotes hepatic lipogenesis via Akt/SREBP-1c pathway and contributes to the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. PMID: 29555473
- Results showed that Glrx(-/-) mice exhibited decreased SirT1 activity that leads to hyperacetylation and activation of SREBP-1 and upregulation of key hepatic enzymes involved in lipid synthesis. PMID: 27958883
- Inhibition of NAMPT aggravates high fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in mice through regulating Sirt1/AMPKalpha/SREBP1 signaling pathway. PMID: 28449683
- SREBP1 is dramatically reduced in dysbindin-1 knockout mice; possibly related to cognitive deficits. PMID: 26873854
- Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling enhances miR-29 expression in glioblastoma cells via upregulation of Sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 PMID: 27477273
- The expression of hHL promoted hepatic triglyceride accumulation and de novo lipogenesis without affecting triglyceride secretion, and this was associated with an upregulation of Srebf1 as well as the main genes controlling the synthesis of fatty acids. Transgenic mice also exhibited more adiposity and an increased LPL-mediated FFA influx into the WAT without affecting glucose tolerance PMID: 29244870
- Data show that miR-200b and miR-200c could directly bind the 3' UTR of JUN, and JUN activated the transcription of srebp1 to increase lipid accumulation. PMID: 27166182
- a novel role for SREBP-1 as a cell surface retention factor for TbetaRI in mesangial cells, is reported. PMID: 27826032
- Srebp1c is a key regulator of metabolic remodeling leading to the beneficial effects of caloric restriction. PMID: 28256090
- The present study indicates a requirement for C/EBPbeta in the insulin-mediated induction of SREBP-1c mRNA expression in rodent liver. Coupled with previous data showing that this induction requires LXRalpha, our data reported herein indicate a requirement for both transcription factors. PMID: 27382175
- The deletion of Srebf-2 and subsequent lower sterol synthesis in hepatocytes eliminated the production of an endogenous sterol ligand required for LXR activity and SREBP-1c expression. PMID: 28244871
- The fasting-induced transcription factor KLF15, a key regulator of gluconeogenesis, forms a complex with LXR/RXR, specifically on the Srebf1 promoter. PMID: 27545894
- Exposure to a xenobiotic during early development induced persistent fat accumulation via hypomethylation of lipogenic genes. Moreover, increased Nrf2 recruitment to the Srebp-1c promoter in livers of BPA-exposed mice was observed. PMID: 28796629
- suggesting a specific effect of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c on neurosteroidogenesis PMID: 28467654
- Transforming growth factor-beta activated kinase 1 (TAK1) regulation of sterol-regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) critically contributes to the maintenance of liver homeostasis to prevent steatosis, which is a potentially important mechanism to prevent hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. PMID: 26973245
- miR-185 negatively regulates the differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells by targeting SREBP-1 PMID: 28701079
- SREBP1 pathway plays an important role in hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. PMID: 28027595
- In hepatocytes, E4BP4 interacts with nuclear SREBP-1c to preserve its acetylation, and subsequently protects it from ubiquitination-dependent degradation PMID: 27252523
- SREBP1 also contributes to the resolution phase of TLR4-induced gene activation by reprogramming macrophage lipid metabolism. PMID: 28041958
- 27OH is not an important regulator of Srebp- or LXR regulated genes under basal conditions in mouse liver PMID: 26851362
- Collectively, these findings demonstrate that LXRalpha activation induces 17beta-HSD13 expression in a SREBP-1c-dependent manner. PMID: 28270440
- These results demonstrate that HDAC3 and SCAP control symbiotic pathways of liver lipid metabolism that are critical for suppression of lipotoxicity. PMID: 27866836
- data indicate that ATF4 regulates SREBP1c expression to control fatty acids synthesis PMID: 27452504
- luteolin can abolish lipid accumulation induced by LXR-SREBP-1c activation both in vivo and in vitro PMID: 27888103
- results identify PLIN2 as a determinant of global changes in the hepatic lipidome and suggest the hypothesis that these actions contribute to SREBP-regulated de novo lipogenesis involved in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PMID: 27679530
- the synergistic action of ChREBP and SREBP-1c is necessary for the maximal induction of Elovl6 expression in the liver. PMID: 27524233
- observations suggest that MALAT1 promotes hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance by increasing nuclear SREBP-1c protein stability. PMID: 26935028
- Advanced glycation end products overproduction in mice liver and skeletal muscle is associated to increased lipogenesis due to the activation of SREBP-1c. PMID: 26721591
- Srebp-1 interacts with c-Myc, facilitates its binding to downstream pluripotent targets. PMID: 26388522
- SREBP1a or -1c could be acting as transcriptional repressors for rarg2 and when srebf1a expression is down-regulated, its repressing activity disappears. PMID: 26271478
- SREBP-2 is critical for survival and limb patterning during development PMID: 26685326
- The two cereal dietary fibers potently decreased protein expressions of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 and key factors involved in lipogenesis PMID: 26510459
- regulatory mechanism by which insulin inhibits cardiac UCP3 expression through activation of the lipogenic factor SREBP-1. PMID: 26555260
- Mice lacking sterol regulatory element-binding factor-1c (Srebf1c) have blunted peripheral nerve fatty acid synthesis that results in development of peripheral neuropathy. PMID: 25817536
- Taken together, our results suggest that an NCE-box within the clusterin promoter is necessary for insulin-stimulated hepatic expression of clusterin via SREBP-1c. PMID: 26282207
- both Smad3 and SREBP-1a activation cooperatively regulate TGFbeta transcriptional responses. PMID: 25348957
- Endoplasmic reticulum stress and SREBP-1-dependent effects were induced in glomeruli of angiotensin II-infused mice. PMID: 25398788
- Data show that knock-in (KI) mice in which a human miR-33b is inserted within sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (Srebf1) intron had reduced HDL cholesterol (HDL-C). PMID: 24931346
- CREB regulated transcription coactivator 2 (CRTC2) functions as a mediator of mTOR signalling to modulate COPII-dependent SREBP1 processing PMID: 26147081
- Thyrotropin increases hepatic triglyceride content through upregulation of SREBP-1c activity. PMID: 25016220
- Hepatic genes expression profiles demonstrated that LBP can activate the phosphorylation of AMPK, suppress nuclear expression of SREBP-1c, and decrease protein and mRNA expression of lipogenic genes in vivo or in vitro PMID: 25013763
- Fucoidan from Acaudina molpadioides suppressed the mRNA expressions of SREBP-1c, C/EBPa and PPARg in mice. PMID: 24847504
- Data show that liver X receptor (LXR) agonist TO901317 increases hepatic fatty acid desaturation via induction of stearoyl CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1) expression in an LXRalpha-dependent and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP1c)-mediated manner. PMID: 23945440
- studies indicate that DEC1 is an important regulator of Srebp-1c expression and links circadian rhythm to hepatic lipogenesis. Activation of Dec1 can alleviate the nonalcoholic fatty liver phenotype PMID: 24993831
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:[Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1]: Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Golgi apparatus membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle, COPII-coated vesicle membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.; [Processed sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1]: Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:SREBP family
-
组织特异性:[Isoform SREBP-1C]: Predominant isoform expressed in most tissues. Predominates in liver, adrenal gland, brain and adipose tissue. Also found in kidney, thymus, testis, muscle, jejunum, and ileum.; [Isoform SREBP-1A]: Expressed only in select tissues, suc
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:20787
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000020846
UniGene: Mm.278701
Most popular with customers
-
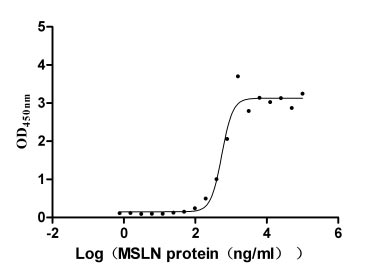
Recombinant Human Mucin-16 (MUC16), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
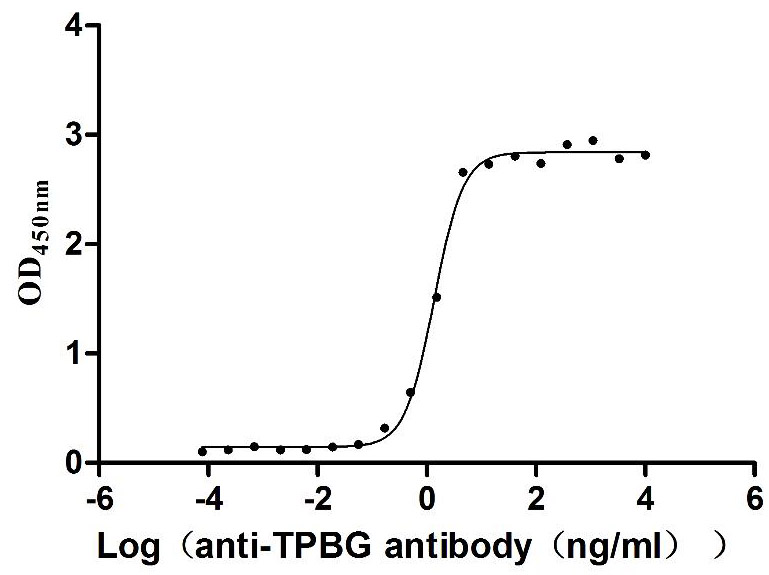
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
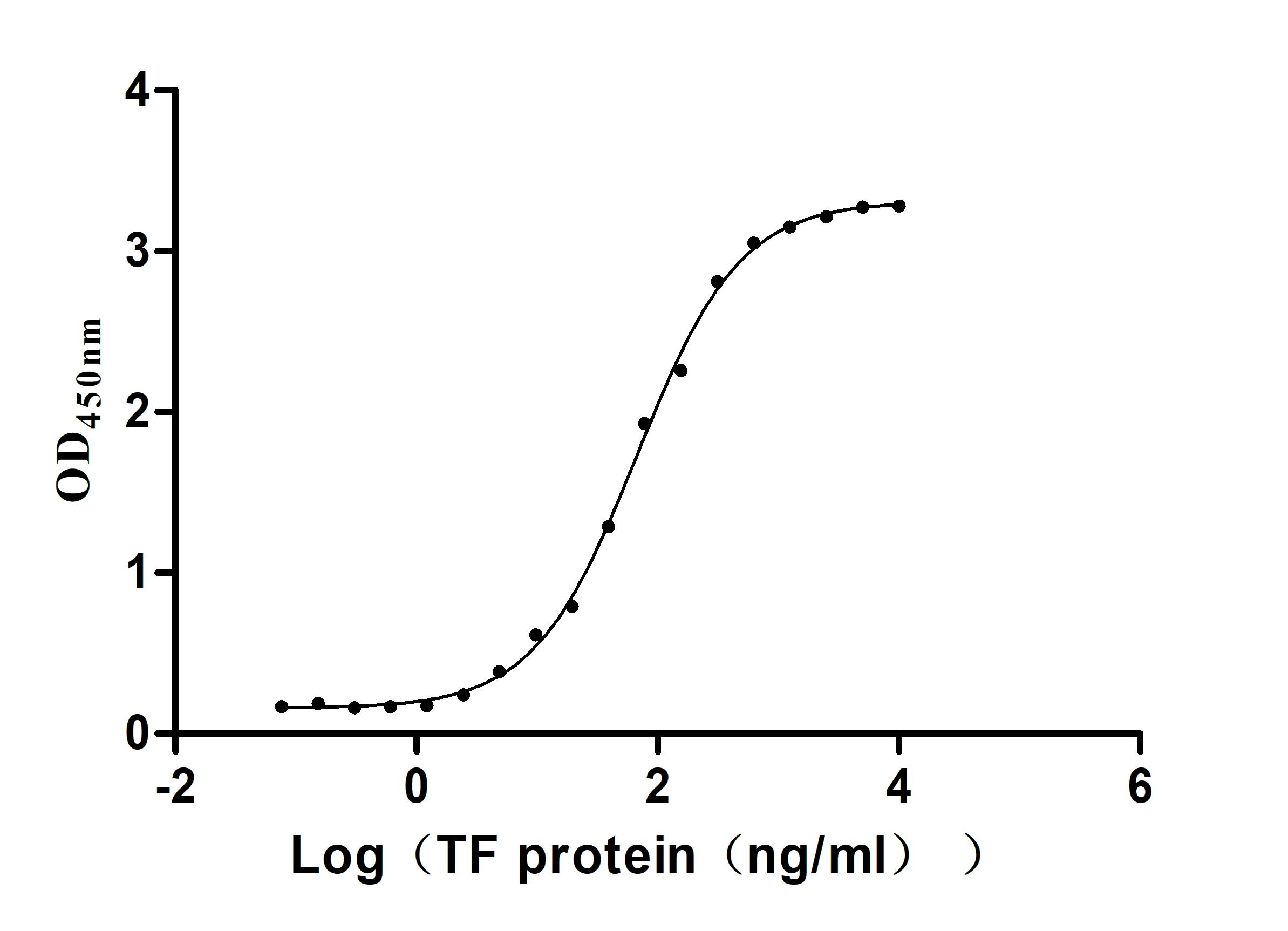
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
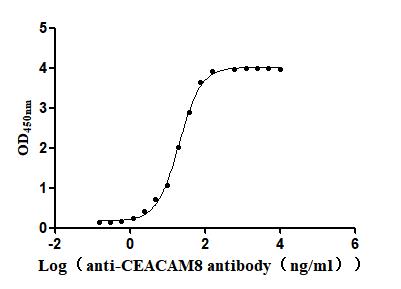
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
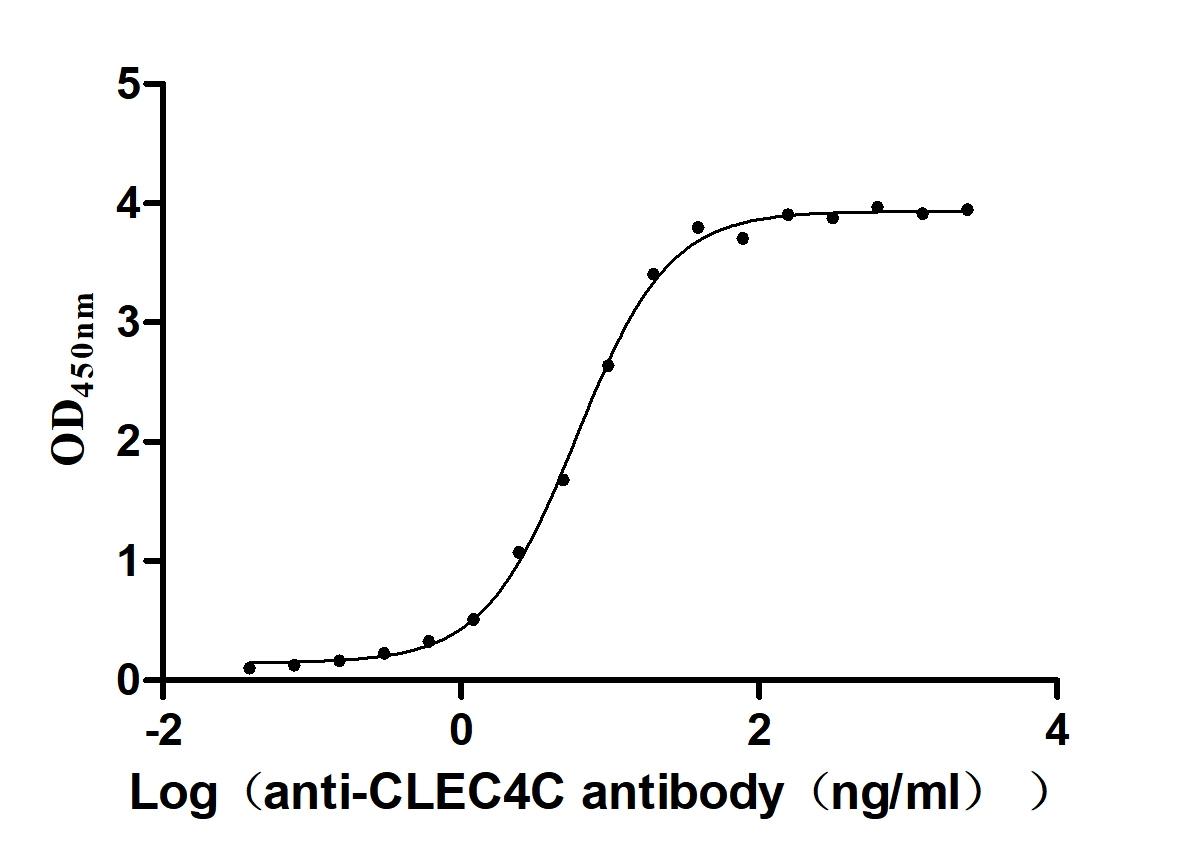
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis C-type lectin domain family 4 member C(CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
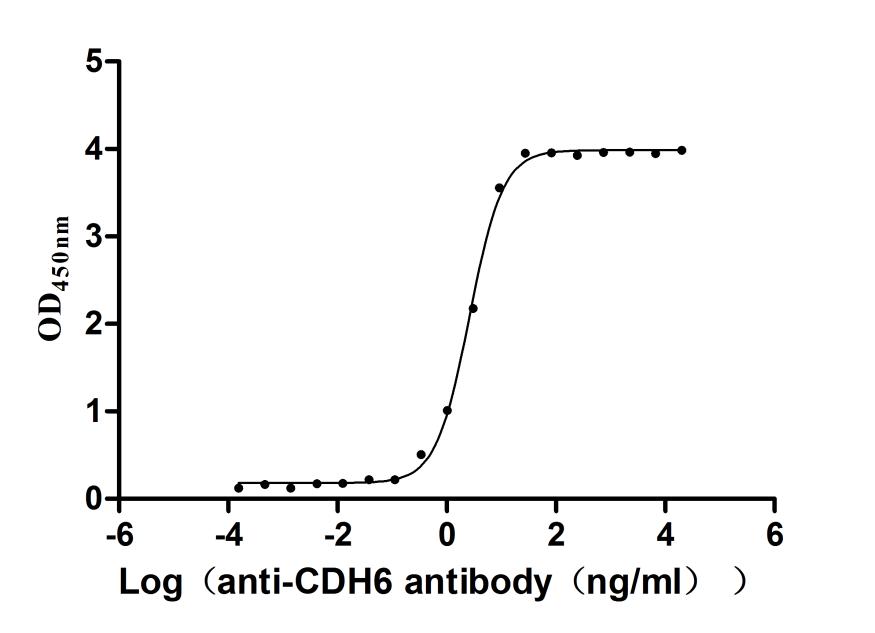
Recombinant Human Cadherin-6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
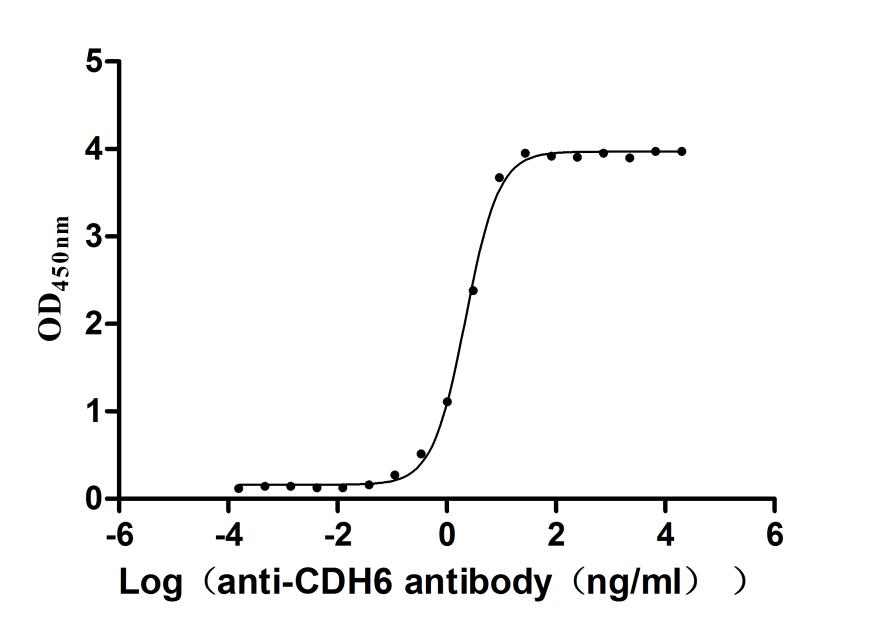
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Cadherin 6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)