Recombinant Mouse Natural killer cells antigen CD94 (Klrd1)
-
货号:CSB-CF012470MO
-
规格:
-
来源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
其他:
产品详情
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Klrd1; Cd94; Natural killer cells antigen CD94; Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily D member 1; CD antigen CD94
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-179
-
氨基酸序列MAVSRITRWRLMSVIFGIKCLFLMVTLGVLLINSFTIQNIQSTPSPTTTVEFQEVSECCVCLDKWVGHQCNCYFISKEEKSWKRSRDFCASQNSSLLQPQSRNELSFMNFSQTFFWIGMHYSEKRNAWLWEDGTVPSKDLFPEFSVIRPEHCIVYSPSKSVSAESCENKNRYICKKLPI
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Immune receptor involved in self-nonself discrimination. In complex with KLRC1 or KLRC2 on cytotoxic and regulatory lymphocyte subsets, recognizes non-classical major histocompatibility (MHC) class Ib molecule MHC-E loaded with self-peptides derived from the signal sequence of classical MHC class Ia and non-classical MHC class Ib molecules. Enables cytotoxic cells to monitor the expression of MHC class I molecules in healthy cells and to tolerate self. Primarily functions as a ligand binding subunit as it lacks the capacity to signal.; KLRD1-KLRC1 acts as an immune inhibitory receptor. Key inhibitory receptor on natural killer (NK) cells that regulates their activation and effector functions. Dominantly counteracts T cell receptor signaling on a subset of memory/effector CD8-positive T cells as part of an antigen-driven response to avoid autoimmunity. On intraepithelial CD8-positive gamma-delta regulatory T cells triggers TGFB1 secretion, which in turn limits the cytotoxic programming of intraepithelial CD8-positive alpha-beta T cells, distinguishing harmless from pathogenic antigens. In MHC-E-rich tumor microenvironment, acts as an immune inhibitory checkpoint and may contribute to progressive loss of effector functions of NK cells and tumor-specific T cells, a state known as cell exhaustion. Upon MHC-E-peptide binding, transmits intracellular signals through KLRC1 immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIMs) by recruiting INPP5D/SHIP-1 and INPPL1/SHIP-2 tyrosine phosphatases to ITIMs, and ultimately opposing signals transmitted by activating receptors through dephosphorylation of proximal signaling molecules.; KLRD1-KLRC2 acts as an immune activating receptor. On cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets recognizes MHC-E loaded with signal sequence-derived peptides from non-classical MHC class Ib MHC-G molecules, likely playing a role in the generation and effector functions of adaptive NK cells and in maternal-fetal tolerance during pregnancy. Regulates the effector functions of terminally differentiated cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets, and in particular may play a role in adaptive NK cell response to viral infection. Upon MHC-E-peptide binding, transmits intracellular signals via the adapter protein TYROBP/DAP12, triggering the phosphorylation of proximal signaling molecules and cell activation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Segregation of a spontaneous Klrd1 mutation in DBA/2 mouse substrains PMID: 25520036
- The transmembrane region sequences of CD94 and NKG2 in mouse and rat differ markedly from other mammalian orthologs by the presence of a lysine residue in the transmembrane region. PMID: 22084441
- show that CD94, a molecule preferentially expressed by NK cells, is essential for the resistance of C57BL/6 mice to mousepox, a disease caused by the Orthopoxvirus ectromelia virus PMID: 21439856
- CD94 and NKG2 were both expressed early in NK cell development, sometimes in the absence of NK1.1, with CD94 invariably being expressed at two different levels. IL-4 differentially inhibited the expression of CD94 and Ly49 receptors. PMID: 11870631
- Inhibitory receptor CD94 is expressed on mature fetal thymic and adult epidermal TCR Vgamma3+ lymphocytes. PMID: 11907085
- The acquisition of individual receptor gene expressions during various stages of differentiation in culture from embryonic stem cells to NK cells follows a predetermined order, with the order of receptor acquisition being first CD94. PMID: 11994449
- There is no evidence that CD94 inhibits either the lytic function of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-specific T cells or their capacity to produce effector cytokines upon peptide stimulation. PMID: 12097371
- The engagement of the activating isoforms of C-type lectin inhibitory receptor (CD94)by their natural ligands, represented by soluble HLA-I molecules, induced programmed cell death of natural killer cells PMID: 12393468
- CD94 heterodimers costimulate effector functions of differentiated Th1 cells, but not Th2 cells. PMID: 12421909
- A high level of expression of CD94/NKG2 receptors is correlated with a lower level of apoptosis and may play an important role in the maintenance of CD8 T and NK cells. PMID: 12574337
- Identification of a novel second CD94 upstream CD94 promoter and the observation that various lymphoid cells use the two promoters differentially offer a theoretical mechanism for the expression of NK receptors on non-NK cells. PMID: 14530345
- CD94-expressing anti-polyoma virus CD8 T cells appear to be essential for antigen-specific recall responses in mice persistently infected by polyoma virus. PMID: 16670321
- CD94 is an Ag that can be used to identify functionally distinct NK cell subsets in mice and could also be relevant to late-stage mouse NK cell development. PMID: 19801519
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:16643
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000107694
UniGene: Mm.391515
Most popular with customers
-
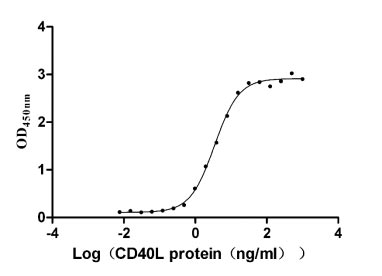
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5 (CD40), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
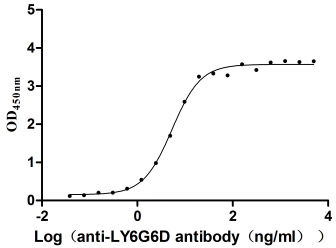
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
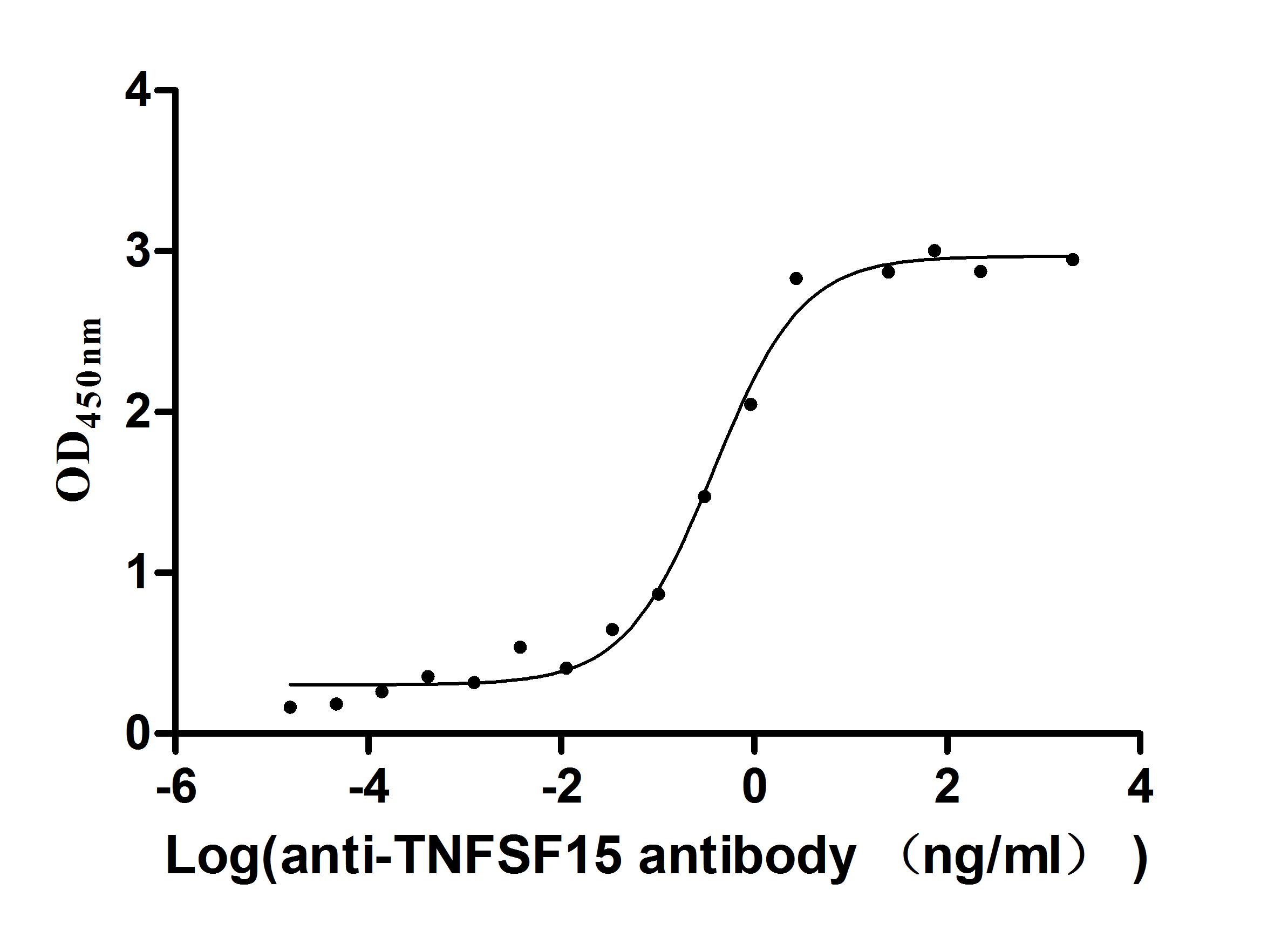
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
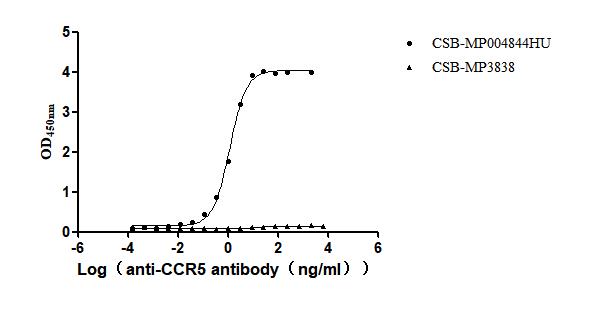
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)