Recombinant Mouse Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (Lpar1)
-
货号:CSB-CF013047MO
-
规格:
-
来源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
其他:
产品详情
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Lpar1; Edg2; Gpcr26; Lpa1; Vzg1; Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1; LPA receptor 1; LPA-1; Lysophosphatidic acid receptor Edg-2; Rec1.3; VZG-1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-364
-
氨基酸序列MAAASTSSPVISQPQFTAMNEQQCFYNESIAFFYNRSGKYLATEWNTVSKLVMGLGITVC VFIMLANLLVMVAIYVNRRFHFPIYYLMANLAAADFFAGLAYFYLMFNTGPNTRRLTVST WLLRQGLIDTSLTASVANLLAIAIERHITVFRMQLHTRMSNRRVVVVIVVIWTMAIVMGA IPSVGWNCICDIDHCSNMAPLYSDSYLVFWAIFNLVTFVVMVVLYAHIFGYVRQRTMRMS RHSSGPRRNRDTMMSLLKTVVIVLGAFIVCWTPGLVLLLLDVCCPQCDVLAYEKFFLLLA EFNSAMNPIIYSYRDKEMSATFRQILCCQRNENPNGPTEGSDRSASSLNHTILAGVHSND HSVV
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Receptor for lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). Plays a role in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, cell migration, differentiation and proliferation, and thereby contributes to the responses to tissue damage and infectious agents. Activates downstream signaling cascades via the G(i)/G(o), G(12)/G(13), and G(q) families of heteromeric G proteins. Signaling inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity and decreases cellular cAMP levels. Signaling triggers an increase of cytoplasmic Ca(2+) levels. Activates RALA; this leads to the activation of phospholipase C (PLC) and the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Signaling mediates activation of down-stream MAP kinases. Contributes to the regulation of cell shape. Promotes Rho-dependent reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in neuronal cells and neurite retraction. Promotes the activation of Rho and the formation of actin stress fibers. Promotes formation of lamellipodia at the leading edge of migrating cells via activation of RAC1. Through its function as lysophosphatidic acid receptor, plays a role in chemotaxis and cell migration, including responses to injury and wounding. Plays a role in triggering inflammation in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) via its interaction with CD14. Promotes cell proliferation in response to lysophosphatidic acid. Required for normal skeleton development. May play a role in osteoblast differentiation. Required for normal brain development. Required for normal proliferation, survival and maturation of newly formed neurons in the adult dentate gyrus. Plays a role in pain perception and in the initiation of neuropathic pain.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Study shows that lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) propagates post-injury schwann cell (SC) dedifferentiation through lysophosphatidic acid 1 signaling. These data indicate that LPA may be a critical factor that shifts SCs towards a post-injury phenotype and contributes to the onset of Wallerian degeneration. PMID: 29051083
- we demonstrate that LPA1/3 antagonism mildly reduced plasma LDL cholesterol levels. Therefore, pharmacological inhibition of LPA1/3 receptors may prove a promising approach to diminish atherosclerosis development. PMID: 27883026
- LPA receptor 1 signaling increased TGFbeta expression via GSK3beta phosphorylation and SREBP1 activation, contributing to the development of diabetic nephropathy. PMID: 28111010
- Our data suggest that LPAR signaling stimulates SS development by induction of IL-17 production via ROCK and p38 MAPK pathways. Thus, LPAR inhibition could be a possible therapeutic strategy for SS. PMID: 28460477
- Our results suggest that LPA-enhanced foam cell formation is mediated by LPA1/3 -AKT activation and subsequent SRBI expression. PMID: 28765047
- Lysophosphatidic acid-LPA1 signaling is critically required for septation during alveolarization. PMID: 27082727
- Data show that lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPA1)-green fluorescent proteins can be used to directly quantify the running-induced increase in precursor proliferation. PMID: 27050949
- Results suggest a relevant role for the Lysophosphatidic acid/Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 signaling system in alcoholism. In addition, the LPA1-null mice emerge as a new model for genetic vulnerability to excessive alcohol drinking PMID: 26700247
- Findings describe a functional role for lysophosphatidic acid 1 receptor in the regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination in the central nervous system. PMID: 25226845
- Data show that lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) induces phosphorylation of trkA receptor (TrkA) through lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPA1) binding to TrkA PMID: 26597701
- LPA receptor has a role in bone loss in ovariectomized mice, but the favorable effect of its inhibition on bone remodeling is less general than hypothesized PMID: 24994065
- These findings suggest that tumor and stromal LPA receptors, in particular LPA1 and LPA5, play different roles in invasion and the seeding of metastasis PMID: 25158955
- LPA1 receptor is involved in emotional behaviors and in the anatomical integrity of the corticolimbic circuit, the deregulation of which may be a susceptibility factor for anxiety disorders. PMID: 23775489
- These results suggest that Ile325, Tyr85, and Leu87 within LPA1 are essential for LPA1 protein properly folding in the ER. PMID: 25025571
- These results suggest that LPA1 receptor-mediated amplification of spinal LPA production is required for the development of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. PMID: 25411045
- these results demonstrate that LPA1 is essential for in vitro and in vivo osteoclast activities. PMID: 24429286
- Ultrastructural analyses of peripheral nerves in mouse null-mutants for LPA1 showed delayed schwann cell-to-axon segregation, polyaxonal myelination by single schwann cells, and thinner myelin sheaths. PMID: 24115248
- This study demonstrate a correlation between gene expression and cell birthdates. Lpar1 cells are preferentially generated on E11.5 and survive preferentially after the first postnatal week compared with other subplate neurons PMID: 22628460
- Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 is necessary for development of arthritis. PMID: 23666827
- LPA1 receptor signaling plays key roles in the development of central neuropathic pain following cerebral ischemia PMID: 23318243
- Galphaq-coupled Lpar1 regulates cell proliferation and migration by activating two distinct PLC-beta isozymes, PLC-beta1 and PLC-beta2, respectively. PMID: 23478264
- LPA(1) is involved in bone development by promoting osteogenesis. PMID: 22867754
- LPA(1)-null mice displayed a basal c-Fos hyperactivity in the hippocampus and in the medial prefrontal cortex, which was regulated differently by the two different memory tasks employed. PMID: 22537775
- findings suggest that LPA1 receptor may be necessary for a normal associative contextual learning associated to cocaine, probably through the modulation of hippocampal glutamatergic circuits. PMID: 21887497
- The ability of LPA-LPA(1) signaling to promote epithelial cell apoptosis and fibroblast resistance to apoptosis may therefore contribute to the capacity of this signaling pathway to regulate the development of pulmonary fibrosis after lung injury. PMID: 22021336
- the ATX-LPA-LPAR axis is a critical regulator of embryonic vascular development that is conserved in vertebrates PMID: 21971049
- These results suggest that LPA1 strongly influences bone development both qualitatively and quantitatively and that, in vivo, its absence results in decreased osteogenesis with no clear modification of osteoclasis. PMID: 21569876
- the absence of the LPA receptor aggravates the chronic stress-induced impairment to hippocampal neurogenesis and its dependent functions PMID: 21980482
- Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in alveolar epithelial cells and murine lungs. PMID: 21821728
- These results suggest defined pathways for signaling through the lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 to promote lysophosphatidic acid-mediated myosin II activation and subsequent cell migration in 4T1 breast cancer cells. PMID: 21302283
- This study shows that CaMKII and related synaptic mechanisms at glutamatergic synapses are strongly dysregulated in LPA1 KO mice. PMID: 20942999
- These data identify stereotyped and selective hypoxia-induced cerebral cortical disruption requiring LPA(1) signaling. PMID: 21878565
- LPA1 receptor has a role in angiogenesis in tumor cells and xenografts PMID: 20708100
- These results suggest that lysophosphatidic acid, which is converted from lysophosphatidylcholine by ATX, activates LPA1 receptors and induces dorsal root demyelination following nerve injury, which causes neuropathic pain. PMID: 21062487
- LPA(1-3) are differentially expressed in the central nervous system and their expression is upregulated in response to injury. PMID: 20495828
- exploratory and emotional impairments did not account for the cognitive deficits that may be attributed to maLPA(1) nulls' hippocampal malfunction PMID: 20388543
- LPA(1) and LPA(3) (lysophosphatidic acid)receptors promote neointima formation through activation of CXCL12-mediated mobilization and recruitment of smooth muscle progenitor cells. PMID: 20360252
- lysophosphatidic acid receptor-1 has a role in diet-induced obesity PMID: 20358347
- We propose that the LPA(1) receptor may play a major role in both spatial memory and response to anxiety-like conditions. PMID: 19689455
- LPA stimulation promotes the interaction of the LPA(2) receptor with a focal adhesion molecule, TRIP6 PMID: 14688263
- A marked deficit in prepulse inhibition, changes in the levels of brain 5-HT and a craniofacial dysmorphism is seen in LPA1 receptor-deficient mice, defects resembling those found in psychiatric disease. PMID: 14697676
- LPA and angiotensin II were also capable of inducing LPA1 receptor phosphorylation, showing that LPA1 receptor can be subjected to homologous and heterologous desensitization PMID: 15369458
- LPA does not behave as a potent PPARgamma agonist in adipocytes but, conversely, inhibits PPARgamma expression and adipogenesis via LPA(1) receptor activation PMID: 15710620
- LPA(1) function in normal cortical development and suggest that the presence of genetic modifiers of LPA(1) influences cerebral cortical development PMID: 17656621
- LPA1 links pulmonary fibrosis to lung injury by mediating fibroblast recruitment and vascular leak PMID: 18066075
- distinct molecular mechanisms regulate agonist-dependent and PMA-dependent internalization of the LPA 1 receptor. PMID: 18089565
- The results demonstrated that in C9 cells estrogens modulate LPA(1) action through estrogen receptor alpha with the participation of protein kinase C alpha and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. PMID: 18166159
- A novel in vivo function for LPA signaling as a germ cell survival factor during spermatogenesis. PMID: 18448840
- Results support the operation of lysophosphatidic acid receptor (1) signaling pathways in normal proliferation, maturation and differentiation of neuronal precursors. PMID: 18708146
- a direct role for LPA receptor signaling in cell transformation and tumorigenesis in conjunction with c-Myc PMID: 18762810
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell surface. Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endosome.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
-
组织特异性:Detected in lung. Detected in oligodendrocytes in corpus callosum in brain cortex (at protein level). Expressed within the embryonic cerebral cortex, where it is enriched in the ventricular zone. In the adult brain, also expressed in oligodendrocytes, as
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:14745
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000052581
UniGene: Mm.4772
Most popular with customers
-
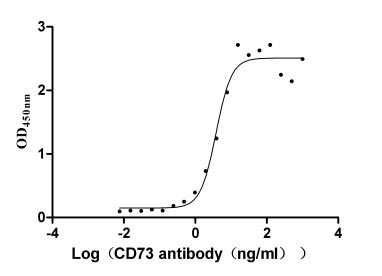
Recombinant Human 5'-nucleotidase (NT5E) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human T-cell surface protein tactile (CD96), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
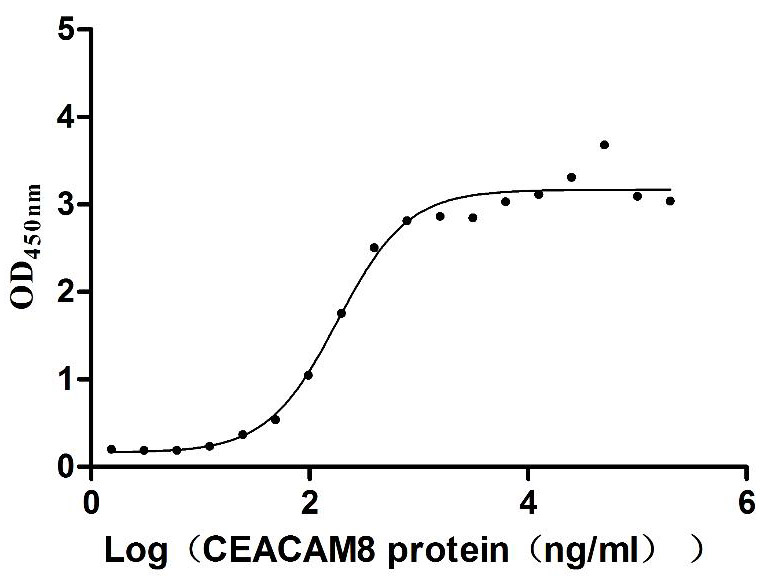
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
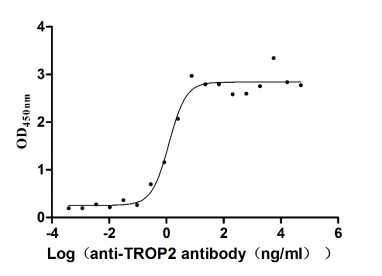
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
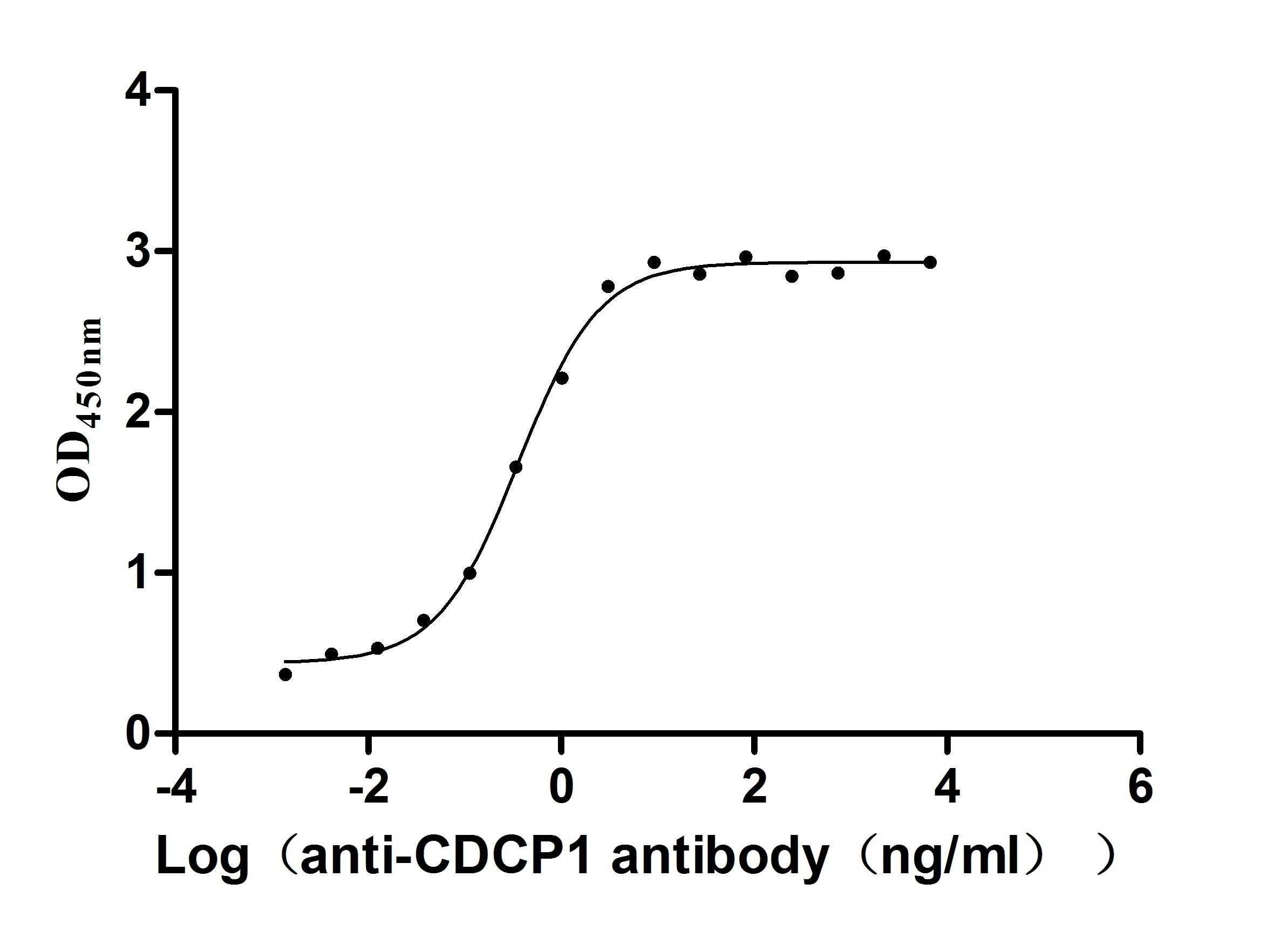
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
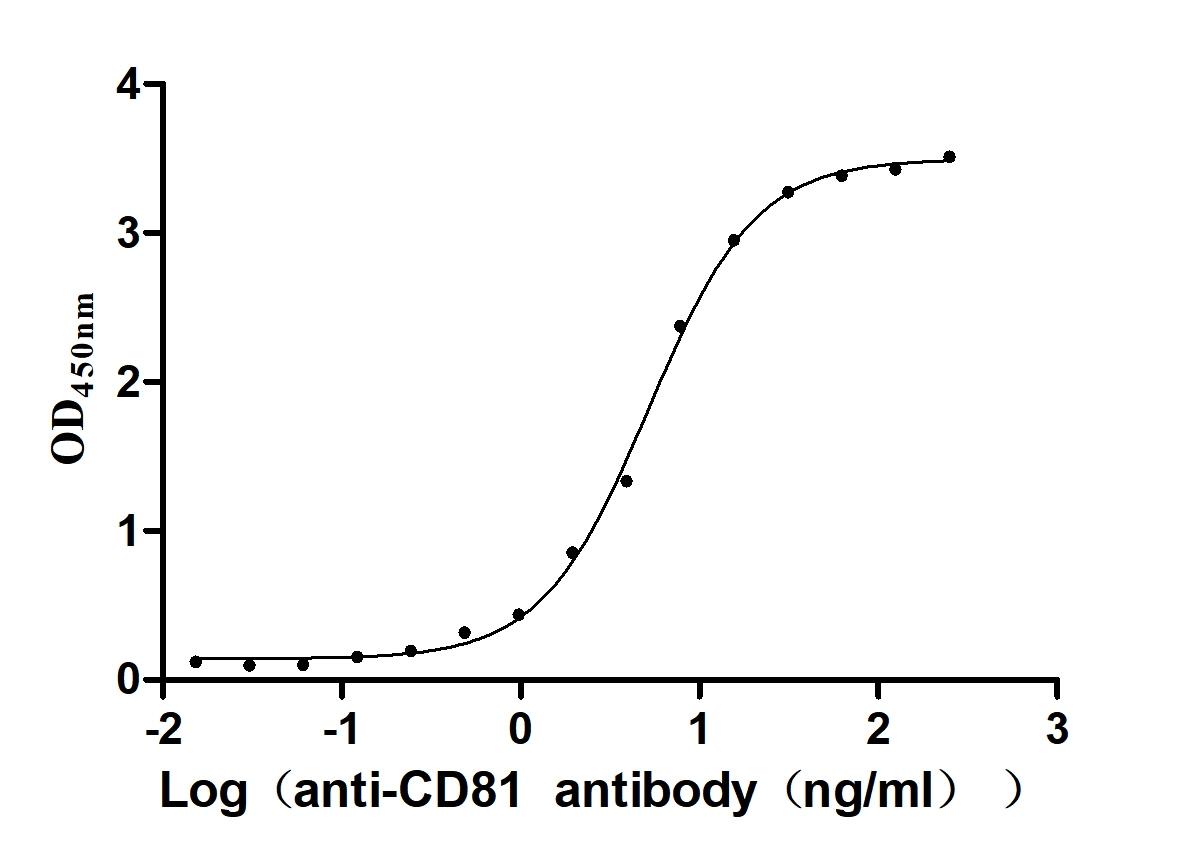
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
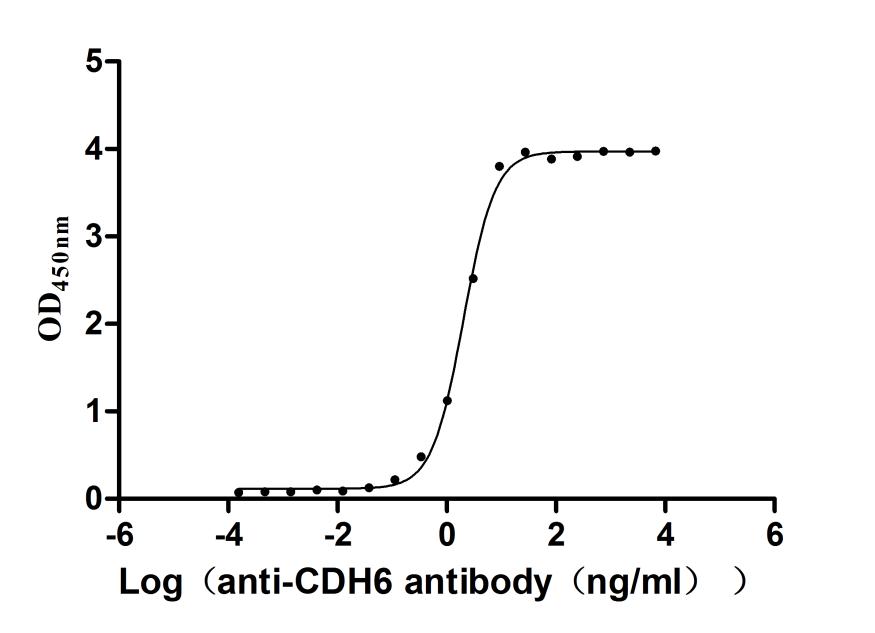
Recombinant Mouse Cadherin-6(Cdh6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)


-AC1.jpg)